Overview of the Roman Empire | World History | Khan Academy
TLDRThe video script provides an insightful journey through the extensive history of Rome, from its legendary founding by Romulus in the 8th century BCE to the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century CE. It highlights the transformation of Rome from a small city-state to a republic, and subsequently to an empire under Julius Caesar and Augustus. The script also touches upon the significant influence of the Roman Empire on Western civilization and its legacy, including the Byzantine Empire, which lasted until the Ottoman conquest in 1453 CE. The narrative is enriched with references to the Punic Wars, the conquest of Gaul, and the eventual split of the empire into eastern and western halves, with the eastern empire outlasting its western counterpart.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ The Roman legions, Senate, Julius Caesar, Augustus, and famous architecture are iconic symbols associated with ancient Rome.
- 📜 Rome's history spans over a thousand years, from the 8th century BCE to the 5th century CE for the Western Roman Empire, and continues with the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) until 1453 CE.
- 🗺️ The Roman Empire's legacy is significant, influencing much of Western civilization, especially in Europe and the Mediterranean.
- ⛲ The term 'great' in reference to the Roman Empire should be taken with a grain of salt, acknowledging their power and size, but also their cruel and violent aspects, including slavery.
- 🏕️ Rome was founded in the 8th century BCE, with the traditional date being 753 BCE, by Romulus, though the story is likely more legendary than factual.
- 👑 At its founding, Rome was not a significant power and was overshadowed by the Etruscan civilization.
- 🏙️ The Roman Republic was established in 509 BCE, marking the beginning of Rome's rise to dominance in the region.
- 🏺 The Roman Republic transitioned into the Roman Empire under Julius Caesar and his adopted son Augustus, with Augustus being declared Emperor in 27 BCE.
- 📉 The Western Roman Empire began to decline in the 200s and 300s CE, with the end typically marked by the sack of Rome in the 5th century and the deposition of the last emperor in 476 CE.
- 🌏 The Roman Empire split into Eastern and Western halves in the 4th century CE, with the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) lasting until the Ottoman conquest in 1453 CE.
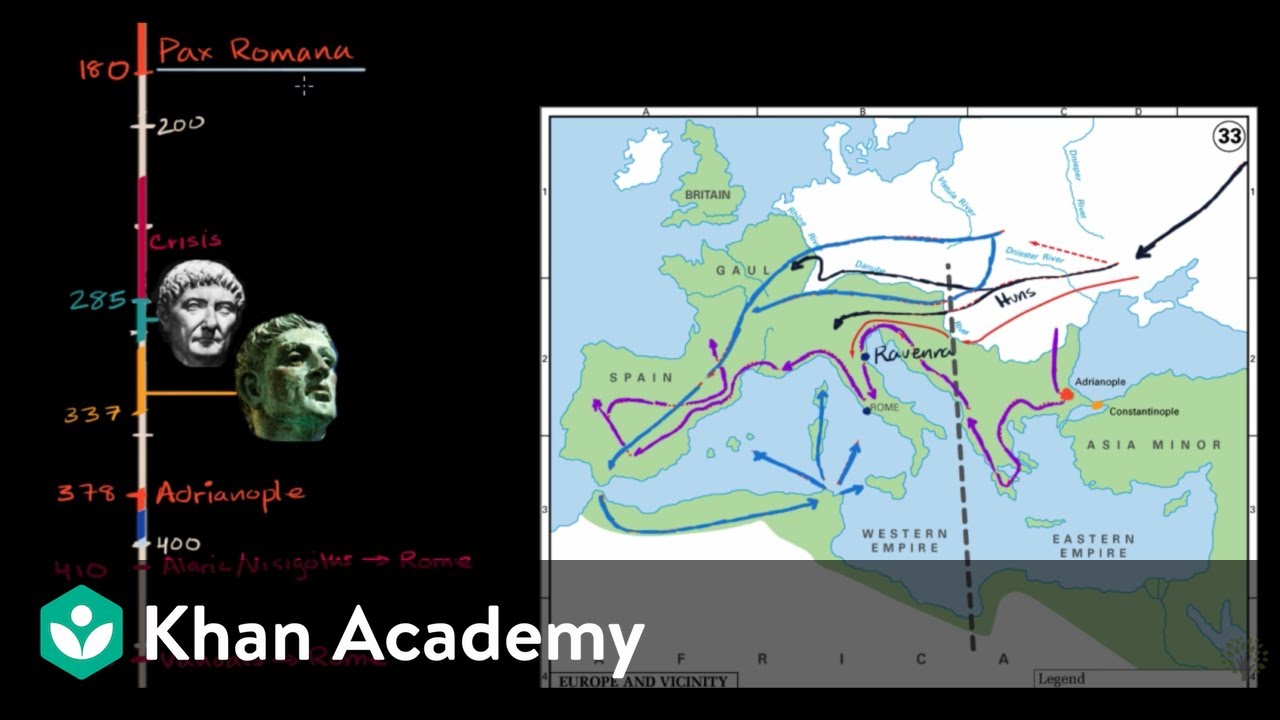
- 🏛️ The growth and decline of the Roman Empire can be visualized through historical maps, showing its territorial expansion and eventual contraction.
Q & A
What is the traditional date given for the founding of Rome?
-The traditional date given for the founding of Rome is 753 BCE.
Who are the legendary founders of Rome, according to Roman mythology?
-The legendary founders of Rome are the twin brothers Romulus and Remus, who were raised by a she-wolf.
What civilization was dominant in the Italian Peninsula during the early period of the Roman Kingdom?
-The Etruscan civilization was the dominant power in the Italian Peninsula during the early period of the Roman Kingdom.
When was the Roman Republic established?
-The Roman Republic was established in 509 BCE.
Who are two notable figures from the Roman Republic that are often mentioned in historical discussions?
-Two notable figures from the Roman Republic are Julius Caesar and Augustus.
What is the significance of the year 476 CE in the context of the Roman Empire?
-The year 476 CE is typically given as the end of the Western Roman Empire, when it was sacked and the last Roman emperor was deposed.
What is the term used to describe the series of wars between the Romans and the Carthaginians?
-The series of wars between the Romans and the Carthaginians are known as the Punic Wars.
When did Julius Caesar conquer Gaul for the Roman Republic?
-Julius Caesar conquered Gaul for the Roman Republic in the first century BCE.
Who was declared Emperor in 27 BCE, marking the beginning of the Roman Empire?
-Augustus, Julius Caesar's adopted son, was declared Emperor in 27 BCE, marking the beginning of the Roman Empire.
What is the term used to describe the eastern half of the Roman Empire after the fourth century CE?
-The eastern half of the Roman Empire after the fourth century CE is often known as the Byzantine Empire.
How did the Roman Empire's legacy continue after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE?
-The Roman Empire's legacy continued through the Byzantine Empire, which lasted for another 1,000 years until it was conquered by the Ottomans in 1453 CE.
What should one consider when interpreting the term 'great' in the context of the Roman Empire?
-When interpreting the term 'great' in the context of the Roman Empire, one should consider that it refers to its size and power, but not necessarily to the moral value of its actions, as the empire was also marked by slavery, cruelty, and violence.
Outlines
🏛 Introduction to the Roman Empire's History
This paragraph introduces the Roman Empire, touching on its legions, Senate, famous figures like Julius Caesar and Augustus, and iconic architecture. The instructor emphasizes that Rome's beginnings were humble and not immediately powerful. A timeline is presented, spanning from the 8th century BCE to the 5th century CE, covering the rise and fall of the Roman Empire, including the division into eastern and western empires and the eventual fall to the Ottomans. The paragraph also notes the Roman Empire's significant legacy on western civilization and its status as a major world power, while acknowledging the empire's darker aspects, such as slavery and cruelty.
🌍 Expansion and Decline of the Roman Empire
The second paragraph delves into the growth and eventual decline of the Roman Empire. It discusses the Roman Republic's establishment in 509 BCE and its evolution into an empire under Julius Caesar and Augustus. The instructor uses maps to illustrate the empire's expansion from the 3rd century BCE, through the Punic Wars with Carthage, to its peak in the 1st century BCE. The narrative continues with the transformation of Rome from a republic to an empire, the civil war, and the rise of Augustus as Emperor in 27 BCE. The split of the empire into eastern and western halves in the 4th century CE is also covered, with a focus on the decline and fall of the western empire in the 5th century, while the eastern empire, later known as the Byzantine Empire, persisted until the Ottoman conquest in 1453 CE.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Roman legions
💡Roman Senate
💡Julius Caesar
💡Augustus
💡Roman architecture
💡Etruscan civilization
💡Roman Republic
💡Roman Empire
💡Byzantine Empire
💡Punic Wars
💡Ottomans
Highlights
Ancient Rome is often associated with Roman legions, the Roman Senate, famous figures like Julius Caesar and Augustus, and iconic architecture.
The video aims to provide an overarching arc of Rome's history, situating it within a timeline of over 1,000 years.
The Roman Empire's legacy, including the Byzantine Empire, extends for another 1,000 years until the Ottoman conquest in 1453 CE.
Western civilization, particularly Europe and the Mediterranean, has deep roots in the Roman Empire and Greek civilization.
The term 'great' when referring to the Roman Empire should be taken with a grain of salt, acknowledging their power but also their cruel and violent aspects.
Rome was founded in the 8th century BCE, with the traditional date being 753 BCE, by Romulus, one of the twin brothers raised by a she-wolf.
The founding story of Rome is likely very legendary, with historians suggesting the city's name may have come first.
At its founding, Rome was not a significant power on the Italian Peninsula, overshadowed by the Etruscan civilization.
The Roman Republic was established in 509 BCE, marking a shift from the kingdom to a more dominant regional influence.
The Roman Republic grew in power and influence for several hundred years before transitioning to an empire.
The Roman Empire began with Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul and subsequent civil war, leading to his declaration as dictator.
Augustus, Julius Caesar's adopted son, was declared Emperor in 27 BCE, formalizing the start of the Roman Empire.
The Roman Empire saw a significant decline starting in the 200s and 300s CE, with the western empire being sacked multiple times in the 5th century.
The traditional end of the Roman Empire is marked in 476 CE, although the eastern empire, later known as the Byzantine Empire, continued for another 1,000 years.
The Byzantine Empire, the eastern continuation of the Roman Empire, lasted until 1453 CE when it was conquered by the Ottomans.
The growth and decline of the Roman Empire can be visualized through a series of maps showing territorial changes over time.
The Punic Wars between the Romans and Carthaginians were a series of conflicts that ended with Rome's victory and the destruction of Carthage in 146 BCE.
The transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire is marked by Julius Caesar's conquests and the subsequent rise of Augustus as Emperor.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Fall of the Roman Empire | World History | Khan Academy

The Middle Ages|part 5 | Oxford world watch History 2

Fall of The Roman Empire...in the 15th Century: Crash Course World History #12

Justinian and the Byzantine Empire | World History | Khan Academy

Chapter 06 - World History, Vol. 1 - OpenStax (Audiobook)

E.H. Gombrich 'A Little History of the World' 18. The Storm
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: