Ancient Rome for Kids | Learn all about the History of the Roman Empire for Kids
TLDRThis video script transports viewers back over 2,000 years to explore the origins and evolution of Rome, which began as a small town on the Tiber River and grew into a vast empire. It highlights Rome's unique government structure, initially a republic with representatives from wealthy families, which later transitioned into an empire under leaders like Julius Caesar and his adopted son, Octavian, who became Emperor Augustus. The script also delves into the socio-economic disparities of the time, the plight of the poor and the rise of Christianity. It touches on the cultural aspects of Rome, including the polytheistic religion, the legal system that influenced modern law, and the popular entertainment such as gladiator fights and chariot races. The summary concludes with the empire's eventual collapse and the lasting impact of Rome's contributions to the world.
Takeaways
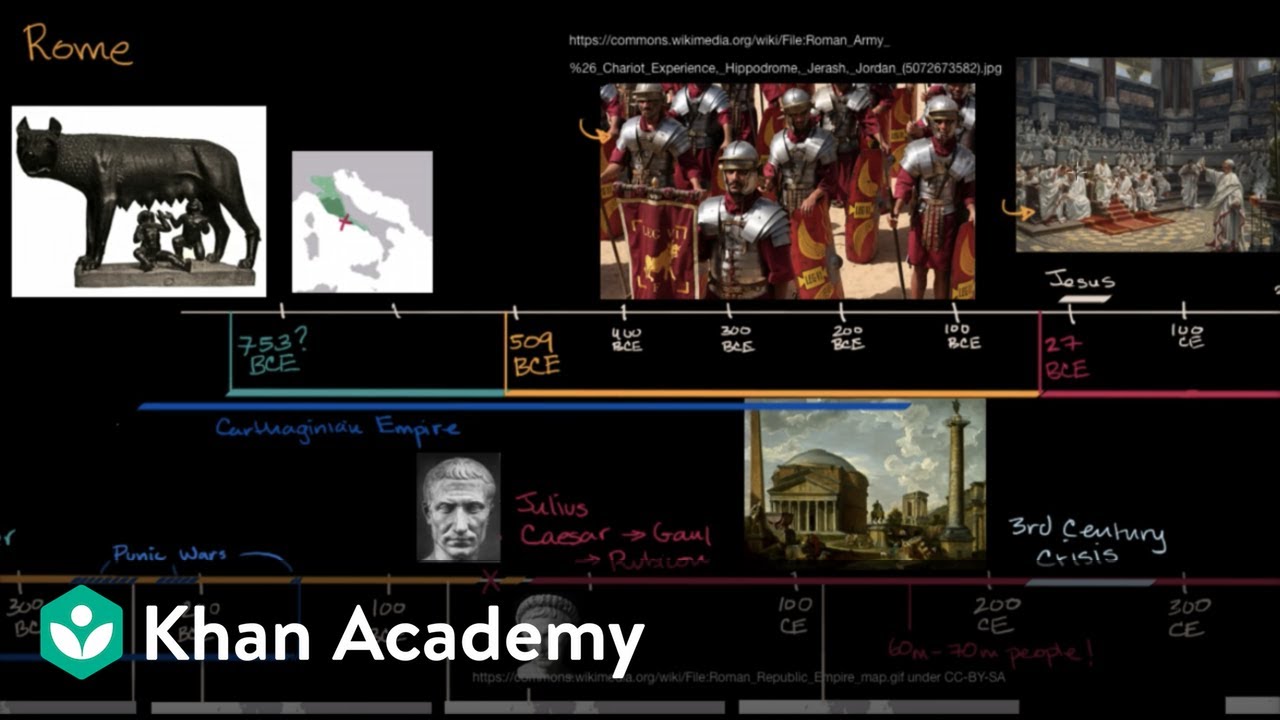
- 🏙️ Rome began as a small town along the Tiber River in central Italy over 2,000 years ago and grew into a significant empire.
- 🌐 The city was strategically built on seven hills for defense and had access to water and travel routes.
- 🗳️ Rome started as a republic where male citizens voted for representatives, mainly from wealthy landowning families.
- 🏛️ The Roman government was divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial, similar to the U.S. today.
- 💰 Economic disparity led to social unrest, with the rich becoming richer while the poor struggled with limited resources and job opportunities.
- 👥 Slavery was prevalent, with thousands of poor people captured and forced to work on large properties owned by the wealthy.
- 👬 Tiberius and Gaius, representatives of the poor, were killed for suggesting improvements, leading to a civil war.
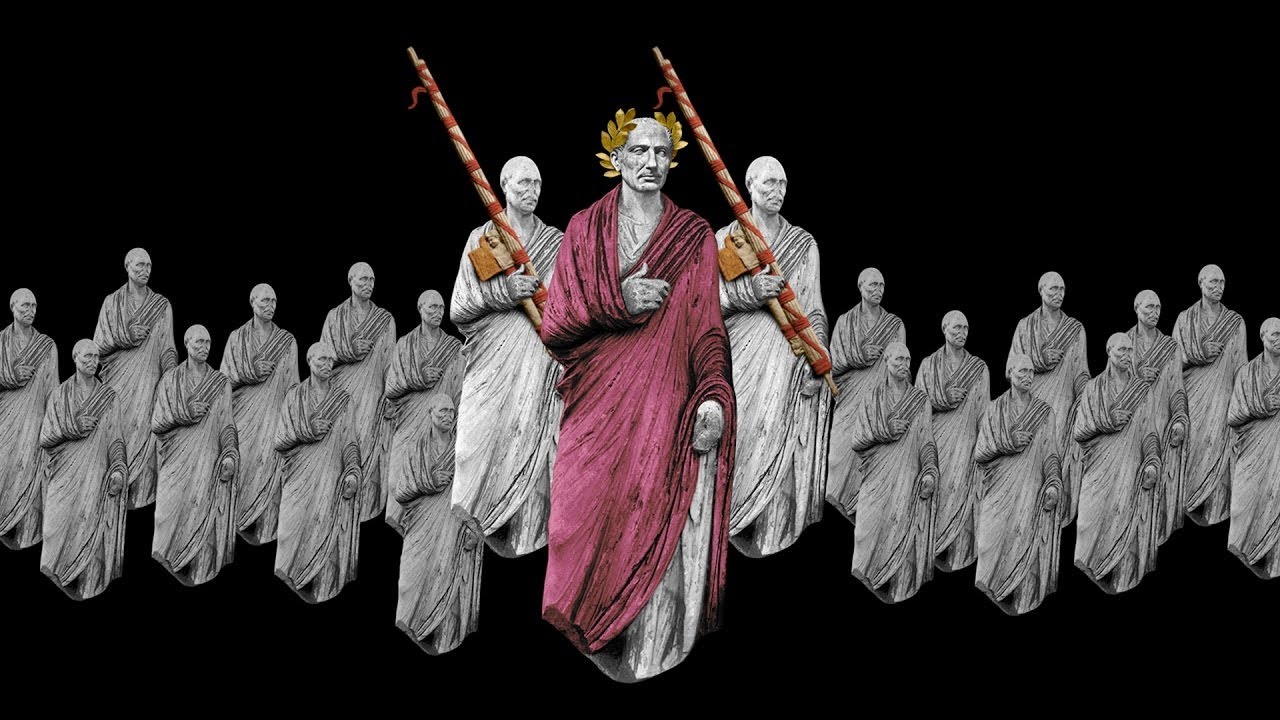
- 👑 Julius Caesar rose to power as a dictator, making significant reforms like creating jobs and increasing soldier pay, before being assassinated.
- ⚔️ Following Caesar's death, a power struggle led to the end of the Roman republic and the establishment of the Roman empire under Augustus.
- 📜 Roman law, such as the principle of 'innocent until proven guilty,' has had a lasting impact and is still practiced in many legal systems.
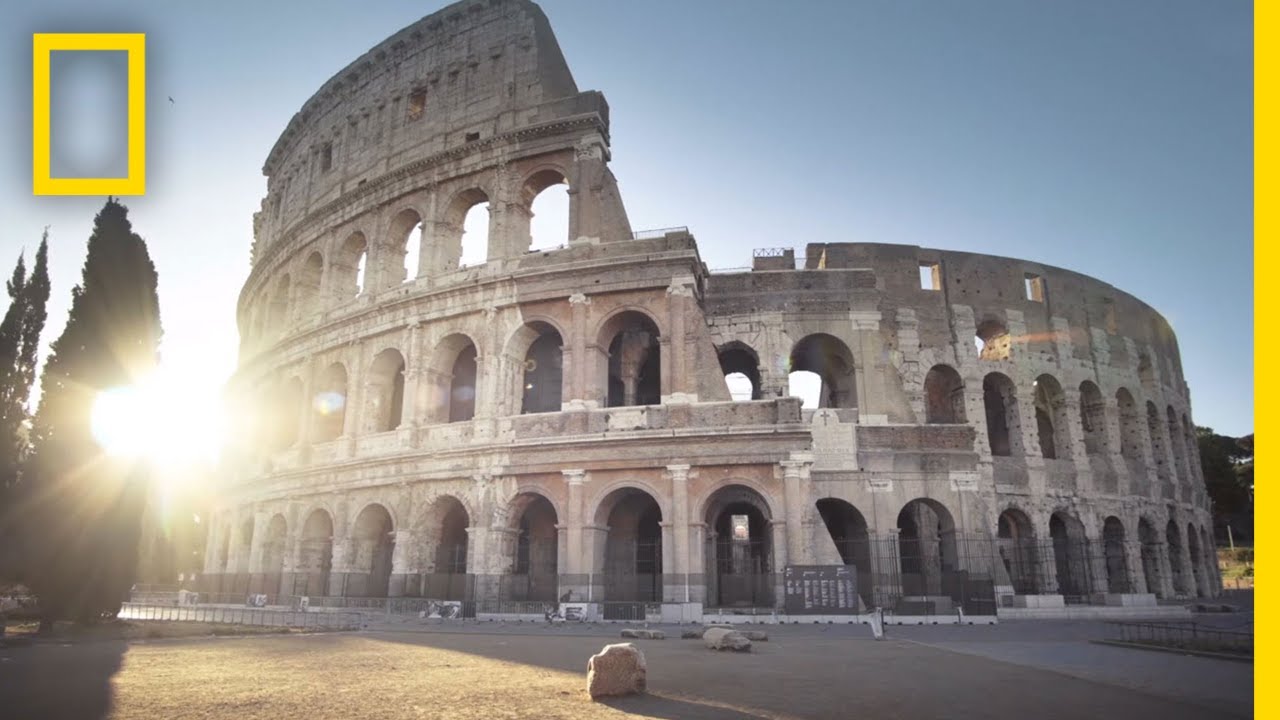
- 🏛️ The Colosseum is a lasting symbol of Rome's entertainment culture, which included gladiator fights and chariot races.
- 📊 The Roman empire eventually collapsed due to its vast size and the loss of territories over time, but its influence endures globally.
Q & A
What was the geographical significance of the Tiber River to ancient Rome?
-The Tiber River was significant to ancient Rome as it provided a source of water and a means of transportation, enabling the Romans to travel to nearby places.
Why was Rome built on seven hills?
-Rome was built on seven hills to offer natural protection to the people from potential enemies, due to the strategic height and defensibility these hills provided.
What does the term 'empire' signify in the context of ancient Rome?
-An empire refers to a group of countries or territories under the rule of an emperor or empress, which is akin to a king or queen. The Roman Empire included many European countries at its height.
How did the Roman Republic function in terms of its government structure?
-The Roman Republic was governed by representatives elected by the people. These representatives were mostly wealthy landowners. The government was composed of three branches: one to run the government, another to make laws, and a third to act as judges.
What was the economic disparity like in ancient Rome, and how did it affect the citizens?
-There was a significant economic disparity in Rome, with the rich becoming richer and the poor becoming poorer. The rich spent lavishly on homes, gardens, slaves, and luxuries, while the majority of the population struggled with unemployment and poverty.
What role did Tiberius and Gaius play in the government of ancient Rome, and what happened to them?
-Tiberius and Gaius were brothers who worked for the Roman government, representing the poor. They suggested improvements to address societal issues but were killed by angry government officials who did not heed their advice.
How did Julius Caesar's rise to power impact the Roman Republic?
-Julius Caesar became a dictator with complete control over the people. He made significant improvements such as granting citizenship to those living near Rome, creating jobs, starting colonies for landless people, and increasing soldiers' pay. His success and popularity, however, led to his assassination by nervous wealthy citizens and government representatives.
Who was Octavian, and what was his significance in the transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire?
-Octavian, the adopted son of Julius Caesar, became the first emperor of Rome at the age of 18. He changed his name to Augustus, meaning 'exalted one,' and ruled successfully for 40 years, contributing to Rome's wealth and stability.
What is the principle of 'innocent until proven guilty' in Roman law, and how is it relevant today?
-The principle of 'innocent until proven guilty' means that a person is considered not guilty of a crime until evidence proves otherwise. This principle, originating from Roman law, is still practiced in legal systems around the world, including the U.S., ensuring that individuals have a chance to defend themselves in court.
What was the religious belief system of ancient Romans, and how did it evolve over time?
-Ancient Romans were polytheistic, worshipping multiple gods and goddesses such as Jupiter, Juno, and Minerva. Over time, the worship of the emperor was incorporated into the official religion, and eventually, Christianity emerged and spread throughout the empire, despite initial persecution of its followers.
What forms of entertainment were popular among the people of ancient Rome?
-Popular entertainment in ancient Rome included musical and theatrical performances, chariot races, and gladiator fights. The Colosseum is an iconic example of an arena where gladiators, often slaves or criminals, fought to the death or until one was severely wounded.
Why did the Roman Empire eventually collapse, and what is its lasting influence?
-The Roman Empire collapsed due to a combination of factors, including becoming too large to manage effectively and losing territories one by one. Despite its fall, Rome's influence is still evident today in various aspects such as legal principles, architecture, and cultural practices.
Outlines
🏛️ Ancient Rome: Origins and Transformation
This paragraph introduces the viewer to the concept of historical change and invites them to consider the evolution of their own cities before diving into the history of Rome. Rome, the capital of Italy, is known for its food, architecture, and art. The video outlines Rome's journey from a small settlement on the Tiber River to a vast empire. It discusses the city's strategic location on seven hills, its transformation into a republic, and eventually an empire ruled by an emperor. The paragraph also touches on the socio-economic disparities within Rome, the plight of the poor and slaves, and the political struggles that led to civil wars and the rise of Julius Caesar as a dictator. It concludes with the transition from a republic to an empire under Caesar's adopted son, Octavian, who became Emperor Augustus.
🏺 Roman Law, Religion, and Entertainment
The second paragraph focuses on the legal, religious, and entertainment aspects of ancient Rome. It highlights the enduring influence of Roman law, with the principle of 'innocent until proven guilty' still prevalent today. The Romans' polytheistic religion is explored, with key deities like Jupiter, Juno, and Minerva mentioned. The paragraph also discusses the deification of emperors and the emergence and spread of Christianity in the empire. Entertainment in Rome is another key theme, with references to musical and theatrical performances, chariot races, and the iconic gladiatorial fights. The Colosseum is mentioned as a prime example of an arena where such events took place. The paragraph concludes with a brief mention of the eventual collapse of the Roman empire and its lasting impact on the world.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Ancient Rome
💡Empire
💡Republic
💡Julius Caesar
💡Dictator
💡Octavian (Augustus)
💡Polytheistic
💡Christianity
💡Gladiator
💡Colosseum
💡Innocent Until Proven Guilty
Highlights
Ancient Rome began as a small town along the Tiber River in central Italy over 2,000 years ago.
Rome was built on seven hills for protection against enemies.
The city grew into an empire, including many European countries.
Rome was initially a republic where male citizens voted for leaders.
The government was composed of three groups: one to run the government, one to make laws, and one to act as judges.
The Roman Empire faced social issues with a growing wealth gap between rich and poor citizens.
Many poor people in Rome were given grain by the government, but had limited access to jobs.
Slavery was prevalent, with thousands of people captured and forced to work on large properties.
Tiberius and Gaius, representatives for the poor, were killed after proposing improvements, leading to a civil war.
Julius Caesar became a dictator and implemented reforms to help the poor and increase jobs and soldier pay.
Caesar's assassination led to another war and the end of the Roman republic, transitioning to an empire.
Octavian, Caesar's adopted son, became the first emperor of Rome, later called Augustus.
Augustus's rule led to 200 years of peace and prosperity, with increased trade and a strong military.
Roman law concepts, such as the presumption of innocence until proven guilty, are still practiced today.
Ancient Romans were polytheistic, worshipping a pantheon of gods and goddesses.
Christianity emerged and spread within the empire despite early followers facing persecution.
Popular entertainment in Rome included musical and theatrical performances, chariot races, and gladiator fights.
Gladiators were often slaves or criminals, and winners gained celebrity status and prize money.
The Colosseum in Rome is a surviving example of an arena where gladiators fought.
The Roman Empire eventually collapsed due to its vast size and loss of territories.
The influence of Rome is still evident worldwide, from its legal concepts to architectural styles.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: