The Guess Method to Solve Every Physics Problem (Easy)
TLDRThe video script introduces a problem-solving technique called 'Guess' for tackling physics problems without prior knowledge of physics. The acronym stands for Given, Unknown, Equation, and Solve. The method involves identifying given variables, determining the unknown, and selecting the appropriate equation to find the solution. The script demonstrates this by solving a physics problem involving a car's acceleration and change in position, using kinematic equations and algebraic manipulation to arrive at the answer. The technique emphasizes understanding the problem's requirements and applying the correct formula to find the solution.
Takeaways
- 🎯 The video introduces a 'trick' or method, called GUESS, to solve physics problems without extensive prior knowledge of physics.
- 🔍 GUESS is an acronym standing for Given, Unknown, Equation, Solve, and Substitute, which is a systematic approach to tackle physics problems.
- 📝 The first step in the GUESS method is to identify all the given variables in the problem, such as velocities, forces, and masses.
- 🤔 The second step is to determine the unknown variable that the problem is asking you to solve for.
- 🧩 The third step involves finding the appropriate equation that includes all the given variables and the unknown.
- 🔢 The fourth step is to substitute the known values into the chosen equation.
- 👓 The video provides a brief overview of common physics variables like vf (final velocity), v₀ (initial velocity), Δx (change in position), a (acceleration), and t (time).
- 🚗 An example problem is solved using the GUESS method, where a car accelerates from 30 m/s to 50 m/s over a certain distance.
- 📊 The kinematic equations shared in the video are useful for solving physics problems involving motion.
- 📝 The final step is to solve for the unknown by performing the necessary calculations with the substituted values.
- 📚 The video encourages viewers to keep this information handy and offers more help on the creator's YouTube channel for further physics problem-solving.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is teaching a method to solve physics problems without knowing physics, using a process called 'guess'.
What does the acronym 'GUESS' stand for in the context of the video?
-In the context of the video, 'GUESS' stands for Givens, Unknown, Equation, Solve, and Substitute, which is a process to solve physics problems.
What are the three key variables in the physics problem discussed in the video?
-The three key variables are initial velocity (v₀), acceleration (a), and final velocity (vf).
How does the 'G' in GUESS represent the first step of the process?
-The 'G' in GUESS stands for Givens, which means identifying all the variables and information provided in the physics problem.
What does the 'U' in GUESS represent?
-The 'U' in GUESS stands for Unknown, which refers to the variable or value that the problem is asking to find.
What is the significance of the 'E' in GUESS?
-The 'E' in GUESS stands for Equation, which involves finding the correct equation that relates the givens and the unknown to solve the physics problem.
What is the final step in the GUESS process?
-The final step in the GUESS process is 'S' for Solve, where you substitute the given values into the chosen equation and solve for the unknown.
What is the specific physics problem solved in the video?
-The specific physics problem solved in the video is calculating the distance a car travels while accelerating from 30 m/s to 50 m/s at a rate of 1.5 m/s².
Which equation was used to solve the car acceleration problem in the video?
-The equation used to solve the car acceleration problem is vf² = v₀² + 2aΔx.
What was the final answer to the car acceleration problem in the video?
-The final answer to the car acceleration problem was 533.3 meters, representing the distance the car traveled during the acceleration period.
Why is it important to include units in the final answer when solving physics problems?
-It is important to include units in the final answer when solving physics problems because it provides context and accuracy, ensuring the solution is understood in the correct physical context.
Outlines
🎓 Introducing the GUESS Method for Solving Physics Problems
This paragraph introduces the GUESS method, a technique for tackling physics problems without prior knowledge of physics. The speaker explains that GUESS is an acronym for a process that involves identifying given variables, determining the unknown, and selecting the appropriate equation to solve the problem. The paragraph also provides basic definitions for common physics variables such as velocity (v, vf, v₀), change in position (Δx), acceleration (a), and time (t), and presents three fundamental kinematic equations that will be useful in solving physics problems.
🚗 Applying the GUESS Method to a Kinematics Problem
In this paragraph, the speaker applies the GUESS method to a specific physics problem involving a car's acceleration and change in velocity. The problem states that a car accelerates from 30 m/s to 50 m/s at a rate of 1.5 m/s² and asks for the distance traveled during this acceleration. The speaker demonstrates how to identify the givens (initial velocity, acceleration, and final velocity), determine the unknown (change in position or Δx), and choose the correct equation (v² = u² + 2as) to solve for the unknown. The step-by-step calculation leads to the final answer of 533.3 meters, highlighting the effectiveness of the GUESS method in solving physics problems.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Physics problems
💡Guess method
💡Variables
💡Acceleration
💡Velocity
💡Equations
💡Kinematic equations
💡Change in position (delta x)
💡Initial velocity (v₀)
💡Final velocity (vₓ)
💡Units
Highlights
The presentation introduces a method to solve physics problems without prior knowledge of physics.
The acronym GUESS is introduced as a process to approach physics problems.
GUESS stands for Given, Unknown, Equation, Substitute, and Solve.
The first step in the GUESS method is to list all given variables in the problem.
The second step is to identify the unknown variable that the problem is asking to solve.
The third step involves finding the right equation that contains the given and unknown variables.
Substitute the given values into the chosen equation to solve the problem.
Basic physics variables like final velocity (vf), initial velocity (v), change in position (delta x), acceleration (a), and time (t) are explained.
Three kinematic equations are provided for solving physics problems involving motion.
A practical example is given where a car accelerates from 30 m/s to 50 m/s over a certain distance.
The example demonstrates how to apply the GUESS method to find the distance traveled by the car during acceleration.
The equation used to solve the example problem is vf^2 = v^2 + 2a(delta x).
The solution process involves substituting known values and solving for the unknown (delta x).
The final answer is 533.3 meters, showcasing how the GUESS method can lead to the correct solution.
The importance of including units in the final answer is emphasized.
The presentation encourages further exploration of physics through the speaker's YouTube channel.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
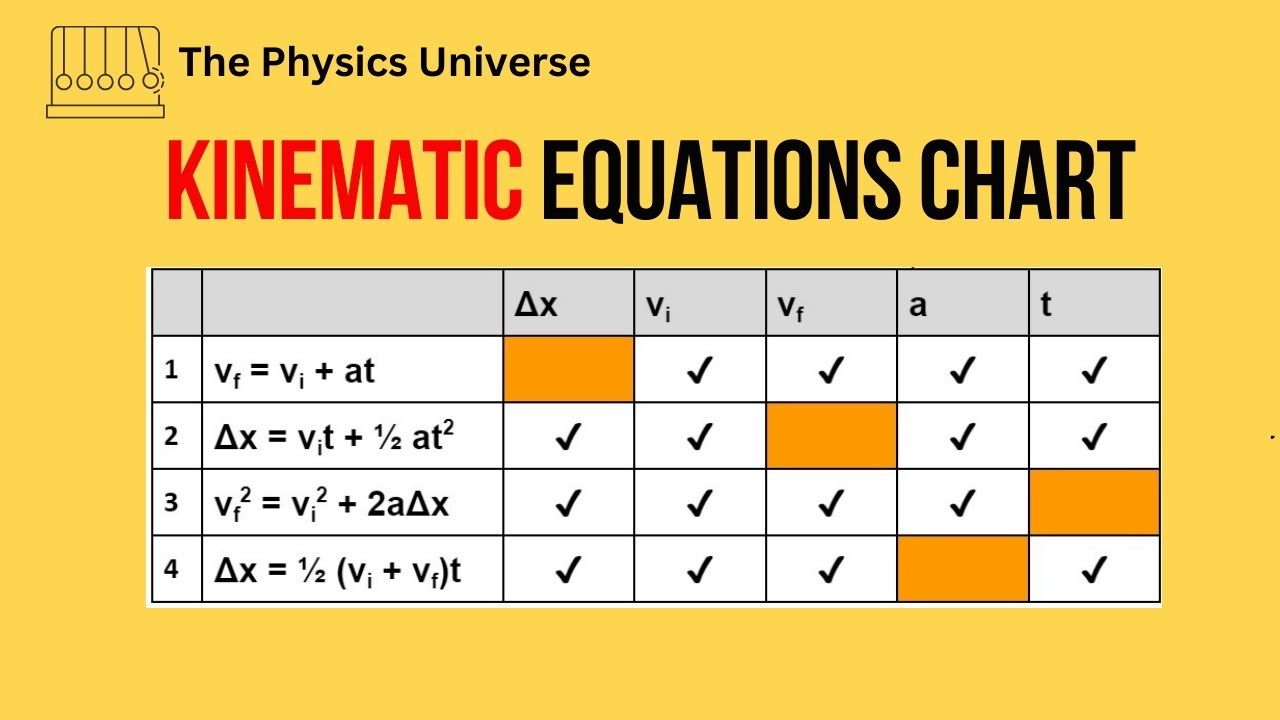
Creating And Using Kinematic Equations Chart - Kinematics - Physics
Determine Cubic Equation grade 12
Kinetic Energy - Introductory Example Problems
Calculus AB/BC – 7.2 Verifying Solutions for Differential Equations
Treating systems (the hard way) | Forces and Newton's laws of motion | Physics | Khan Academy
Calculus 1: Separation of Variables Examples
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: