Types of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Dave explains the fundamental concepts of matter, which is anything with mass and occupies space. He describes the three common phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, detailing their properties and how they differ. The video delves into the distinction between physical and chemical changes, emphasizing that physical changes involve a change in state without altering the chemical composition, while chemical changes result in the formation of new substances. The concepts of pure substances, elements, compounds, and mixtures are also explored, with examples provided to illustrate these distinctions. The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to subscribe for more informative content and to engage with the presenter via email.
Takeaways
- 🧠 **Matter Definition**: Matter is anything with mass that occupies space and can exist in various forms.
- 📏 **Solid Properties**: A solid has a fixed shape and volume; its particles are in contact and do not move.
- 💧 **Liquid Properties**: A liquid has a fixed volume but no fixed shape; it takes the shape of its container with particles still in contact but moving.
- ☁️ **Gas Properties**: A gas has neither a fixed volume nor shape; it fills its container with particles far apart and moving freely.
- 🔄 **Phase Changes**: Matter often changes phases, which is a physical change as the chemical composition remains the same.
- 🧬 **Chemical Changes**: A chemical change involves a change in the chemical composition where new substances with new bonds are formed.
- 🌊 **Pure Substances**: A pure substance cannot be separated into other materials by physical processes, such as an element or a compound like water.
- ⚛️ **Elements and Compounds**: An element cannot be broken down into smaller parts, whereas a compound, like water, is made of two or more elements.
- 🤝 **Mixtures**: A mixture consists of two or more pure substances that can be separated by physical processes and can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- 🔍 **Homogeneous Mixtures**: In a homogeneous mixture, substances are evenly distributed, so every part looks the same, like sugar in water.
- 🔍 **Heterogeneous Mixtures**: In a heterogeneous mixture, substances are not evenly distributed, leading to different appearances in different sections, like oil and water.
- 📚 **Understanding Chemistry**: Chemistry is fundamentally about understanding the changes in matter, whether they are physical or chemical, and the composition of substances.
Q & A
What is the definition of matter?
-Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space, and it can exist in various forms.
How many phases are commonly used to describe matter?
-Matter is commonly divided into three phases: solid, liquid, and gas.
What are the characteristics of a solid?
-A solid has a fixed shape and volume, with particles that are touching and do not move.
How do the particles in a liquid behave?
-In a liquid, the particles are still touching each other but they can move fluidly, allowing the liquid to take the shape of its container.
What defines a gas?
-A gas has no fixed volume or shape and will completely fill its container. The particles are far apart, move freely, and seldom touch.
What is a physical change?
-A physical change is a change in which the chemical composition of the substance remains unchanged, such as when ice melts into water.
How is a chemical change different from a physical change?
-A chemical change involves a change in the chemical composition of a substance, where chemical bonds between atoms break and form to create new substances.
What is a pure substance?
-A pure substance is one that cannot be separated into other materials by any physical process, such as water, which remains water regardless of boiling or freezing.
What is an element?
-An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into smaller parts by physical or chemical means, consisting of only one type of atom.
How is a compound different from an element?
-A compound is made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together, unlike an element which is made of only one type of atom.
What are the two types of mixtures?
-There are two types of mixtures: homogeneous, where substances are evenly distributed, and heterogeneous, where substances are not evenly distributed and different sections may look different.
How can you separate substances in a heterogeneous mixture?
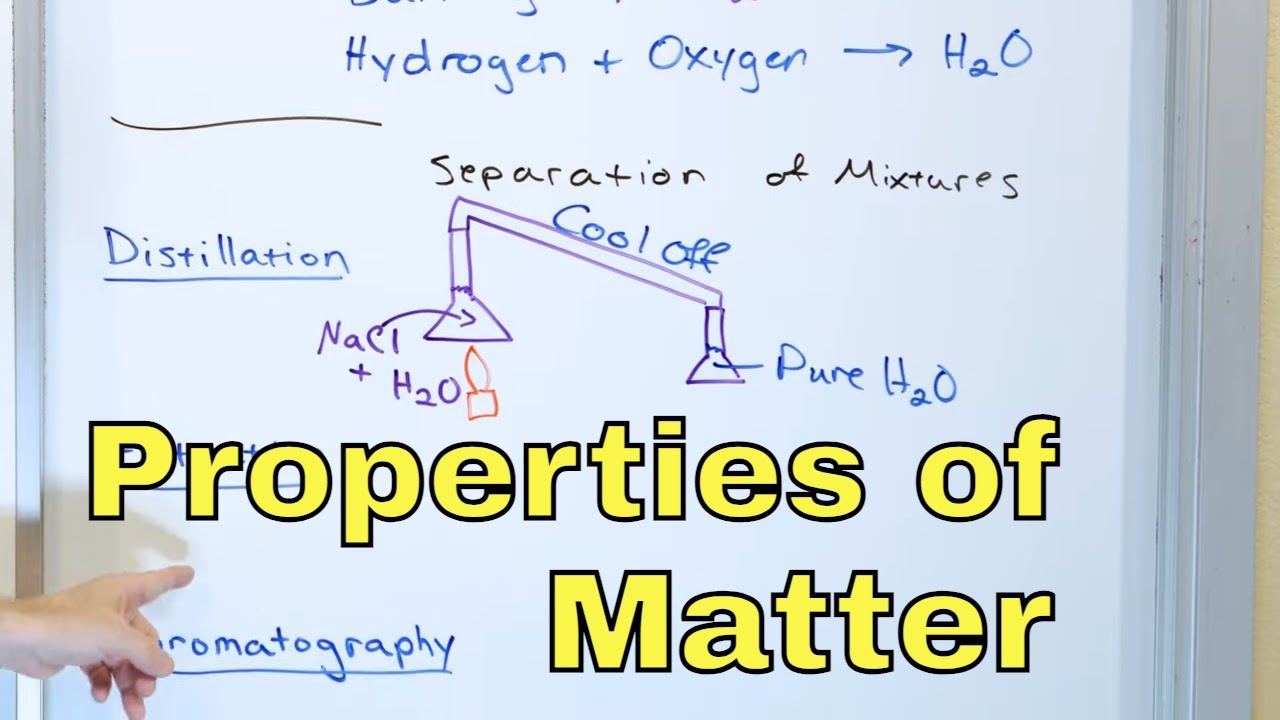
-In a heterogeneous mixture, substances can often be separated by physical processes. For example, boiling saltwater will cause the water to evaporate, leaving the salt behind.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Matter and Its Phases
Professor Dave introduces the concept of matter, which is anything with mass and occupies space. He explains that matter can exist in three phases: solid, liquid, and gas. In a solid, particles are fixed and do not move, while in a liquid, they have a fixed volume but no fixed shape and can move fluidly. Gases have neither fixed volume nor shape and will fill their container with particles that are far apart and rarely touch. The script emphasizes the importance of these phase changes in the study of chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Phases of Matter
💡Physical Change
💡Chemical Change
💡Pure Substance
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Mixture
💡Homogeneous Mixture
💡Heterogeneous Mixture
💡Molecule
Highlights
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space.
Matter can exist in three phases: solid, liquid, and gas.
Solids have a fixed shape and volume, with particles that do not move.
Liquids have a fixed volume but no fixed shape, and their particles move fluidly.
Gases have neither a fixed volume nor shape and will fill their container.
Physical changes involve a change in state without altering the chemical composition.
Chemical changes result in the formation of new substances with new chemical bonds.
Pure substances cannot be separated into other materials by physical processes.
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into smaller parts.
A compound, like water, is made up of two or more elements and can be chemically broken down.
Mixtures consist of two or more pure substances that can be separated by physical processes.
Homogeneous mixtures have substances evenly distributed, while heterogeneous ones do not.
Pure substances can be elements, which are made of one type of atom, or compounds with different types of atoms.
Mixtures can be either homogeneous, like sugar and water, or heterogeneous, like oil and water.
Understanding the phases of matter and the differences between physical and chemical changes is fundamental to chemistry.
The ability to distinguish between elements, compounds, and mixtures is key to classifying substances.
Chemical processes can break down compounds into their constituent elements.
The arrangement of atoms in a substance determines whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas.
The concept of matter and its transformations are central to understanding physical and chemical properties.
Professor Dave's tutorials aim to clarify complex scientific concepts for a broader audience.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Changes in the Properties of Matter Physical and Chemical
What is Chemical & Physical Change in Chemistry? - Intensive & Extensive Properties - [1-1-4]

Chemical Reactions and Equations

Is this a CHEMICAL REACTION? | Chemistry | Chemical vs Physical changes

Atoms and Matter for Kids

Physical vs. Chemical Changes - General Science for Kids!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: