Element, Compound and Mixture | Chemsitry
TLDRThe video script provides an insightful explanation of the fundamental concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures in chemistry. It begins by differentiating elements, which are pure substances made from a single type of atom, such as gold, from compounds, which are pure substances formed by chemically combining two or more different types of atoms in a fixed ratio, like table salt (sodium and chlorine) or sugar (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen). The script also clarifies the distinction between chemical and physical combinations, emphasizing that chemical combinations involve the exchange or sharing of electrons between atoms, while physical combinations, as in the case of a salad or a mixture of salt and water, do not involve a change in the fundamental nature of the substances involved. The concept of a mixture is portrayed as an impure substance because it consists of physically combined elements or compounds with different chemical properties. The video aims to educate viewers on these basic chemical principles in an accessible manner, inviting them to explore the periodic table and understand the composition of the universe's 118 known elements, both natural and manmade.
Takeaways
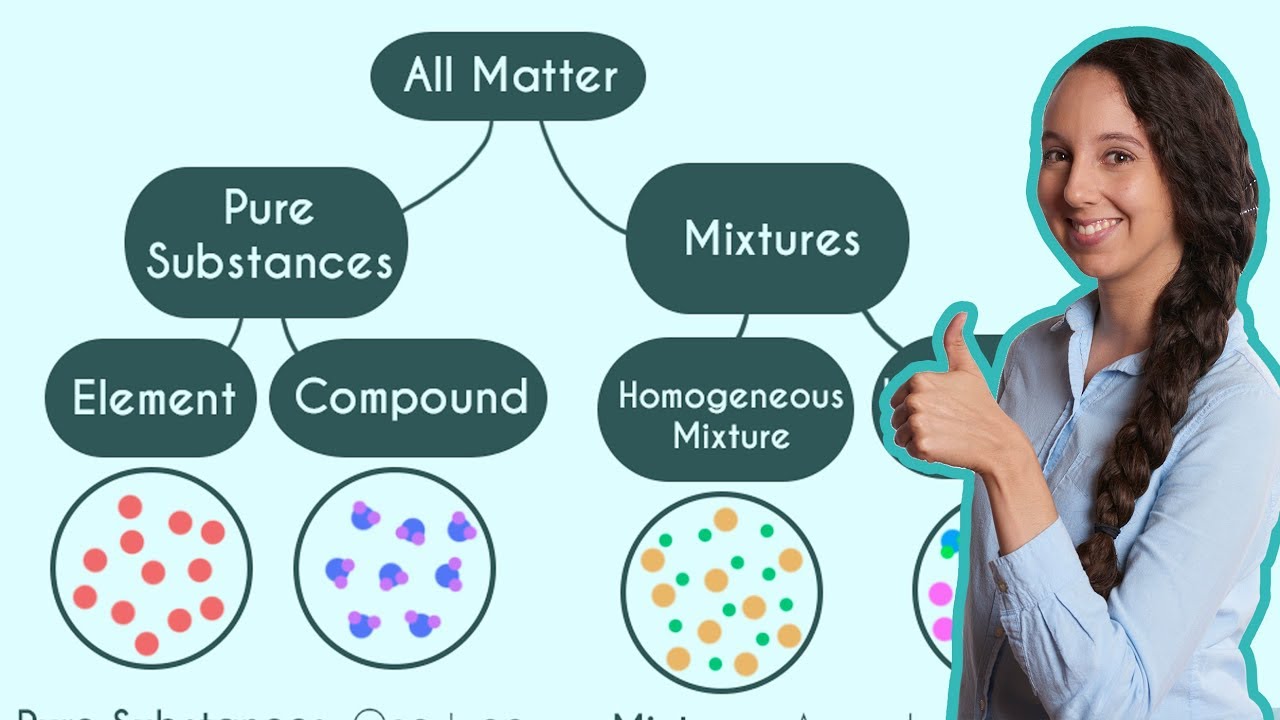
- 🌟 **Elements and Compounds**: An element is a pure substance made from one type of atom, like gold, while a compound is made from two or more different types of atoms chemically combined, such as table salt (sodium and chlorine).
- 🔍 **Definition of Element**: An element cannot be split into simpler substances by physical or chemical means and is represented by a unique symbol in the periodic table.
- 🧪 **Discovery of Elements**: Scientists have discovered 118 elements, 92 of which are natural and 26 are man-made, all listed in the periodic table.
- 🤔 **Atoms vs. Elements**: An atom is the basic unit of an element. For instance, a pencil is made from carbon atoms, which together form the element carbon.
- 🧬 **Compound Formation**: Compounds are pure substances formed by atoms of different elements chemically combining in a fixed ratio by mass, like water (H2O) with two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom.
- 🔬 **Chemical Combination**: Chemical combination occurs when atoms either gain, lose, or share electrons, leading to the formation of compounds.
- 🍹 **Mixtures**: A mixture is a physical combination of two or more substances, like cold drinks or a salad, which are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical means.
- 🚫 **Impurity in Mixtures**: Mixtures are considered impure substances because they consist of different kinds of particles with distinct chemical properties.
- ⚖️ **Fixed Ratio in Compounds**: The ratio of atoms in a compound is fixed by mass, which defines the compound's identity, such as the 2:1 ratio in water (H2O).
- 🔄 **Physical vs. Chemical**: Elements are pure substances with uniform chemical properties, while mixtures lack uniformity due to the combination of different substances.
- 📚 **Understanding Symbols**: Each element has a unique symbol, which is crucial for understanding and representing compounds and their chemical formulas.
Q & A
What is an element in the context of chemistry?
-An element is a pure substance that cannot be split into two or more simpler substances by any physical or chemical process. It is made from only one type of atoms and has the same chemical properties throughout.
How is a compound different from an element?
-A compound is a pure substance that consists of two or more different types of elements chemically combined together in a fixed ratio by mass. Unlike elements, compounds are made up of molecules that consist of more than one kind of atom.
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?
-The periodic table is a chart that lists all the known elements, which currently number 118, of which 92 are naturally occurring and 26 are man-made. It organizes elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
How does a mixture differ from a compound?
-A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically combined together without any chemical bonding. It is considered an impure substance because it contains different kinds of particles with different chemical properties. In contrast, a compound has a fixed composition and properties due to its chemical combination.
What is a chemical combination and how does it occur?
-A chemical combination occurs when two or more atoms join together by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. This process results in the formation of chemical bonds, leading to the creation of a compound with a fixed ratio of atoms.
What is the role of the fixed ratio by mass in defining a compound?
-The fixed ratio by mass is crucial in defining a compound because it determines the exact proportion of different atoms in a molecule. This ratio ensures that the compound has consistent chemical properties and is distinct from other substances.
Why is a mixture considered impure?
-A mixture is considered impure because it consists of two or more substances that are simply combined physically without any chemical reaction. The particles in a mixture retain their individual chemical properties, leading to a substance with varying properties throughout.
How does the structure of table salt (sodium chloride) demonstrate the concept of a compound?
-Table salt (sodium chloride) is an example of a compound because it is made from sodium and chlorine atoms that have chemically combined in a fixed ratio of 1:1 by mass. Sodium loses an electron, and chlorine gains an electron, resulting in a neutral compound with its own set of properties.
What is the basic unit of an element?
-The basic unit of an element is an atom. An element is made up of a large number of identical atoms bonded together. For example, carbon atoms combine to form the element carbon.
How many elements have been discovered and how are they categorized?
-A total of 118 elements have been discovered, of which 92 are naturally occurring and 26 are man-made. These elements are categorized and displayed in the periodic table according to their atomic structure and properties.
What is the difference between a physical combination and a chemical combination?
-A physical combination involves mixing substances together without any change in their chemical identity or the formation of new substances. An example is mixing vegetables in a salad. In contrast, a chemical combination results in the formation of new substances with different properties, as seen when atoms of different elements bond to form a compound.
Can you provide an example of a mixture and explain why it is considered impure?
-An example of a mixture is a cold drink made by combining water with sugar and other ingredients. It is considered impure because the substances are simply mixed at a physical level without any chemical bonding. The individual components, such as sugar and water, retain their own chemical properties within the mixture.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures. It explains that elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom, which cannot be broken down further by physical or chemical means, and are represented by a unique symbol. Compounds, on the other hand, are made from two or more different types of atoms chemically combined in a fixed ratio, forming a pure substance with consistent chemical properties. The paragraph also distinguishes between chemical and physical combinations, using examples like table salt and water to illustrate the concepts. Lastly, it clarifies the difference between natural and artificial elements, and introduces the periodic table as a reference for the known elements.
📚 The Nature of Compounds and Mixtures
This section delves deeper into the characteristics of compounds and mixtures. Compounds are defined as pure substances formed by the chemical combination of different elements in a fixed mass ratio. The paragraph provides examples such as table salt, sugar, and water, and emphasizes the importance of understanding chemical bonds and mass ratios for a thorough comprehension of compounds. It also explains the concept of a chemical combination, where atoms either share or exchange electrons to form a compound. In contrast, mixtures are combinations of substances that are not chemically bonded, such as cold drinks, tea, and dyes. The paragraph illustrates how mixtures are formed through physical processes, like mixing vegetables in a salad, and clarifies that mixtures are considered impure substances due to the presence of different kinds of particles with varying chemical properties.
🎓 Recap of Key Concepts
The final paragraph serves as a recap, summarizing the key concepts discussed in the video. It reiterates the definitions of elements, compounds, and mixtures, and highlights the importance of understanding their differences. The paragraph reinforces the idea that mixtures lack uniform chemical properties, using the example of mixing water and salt to demonstrate this point. It concludes by expressing hope that the viewer has gained a clear understanding of these basic chemical concepts, and thanks the viewer for watching the video.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Mixture
💡Atom
💡Chemical Combination
💡Physical Combination
💡Periodic Table
💡Chemical Properties
💡Impure Substance
💡Molecule
💡Fixed Ratio by Mass
Highlights
Elements and compounds are two fundamental types of substances. Elements are made from one type of atom, while compounds consist of two or more different types of atoms chemically combined together.
Table salt is an example of a compound, as it is made from sodium and chlorine atoms. Gold, on the other hand, is an element since it is composed of only gold atoms.
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any physical or chemical means. Gold is an example of an element.
There are 118 known elements, 92 of which are naturally occurring and 26 are man-made. These elements are organized in the periodic table.
A compound is a pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio by mass. Examples include table salt, sugar, and water.
Chemical combination occurs when atoms gain, lose, or share electrons. This forms a compound with a fixed ratio of atoms, like H2O for water.
Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are physically combined together, such as in a salad or when salt is dissolved in water.
Mixtures are impure substances since they contain different kinds of particles with distinct chemical properties, unlike elements and compounds.
Physical combination involves simply mixing substances together without any change in the particles themselves, as opposed to chemical combination.
Understanding the concepts of chemically combined atoms and fixed ratio by mass is crucial for grasping the nature of compounds.
An atom is the basic unit of an element. For example, a pencil is made from carbon atoms, which combine to form the element carbon.
All elements have unique symbols, such as C for carbon, H for hydrogen, and O for oxygen. These symbols help identify elements in the periodic table.
Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that indicate the types and ratios of atoms in a molecule, like NaCl for table salt and C6H12O6 for glucose.
The periodic table is a comprehensive chart listing all 118 known elements, both natural and man-made, arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
Elements are pure substances made from one kind of atom with the same chemical properties, while mixtures are impure and contain different particles.
The distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures lies in the type of atoms involved and the way they are combined - either chemically or physically.
This lecture provides a clear and easy-to-understand explanation of the fundamental concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures in chemistry.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,

Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances

How to Compare Pure Substances and Mixtures - HSC Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: