Ancient Rome in 20 minutes
TLDRThe video script provides a sweeping overview of Roman history, from its humble beginnings as a tribal settlement to the rise and fall of the Roman Empire. It covers the Roman conquests, the Pax Romana, and the cultural and political developments that shaped the empire. The narrative highlights key figures such as Julius Caesar, Augustus, and Constantine, and explores the social and economic factors that contributed to Rome's decline. The script also touches on the lasting legacy of Rome, including its impact on modern languages, the concept of citizenship, and the spread of Christianity. It concludes by reflecting on the rise of Rome from a migrant-founded city to a global state that endured for over a millennium.
Takeaways
- 📜 The Latin alphabet was adapted by the Romans from the Greek letters for their own needs, which is a significant Roman legacy.
- 🏙 Rome started as a small tribal settlement and grew to become the largest metropolitan city of the ancient world due to its open city policy and opportunities for migrants.
- 🏛 The Roman Republic was established after the expulsion of the last king, with two consuls elected annually and a Senate controlled by the patrician class.
- 🗺️ Rome's military success was due to its alliances with conquered peoples, providing a steady stream of recruits and avoiding the cost of maintaining large standing armies.
- ⛽ The Punic Wars with Carthage were pivotal in Rome's rise to power, with the eventual destruction of Carthage solidifying Roman dominance in the Mediterranean.
- 🏛️ The Pax Romana, or Roman peace, was a period of significant stability and prosperity, with Roman citizenship gradually extended to conquered peoples, laying the groundwork for an empire.
- 👑 Julius Caesar's crossing of the Rubicon marked a turning point in Roman history, leading to a civil war and his eventual assassination, which paved the way for the rule of his grandnephew, Octavian (later Augustus).
- 🕍 Augustus, the first Roman emperor, ruled for 43 years and brought about a period of peace and stability known as the Pax Romana, which lasted for nearly two centuries.
- 🏙️ Rome's urban development included the construction of infrastructure like roads, aqueducts, and the Colosseum, which contributed to its status as a cultural and political center.
- ⛓️ The later Roman Empire faced crises such as economic instability, social inequality, and a shift from a citizen army to a professional military, which contributed to its decline.
- 🌍 The legacy of Rome includes the widespread use of Latin-derived languages, the concept of Roman citizenship, and the enduring influence of Roman law and governance on modern legal systems.
Q & A
What is the significance of the Latin alphabet in the context of the Roman civilization?
-The Latin alphabet was significant as it was adapted from the Greek letters to suit the Romans' own linguistic needs. This adaptation allowed for effective communication and the preservation of their culture and legal systems, which later influenced many modern languages.
How did Rome's geographical location contribute to its early growth?
-Rome's geographical location at the crossroads of trade routes between neighboring peoples such as the Atrans and Greek colonies facilitated trade and interaction. This strategic position allowed Rome to emerge as a significant center and contributed to its early growth.
What was the Roman policy towards migrants and how did it impact the city's population?
-Rome offered migrants a unique opportunity to become fully fledged citizens. This policy attracted a diverse population, including outcasts, murderers, and runaway slaves, making Rome the largest metropolitan city of the ancient world.
Who were the two brothers in Roman mythology credited with the founding of Rome?
-Romulus and Remus were the two brothers in Roman mythology who were credited with the founding of Rome. They were believed to be the great-grandchildren of the Trojan hero Aeneas.
How did the Roman Republic form and what was its significance?
-The Roman Republic formed as a result of the struggle for rights between the patricians and the plebeians. This struggle led to the establishment of the Republic, which was significant as it represented a shift from monarchy to a more democratic system where the Senate and the people had a say in governance.
What was the Pax Romana and why is it considered an early example of globalization?
-The Pax Romana, or Roman peace, was a period of relative peace and stability across the Roman Empire. It is considered an early example of globalization due to the extensive trade networks, cultural exchanges, and the spread of Roman law and language that characterized this era.
How did the Roman military reform in 390 BC impact the Roman Legion's effectiveness in battle?
-The military reform in 390 BC divided the Roman legion into smaller units called manipula, making it more mobile and flexible in battle. This reform allowed the Roman army to form alliances with conquered peoples, creating a steady supply of recruits and enhancing its fighting force.
What was the significance of Julius Caesar crossing the Rubicon with his legions?
-Julius Caesar crossing the Rubicon with his legions was a pivotal moment that signified his defiance of the Senate's authority and his intention to take power. This act led to a civil war and eventually made him the sole ruler of Rome, marking a transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire.
How did the assassination of Julius Caesar impact the Roman political landscape?
-The assassination of Julius Caesar led to a power struggle among his potential successors. It resulted in the rise of his grand-nephew, Octavian (later known as Augustus), who emerged as the first Roman Emperor, marking the end of the Roman Republic and the beginning of the Roman Empire.
What was the impact of the Pax Romana on the Roman economy and society?
-The Pax Romana brought about a period of peace and stability that facilitated economic growth. It led to the construction of infrastructure like roads and aqueducts, the distribution of free bread to citizens, and the emergence of a prosperous middle class. However, it also led to the rise of an unequal society with a growing gap between the rich and the poor.
How did the Roman Empire's approach to citizenship evolve over time?
-Initially, Roman citizenship was limited to those born in Rome. However, as the Empire expanded, citizenship rights were gradually extended to include conquered peoples, allowing them to participate in the state's affairs. This policy helped to integrate diverse populations into the Roman system and contributed to the Empire's stability and longevity.
Outlines
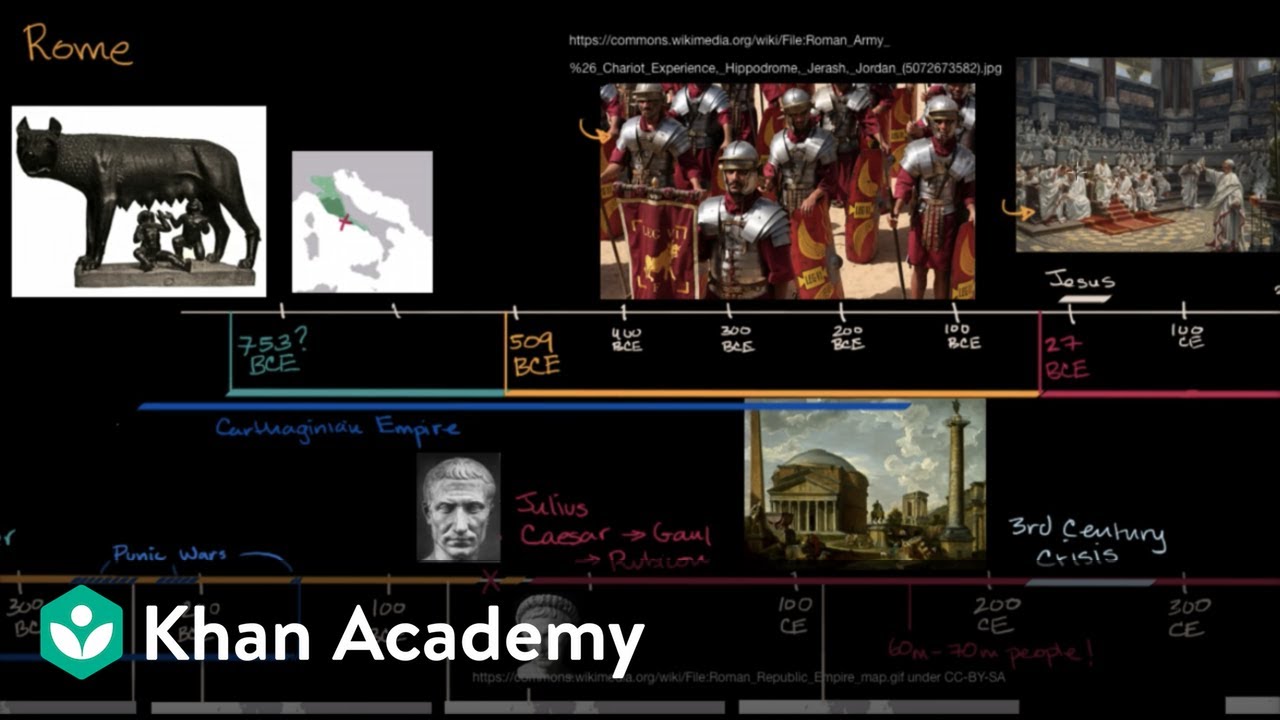
🏛️ The Rise and Legacy of Rome
This paragraph outlines the historical journey of Rome, from its humble beginnings as a small tribal settlement by the Tiber River to its peak as a global empire. The Romans' ability to assimilate and adapt from neighboring cultures, such as the Etruscans and Greeks, played a significant role in their rise. The political evolution from a monarchy to a republic and then to an empire is highlighted, with key events such as the establishment of the Roman calendar, the Roman legal system, and the construction of iconic structures like the Capitoline Temple and aqueducts. The narrative also touches upon Rome's military innovations and the significance of the Latin language in shaping the modern world.
🏺 Roman Conquests and Cultural Exchange
The second paragraph delves into Rome's military conquests and the subsequent cultural exchanges that followed. It discusses the Punic Wars with Carthage, the assimilation of Greek culture, and the expansion of Roman citizenship rights, which were pivotal in the formation of the Roman Empire. The paragraph also highlights the internal struggles within Rome, such as the civil wars and the rise of powerful generals like Julius Caesar and Pompey. The impact of Caesar's assassination and the subsequent rule of Octavian (later known as Augustus) are also covered, emphasizing the transition from a republic to an empire and the beginning of the Pax Romana, a period of relative peace and stability.
👑 The Reign of Emperors and the Cult of Personality
This section explores the reign of various Roman emperors and the development of the imperial cult. It describes how power became hereditary and the Senate's diminishing influence. The paragraph details the rule of emperors like Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero, each with their unique vices and contributions. The narrative also touches upon the role of the Praetorian Guard in the fate of emperors and the territorial expansion of the empire. The economic upswing under Augustus, the construction of the Colosseum, and the introduction of height regulations in Rome are also mentioned. The paragraph concludes with the emergence of Christianity and the empire's shift towards a more centralized, bureaucratic rule under emperors like Diocletian.
🛣️ The Pax Romana and the Infrastructure of the Empire
The fourth paragraph focuses on the Pax Romana, a period of peace and stability within the Roman Empire, and the extensive infrastructure that supported it. It discusses the construction of roads and fortifications, the architectural marvels like the Pantheon, and the cultural achievements such as the poetry of the Golden Age. The paragraph also highlights the rule of the 'Five Good Emperors' and the administrative reforms that allowed the empire to grow and prosper. The narrative then shifts to the crisis of the third century, marked by a series of short-lived emperors and internal strife, leading to the eventual division of the empire and the rise of Constantine the Great, who made Christianity an official religion and founded Constantinople as the new capital.
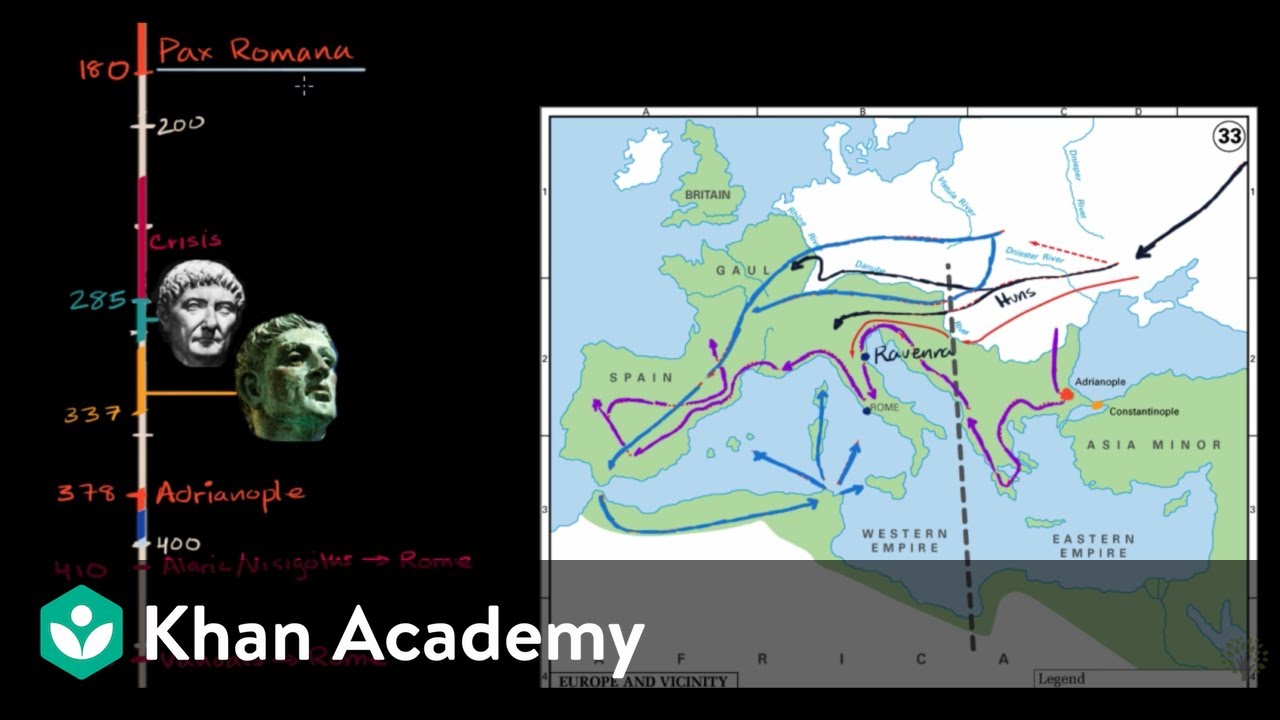
✝️ The Fall of the Roman Empire and the Rise of Christianity
The final paragraph summarizes the decline of the Western Roman Empire and the rise of Christianity. It discusses the end of the Pax Romana under Emperor Commodus and the subsequent period of chaos and instability. The narrative highlights the significant reforms and military conquests under Emperors like Diocletian and Constantine, leading to the empire's division into Western and Eastern halves. The paragraph also touches upon the last emperor, Romulus Augustus, and the ultimate fall of the Western Roman Empire to the Barbarian invasions. It concludes with a reflection on the enduring legacy of Rome, particularly its influence on modern governance, infrastructure, and the global spread of Christianity.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Latin
💡Pax Romana
💡Roman Legion
💡Senate
💡Plebeians
💡Punic Wars
💡Julius Caesar
💡Augustus
💡Gladiatorial Games
💡Aqueducts
💡Globalization
Highlights
The Roman Empire's boundaries, known as Pax Romana, represent an early form of globalization.
Rome's origin as a small tribal settlement of the Latins by the river Tiber evolved into a world-conquering force.
Rome's unique policy of offering full citizenship to migrants contributed to its growth as a large metropolitan city.
The legend of Romulus and Remus, the city's founders, reflects Rome's belief in its Trojan heritage.
The Latin alphabet was created by adapting Greek letters to meet the needs of the Latin language.
The shift from monarchy to a republic in 509 BC marked a significant change in Rome's political structure.
The struggle for rights between the patricians and plebeians led to the formation of the Republic.
The publication of the first written laws in 287 BC was a major achievement for the plebeians.
The Roman military reform after the Gallic invasion in 390 BC increased the army's mobility and effectiveness.
Rome's strategy of forming alliances with conquered peoples created a loyal and reinforcing force.
The Punic Wars were a series of conflicts with Carthage over control of the Mediterranean.
The conquest of Tarentum and Sicily marked Rome's expansion into territories beyond the Italian Peninsula.
Julius Caesar's refusal to disband his legions before entering Rome led to a civil war and his eventual dictatorship.
The assassination of Julius Caesar led to a power struggle, with Octavian (later Augustus) emerging as the sole ruler.
Augustus's reign brought about a period of peace and stability known as the Pax Romana, which lasted for 200 years.
The construction of the Colosseum and other monumental buildings during the Pax Romana era signified Rome's prosperity.
The division of the Roman Empire into Western and Eastern halves by Theodosius I marked a significant shift in the empire's governance.
The fall of the Western Roman Empire to the barbarian invasions and the rise of Byzantium in the East marked the end of ancient Rome's global state.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Fall of the Roman Empire | World History | Khan Academy

E.H. Gombrich 'A Little History of the World' 15. Rulers of the Western World
Overview of the Roman Empire | World History | Khan Academy

Why Did The Roman Empire Collapse With Mary Beard | Empire Without Limit | Odyssey

Ancient Rome for Kids

Ancient Rome for Kids | Learn all about the History of the Roman Empire for Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: