Chemical Reactions and Equations
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the fundamentals of chemical reactions and equations, offering clear explanations and practical examples to demystify the subject for learners. The presenter begins by distinguishing between physical and chemical changes, using everyday scenarios such as cooking and melting ice to illustrate the concepts. The script then transitions into the core topic of chemical reactions, defining them as processes that result in the formation of new substances with distinct properties. Several examples of chemical reactions are provided, emphasizing the importance of reactants and products, and the necessity of balancing chemical equations to adhere to the law of conservation of mass. The process of converting word equations to chemical equations is outlined, highlighting the use of atomicity for elements and valency for compounds. The video also addresses the importance of including physical states in chemical equations and concludes with a discussion on the characteristics of chemical reactions, such as changes in state, color, evolution of gases, changes in temperature, and the formation of precipitates. The presenter encourages viewers to practice balancing equations and to engage with the content by attempting a provided reaction equation. The script is informative, accessible, and designed to build a strong foundation in chemistry for its audience.
Takeaways
- 🍳 The difference between physical and chemical changes: Physical changes are reversible and no new substances are formed, while chemical changes result in the formation of new substances and are irreversible.
- 🔍 Identifying chemical changes involves looking for new substances with new properties, such as cooked food, rusted iron, and ripened fruit.
- 🔬 A chemical reaction is a process where new substances are formed, adhering to the law of conservation of mass.
- ⚖️ Chemical equations must be balanced to ensure the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- 📜 Word equations can be converted to chemical equations using atomic symbols for elements and valency for compounds.
- 🧪 Physical states of substances in a chemical reaction are important and are represented by symbols: solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq).
- 🔑 The characteristics of chemical reactions include changes in state, color, evolution of gas, change in temperature, and formation of a precipitate.
- ✍️ When writing chemical equations, it's crucial to include the physical states of the reactants and products.
- 🧩 Balancing chemical equations can be done by adjusting the multipliers in front of the substances, ensuring equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides.
- 📊 Use the table technique or mental calculation to balance complex chemical equations, starting with the element that is least balanced.
- 🌟 The formation of a precipitate in a reaction indicates the creation of an insoluble solid that settles out of the solution.
- ✅ Always remember to balance chemical equations and include physical states to accurately represent the reaction process.
Q & A
What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
-A physical change is a change in the state or appearance of a substance without forming a new substance, like ice melting to water. A chemical change involves the formation of one or more new substances with different properties, such as cooking food which results in new substances being formed.
What is a chemical reaction?
-A chemical reaction is a process in which new substances with new properties are formed. It involves a chemical change where reactants are transformed into products.
How do you identify reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
-Reactants are the substances present on the left side of a chemical equation, and products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction, which are on the right side of the equation.
Why is it necessary to balance chemical equations?
-Chemical equations must be balanced to obey the law of conservation of mass, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, indicating that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
How do you convert a word equation into a chemical equation?
-To convert a word equation into a chemical equation, use the atomic symbol for elements and the molecular formula for compounds. For elements, represent them in their molecular form based on their atomicity, and for compounds, use their valency to determine the correct formula.
What are the physical states represented by the letters s, l, g, and aq in chemical equations?
-S represents solid, l represents liquid, g represents gas, and aq represents an aqueous solution, which means the substance is dissolved in water.
What are the characteristics of chemical reactions?
-The important characteristics of chemical reactions include a change in state, change in color, evolution of a gas, change in temperature, and formation of a precipitate.
How do you represent the physical states in a chemical equation?
-You represent the physical states in a chemical equation by placing the appropriate state symbol (s, l, g, aq) in parentheses next to the chemical formula of each substance.
What is the significance of the law of conservation of mass in balancing chemical equations?
-The law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Balancing chemical equations ensures that the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products, adhering to this fundamental principle.
What is the difference between a precipitate and a soluble compound in a chemical reaction?
-A precipitate is an insoluble solid that forms in a solution and settles down, while a soluble compound dissolves in the solvent (usually water) and does not settle out as a solid.
How can one determine if a substance is a reactant or a product in a chemical reaction?
-Reactants are the initial substances that undergo a chemical reaction, while products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction. In a chemical equation, reactants are on the left side, and products are on the right side.
What is the role of valency in writing chemical equations for compounds?
-Valency is used to determine the correct molecular formula of a compound in a chemical equation. It helps to ensure that the compound is represented correctly according to how its elements combine, following the principle of valency.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Chemical Reactions
The video begins with an introduction to chemical reactions and equations. The presenter shares tips and tricks on writing chemical reactions and assures that the concepts will be clear by the end. They also promote their website, monitoracademy.com, which offers more courses and practice questions. The video then delves into distinguishing between physical and chemical changes using everyday examples such as cooking food, melting ice, boiling water, rusting iron, ripening fruit, and burning a candle. Each example is explained to show whether it results in the formation of new substances and if the process is reversible or irreversible.
🔍 Understanding Reactants and Products
This paragraph focuses on the definition of a chemical reaction as a process that results in the formation of new substances with new properties. Examples of chemical reactions, such as the combination of hydrogen and oxygen to form water and sodium with chlorine to form sodium chloride, are provided to illustrate this. The presenter explains the terms 'reactants' and 'products', with reactants being the substances that participate in the reaction on the left side, and products being the substances formed as a result on the right side.
🧪 Converting Word Equations to Chemical Equations
The video teaches how to convert word equations into chemical equations using the principles of atomicity for elements and valency for compounds. It explains that for elements, the atomic number should be used to represent a molecule, while for compounds, the valency should be used to determine the molecular formula. The process is demonstrated with examples, such as converting the word equation 'hydrogen plus oxygen gives water' into the chemical equation H2 + O2 → H2O. The importance of balancing equations to adhere to the law of conservation of mass is also emphasized, with a step-by-step guide on how to balance the equations.
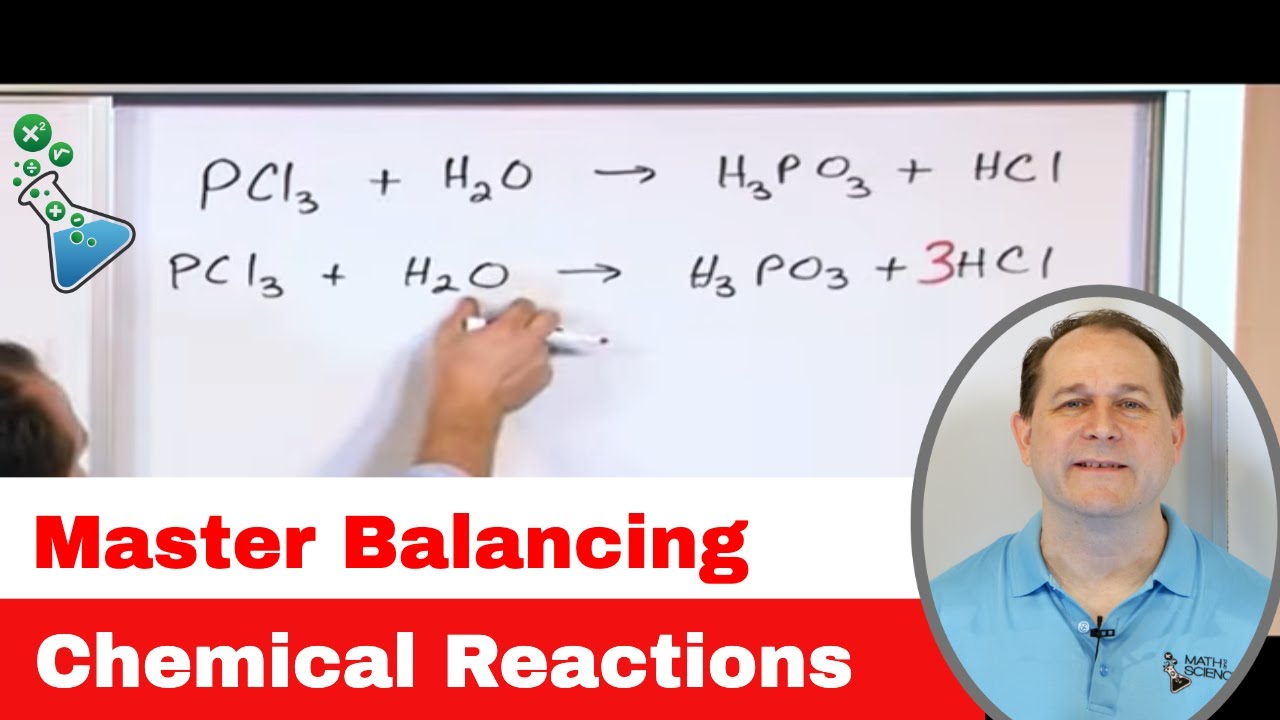
⚖️ Balancing Chemical Equations
This section provides a detailed explanation of how to balance chemical equations by ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. The presenter outlines a method to balance equations by adjusting the multipliers in front of the substances to achieve equality of atoms. The video uses the example of iron combining with sulfuric acid to produce iron sulfate and hydrogen to demonstrate the balancing process. It also encourages the use of a table technique for complex equations and offers to show more balancing techniques in a separate video.
🏭 Writing Physical States in Chemical Equations
The video explains how to include the physical states of substances in chemical equations using symbols (s for solid, l for liquid, g for gas, and aq for aqueous). It clarifies the difference between 'liquid' and 'aqueous' states and provides examples of how to annotate the physical state in chemical equations. The presenter also discusses the characteristics of chemical reactions, including changes in state, color, evolution of gas, change in temperature, and formation of a precipitate, using various examples to illustrate each characteristic.
🌞 Characteristics of Chemical Reactions and Viewer Engagement
The final paragraph discusses the characteristics of chemical reactions in more detail, providing examples for each characteristic, such as the burning of a candle for change in state, ripening of a tomato for change in color, reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid for evolution of gas, reaction of quicklime with water for change in temperature, and reaction of potassium iodide with lead nitrate for the formation of a precipitate. The presenter then poses a question to the viewers, asking them to write a balanced chemical equation for a reaction involving sunlight, silver, and bromine, and to include the physical states of the substances involved. They encourage viewers to share their answers in the comments and to engage with the content by liking, commenting, and sharing the video. They also prompt viewers to subscribe to the YouTube channel and check out the website for more courses and videos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemical Reaction
💡Physical Change
💡Reactants
💡Products
💡Word Equation
💡Atomicity
💡Valency
💡Balancing Equations
💡Physical States
💡Law of Conservation of Mass
💡Characteristics of Chemical Reactions
Highlights
The video explains how to write chemical reactions and equations in chemistry.
It provides tips and tricks for writing chemical reactions clearly.
The presenter uses pictures to illustrate physical vs. chemical changes in everyday life.
Cooking food is an example of a chemical change where new substances are formed.
Melting ice is a physical change as it is reversible and no new substance is created.
Boiling water is also a physical change since water changes into steam reversibly.
Rusting of iron is a chemical change as a new substance (rust) is formed irreversibly.
Ripening of fruit is a chemical change as new substances are formed and the original fruit cannot be regained.
Burning a candle involves both physical (melting wax) and chemical changes (carbon dioxide and water vapor formation).
A chemical reaction is defined as a process where new substances with new properties are formed.
Reactants are the substances on the left side of a chemical reaction, while products are on the right.
Word equations express chemical reactions in words, which can be converted to chemical equations using atomicity for elements and valency for compounds.
Chemical equations must be balanced to obey the law of conservation of mass, ensuring equal mass of reactants and products.
Balancing a chemical equation involves adjusting coefficients to equalize the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
Physical states like solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq) should be indicated in chemical equations.
Characteristics of chemical reactions include change in state, color change, gas evolution, temperature change, and precipitate formation.
Examples are provided to illustrate each characteristic, such as candle burning for change in state and color change in citric acid + potassium permanganate.
The video concludes with a challenge to write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of silver + bromine in sunlight, including physical states.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: