Ancient Rome for Kids
TLDRThe video script offers an engaging journey through the history of Ancient Rome, a civilization that continues to influence modern society. It begins with the city's founding in the 8th century BC, attributed to Romulus, and explores the transition from a monarchy to a republic in 509 BC, following the expulsion of King Tarquin the Proud. The narrative highlights Julius Caesar's rise to power and his assassination, leading to a civil war and the subsequent establishment of the Roman Empire under Augustus, marked by the Pax Romana, a period of relative peace. The script also delves into Rome's architectural marvels, such as the Colosseum, and its advancements in water systems, aqueducts, and roads, which facilitated better living standards and communication across the empire. Additionally, it acknowledges Rome's contribution to fashion with the invention of socks and its enduring linguistic legacy through Latin, the basis for many modern languages and scientific nomenclature. The video emphasizes Rome's impact on history and its role as one of the most powerful civilizations.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ Rome, founded in the 8th century BC, possibly by Romulus, evolved from farming communities on seven hills.
- 🌊 Strategically located along the Tiber River, Rome's access to water was crucial for its development and survival.
- 🏔️ Rome was naturally fortified by the Alps and Apennines, offering protection against invasions.
- 👑 Transition from monarchy to republic happened in 509 BC after ousting the tyrannical king, Tarquin the Proud.
- 📜 The Roman Republic allowed elected officials to govern, which influenced modern republic systems like the USA.
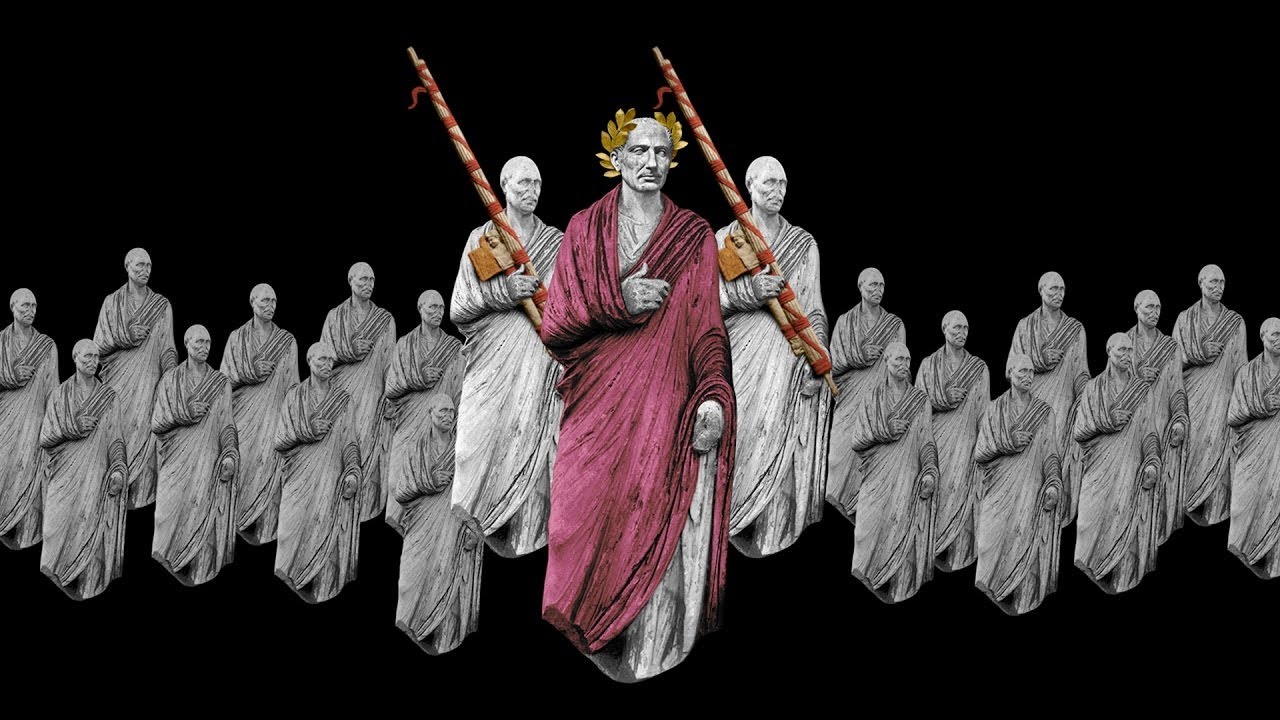
- 🗡️ Julius Caesar, a pivotal figure, transformed Rome with his military and political maneuvers until his assassination in 44 BC.
- 👑 Following Caesar's death, Rome eventually transitioned from a republic to an empire under Augustus, the first emperor.
- 🕊️ The Pax Romana under Augustus marked a period of relative peace and stability across the Roman Empire.
- 🏟️ The Colosseum, an iconic symbol of Roman architectural and engineering ingenuity, hosted events for over 60,000 spectators.
- 🌐 Roman innovations such as roads, aqueducts, sewers, and even socks significantly improved quality of life and infrastructure.
Q & A
What is the significance of the Tiber River to the ancient city of Rome?
-The Tiber River was significant to ancient Rome as it provided access to water, which was essential for life and the development of civilization. Its presence allowed the small city of Rome to grow into a massive civilization.
Why did Rome have natural protection from invasions?
-Rome was naturally protected from invasions due to its location near the Alps and the Apennines mountain ranges, as well as being surrounded by hills. These geographical features made it more difficult for invaders to attack the city.
How did the Roman Republic come into existence?
-The Roman Republic was established in 509 BC after the people of Rome ousted their king, Tarquin the Proud, due to his tyrannical rule. They decided to change the form of government to a republic, where decisions were made by elected officials rather than a single ruler.
What was Julius Caesar's role in Roman history?
-Julius Caesar was a renowned general and an important writer in Roman history. He played a significant role in transforming the Roman Republic into a military dictatorship, which eventually led to a civil war and his own assassination. His death marked a turning point for Rome, leading to the rise of the Roman Empire under his adopted son, Octavian, later known as Augustus.
What was the Pax Romana and why is it significant?
-The Pax Romana, meaning 'Roman Peace,' was a period of relative peace and stability throughout the Roman Empire that began during the rule of Emperor Augustus. It is significant because it allowed for significant cultural, economic, and territorial growth for the empire and provided a better quality of life for many of its inhabitants.
How did ancient Rome's architecture contribute to its legacy?
-Ancient Rome's architecture, such as the Colosseum, has left a lasting legacy due to the structures' enduring presence and the engineering techniques used to build them. Roman architecture is known for its grandeur, functionality, and the use of materials like concrete, which has influenced many modern structures.
What was the purpose of the Roman Colosseum?
-The Roman Colosseum was a massive amphitheater used for public spectacles, including gladiatorial contests, chariot races, and theatrical performances. It was designed to accommodate over 60,000 spectators and was a central part of Roman entertainment and social life.
How did ancient Rome's water and sewage systems improve the quality of life for its citizens?
-Ancient Rome developed advanced water systems and aqueducts to bring fresh water to various parts of the city and constructed sewers to manage waste disposal. These innovations significantly improved public health and the overall quality of life for Roman citizens.
What is a lesser-known contribution of ancient Rome to modern life?
-Ancient Rome is credited with the invention of socks, which has had a significant impact on modern comfort and attire. This seemingly small innovation has had a lasting effect on everyday life.
How did the Roman roads and concrete contribute to the expansion and stability of the Roman Empire?
-The Roman roads, made with concrete, provided stable and reliable transportation and communication networks that connected the vast Roman Empire. These roads facilitated trade, military movement, and the spread of culture, contributing to the empire's expansion and stability.
What is the linguistic legacy of ancient Rome, and how does it continue to impact modern languages?
-The ancient Romans spoke Latin, a language that has significantly influenced many modern languages and is still used in scientific classifications for plants and animals. Latin has left a lasting linguistic legacy, with many words in English and other languages being derived from it.
Outlines
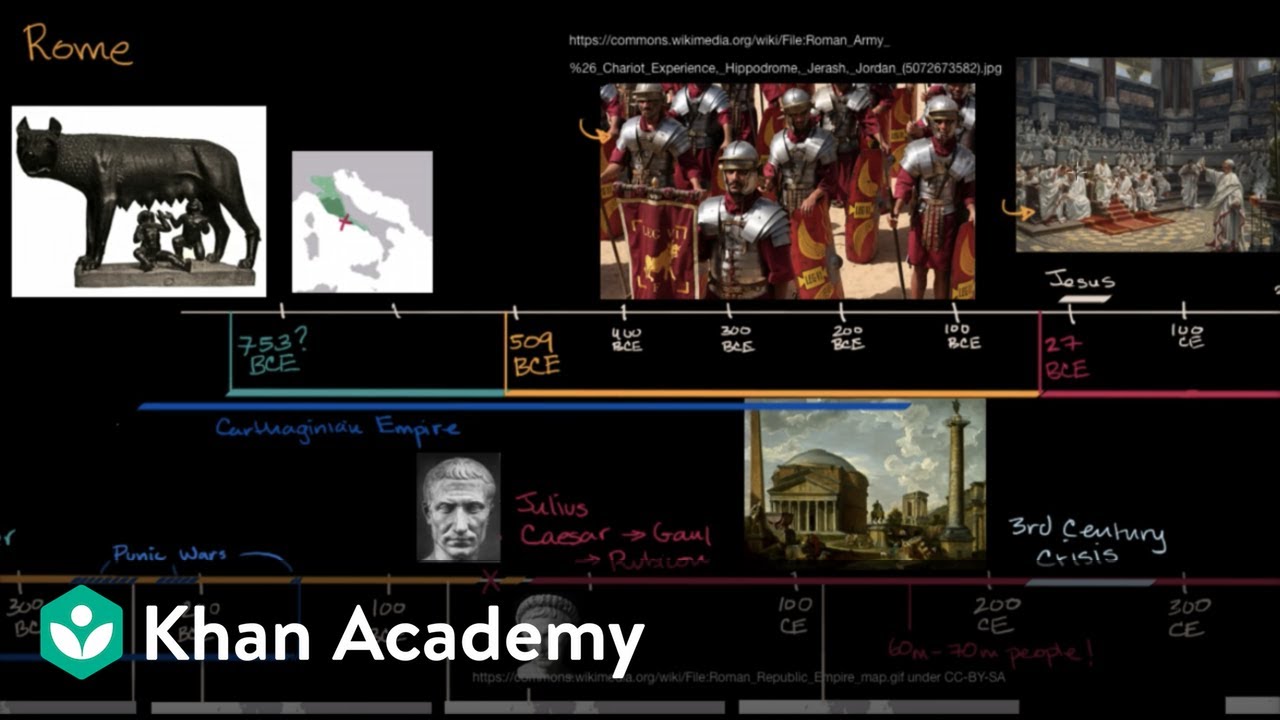
🏛️ Ancient Rome: Origins and Characteristics
This paragraph introduces the video's focus on Ancient Rome, emphasizing its historical significance and ongoing influence. It outlines Rome's geographical advantages, such as its location near the Tiber River and natural barriers like the Alps and Apennines, which contributed to its growth and protection. The narrative also touches on the city's foundation myth involving Romulus and the transition from monarchy to a republic after the expulsion of King Tarquin the Proud.
🏺 Julius Caesar and the Rise of the Roman Empire
The second paragraph delves into the life and impact of Julius Caesar, a renowned general and writer, and his role in the transformation of Rome from a republic to an empire. It discusses Caesar's popularity, the fear he instilled in the Senate, and the civil war that ensued. The summary also covers the aftermath of Caesar's assassination, the rise of his adopted son Octavian (later known as Augustus), and the beginning of the Pax Romana, a period of relative peace and stability in the Roman Empire.
🛕 Legacy of Ancient Rome: Culture and Innovations
The final paragraph highlights the enduring legacy of Ancient Rome, from its architectural marvels like the Colosseum to its advancements in water systems and road construction. It also mentions the invention of socks and the development of concrete for stable roads. The paragraph concludes with the impact of Latin, the language of the Romans, which is still used in scientific nomenclature and has influenced many modern languages, reflecting the civilization's historical power and reach.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Ancient Rome
💡Tiber River
💡Republic
💡Julius Caesar
💡Pax Romana
💡Colosseum
💡Aqueducts
💡Latin
💡Gladiators
💡Roman Roads
💡Imperial Period
Highlights
Ancient Rome is an influential civilization that still impacts us today.
Rome was formed in the 8th century BC, making it a very old city.
Legend has it that Rome was founded by Romulus in 753 BC.
Many historians believe Rome was formed by the union of farm communities on the seven hills.
Rome's location along the Tiber River provided access to water, which was crucial for its growth.
Natural barriers such as mountain ranges and hills protected Rome and made invasions difficult.
In 509 BC, Rome transitioned from a monarchy to a republic after the people overthrew King Tarquin the Proud.
The Roman Republic was one of the first in history and led to Rome's thriving civilization.
Julius Caesar was a famous general and writer who had a significant impact on Rome.
Caesar's popularity and power led to a civil war and his eventual betrayal and death.
Augustus, Caesar's adopted son, became the first emperor of Rome, marking the end of the Republic and the beginning of the Imperial period.
The Pax Romana, under Augustus, was a period of peace and stability for the Roman Empire.
At its peak, the Roman Empire was vast, with its territory colored purple on historical maps.
Ancient Rome is known for its enduring architecture, such as the Colosseum, which could hold over 60,000 people.
Roman water systems and aqueducts were advanced for their time, bringing fresh water to various locations.
Ancient Rome developed roads and concrete, which facilitated transportation and communication across the empire.
Latin, the language of the Romans, is still used in scientific naming and has influenced many modern languages.
Ancient Rome's legacy includes inventions like socks and significant contributions to our understanding of history and civilization.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: