Chemical Reactions
TLDRThe script explains chemical reactions as processes where substances interact to form new ones by altering their chemical bonds. It uses photosynthesis as an example, illustrating how plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using solar energy. The script emphasizes the importance of balancing chemical equations to adhere to the law of conservation of matter, ensuring the same number of atoms for each element in reactants and products. This summary highlights the fundamental concepts of chemical reactions, reactants, products, and the significance of balanced equations.
Takeaways
- 🌱 A chemical reaction is a process where substances interact to form new substances by altering their chemical bonds.
- 🔬 Substances involved in a chemical reaction can be ionic or covalent compounds, as well as atoms, ions, or molecules of elements.
- 🌳 Photosynthesis is given as an example of a chemical reaction, where plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using solar energy.
- 🔄 Reactants are the original substances that undergo change by combining or reacting, while products are the new substances formed as a result.
- 📝 Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations, which list reactants on the left and products on the right.
- 🧬 The law of conservation of matter dictates that the same elements must be present in the same amounts in both reactants and products.
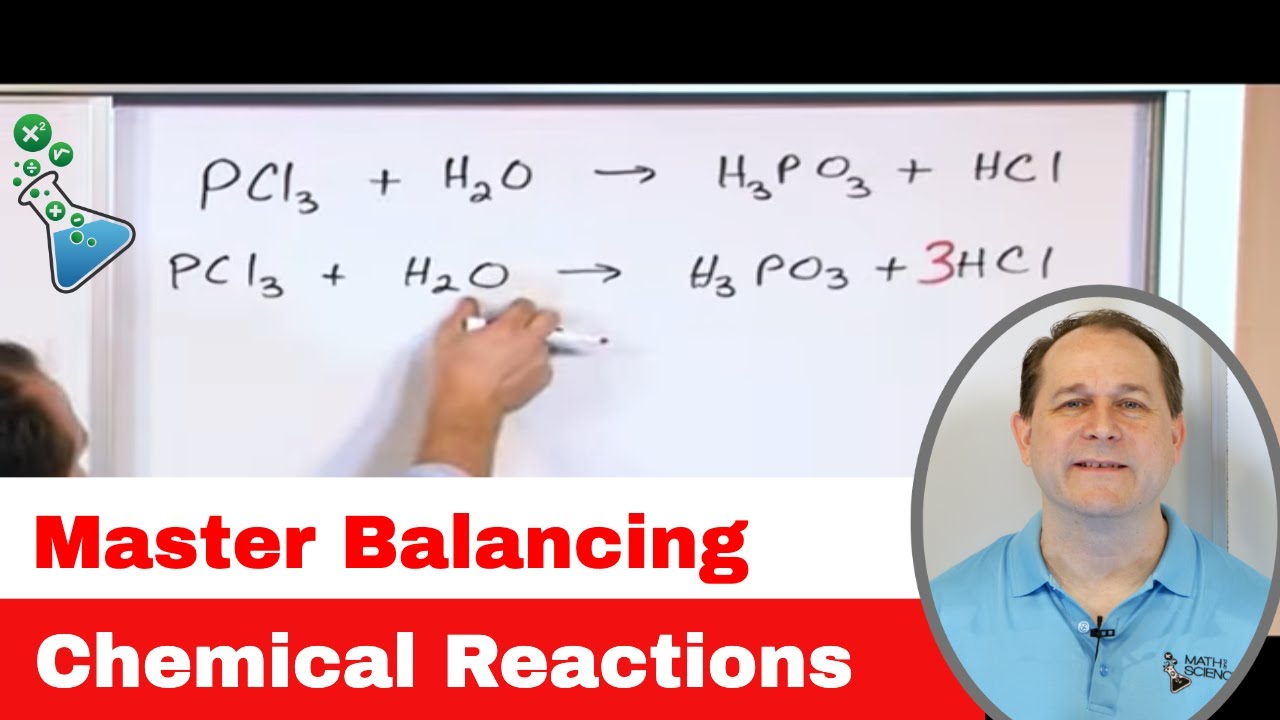
- 🔄 A balanced chemical equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- 📚 The chemical formulas for reactants and products are written in a chemical equation, with coefficients indicating the number of molecules involved.
- ⚖️ Coefficients in a chemical equation are necessary to balance it, reflecting the stoichiometry of the reaction.
- 🔍 The balanced equation for photosynthesis is shown, illustrating the correct stoichiometric ratios of reactants and products.
- 📖 Understanding chemical reactions involves recognizing the roles of reactants and products, as well as the importance of balancing chemical equations according to the conservation of matter.
Q & A
What is a chemical reaction?
-A chemical reaction is a process where substances interact to form different substances by breaking, forming, or rearranging their chemical bonds.
What types of substances can participate in a chemical reaction?
-Substances that can participate in a chemical reaction may be ionic or covalent compounds, as well as atoms, ions, or molecules of some elements.
Can you provide an example of a chemical reaction?
-Photosynthesis is an example of a chemical reaction where plants use the sun's energy to combine carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
What are reactants in the context of a chemical reaction?
-Reactants are the substances that change by combining or reacting together in a chemical reaction.
What are products in a chemical reaction?
-Products are the new substances produced by a chemical reaction.
How are chemical reactions written by scientists?
-Chemical reactions are written in the form of a chemical equation, which includes the reactants' chemical formulas on the left and the products' chemical formulas on the right.
What is the law of conservation of matter, and how does it relate to chemical reactions?
-The law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed but can only change forms. In a chemical reaction, this law ensures that the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to those in the products.
What is the purpose of balancing a chemical equation?
-Balancing a chemical equation is necessary to adhere to the law of conservation of matter, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals those in the products.
What are coefficients in a chemical equation?
-Coefficients in a chemical equation indicate the number of molecules of each reactant and product involved in the reaction.
What does it mean if there is no coefficient in front of a chemical formula in an equation?
-If there is no coefficient in front of a chemical formula, it is understood to mean one molecule of that substance.
What is the significance of the balanced chemical equation for the reactants CO2 and H2O, and the products C6H12O6 and O2?
-The balanced chemical equation signifies that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water react to produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen, adhering to the law of conservation of matter.
Outlines
🌿 Photosynthesis: The Essence of Chemical Reactions
This paragraph introduces the concept of chemical reactions, which are processes where substances interact to form new substances through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. It highlights that reactants, such as ionic or covalent compounds, atoms, ions, or molecules, are transformed into products. The example of photosynthesis is used to illustrate a chemical reaction where plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using solar energy. The paragraph explains the roles of reactants and products in a reaction and emphasizes the importance of the law of conservation of matter, which dictates that the number of atoms of each element must be conserved in a balanced chemical equation. The chemical formulas for the reactants and products of photosynthesis are provided, and the process of balancing the equation is discussed, with coefficients indicating the number of molecules involved.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemical Reaction
💡Chemical Bonds
💡Reactants
💡Products
💡Chemical Equation
💡Balancing Equation
💡Law of Conservation of Matter
💡Coefficients
💡Photosynthesis
💡Ionic and Covalent Compounds
💡Stoichiometry
Highlights
A chemical reaction is a process where substances interact to form different substances by altering their chemical bonds.
Substances in a chemical reaction can be ionic or covalent compounds, as well as atoms, ions, or molecules of elements.
Photosynthesis is an example of a chemical reaction where plants use the sun's energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
In a chemical reaction, reactants are the substances that change by combining or reacting together.
Products are the new substances produced by a chemical reaction.
Chemical equations represent the reactants and products in a chemical reaction, following the law of conservation of matter.
Reactants and products in a chemical equation must be composed of the same elements.
The chemical formulas for reactants and products are written in a balanced chemical equation to reflect the conservation of matter.
The balanced equation for photosynthesis involves six molecules of carbon dioxide and water producing one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Coefficients in a chemical equation indicate the number of molecules of each reactant and product.
The absence of a coefficient implies one molecule of that substance.
Chemical reactions involve the breaking and reforming of chemical bonds in reacting substances to create different substances.
A chemical equation is a written expression of a chemical reaction, including the chemical formulas of both reactants and products.
In a balanced chemical equation, the number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals those in the products.
The law of conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only changed in form.
Chemical reactions must abide by the law of conservation of matter, ensuring no atoms are created or destroyed.
The process of balancing a chemical equation ensures that the reaction adheres to the conservation of matter.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: