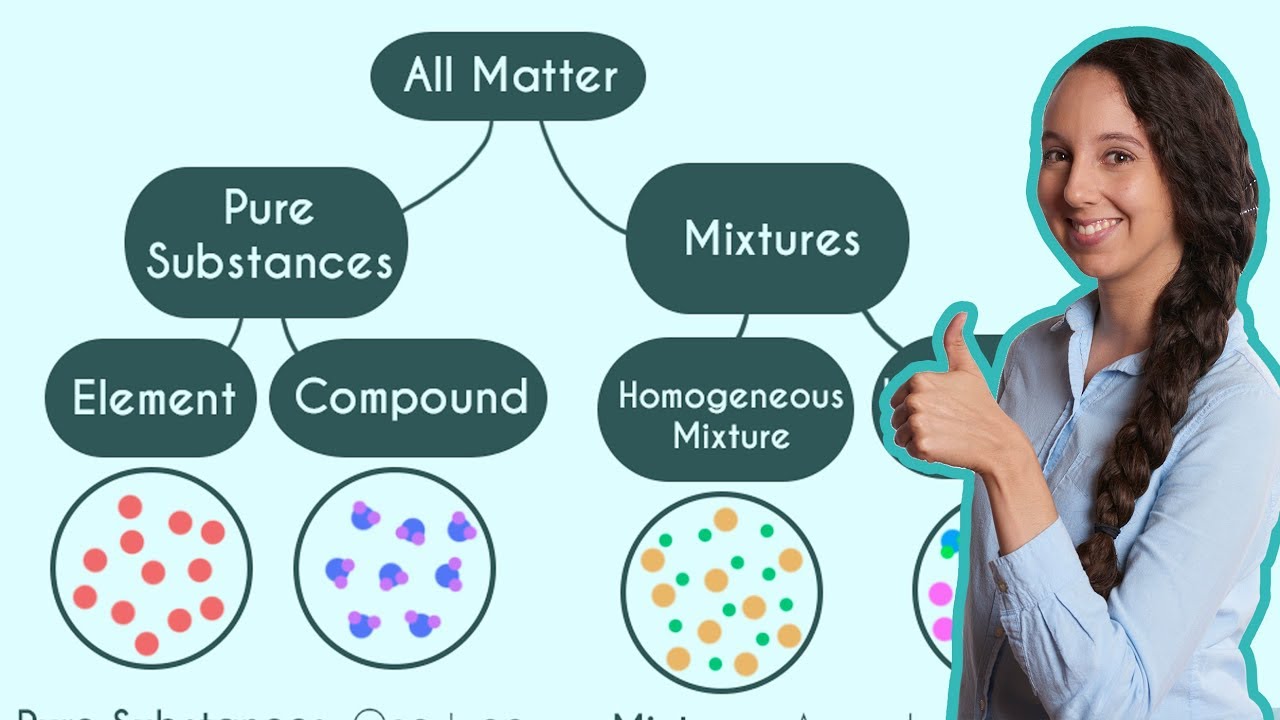
Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances
TLDRThis video script introduces the fundamental concepts of matter in chemistry, differentiating between pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are further categorized into elements, which consist of a single type of atom, and compounds, composed of two or more different elements. Mixtures are classified as either homogeneous, where components are uniformly distributed, or heterogeneous, with visibly distinct parts. Examples like water (a compound), oxygen gas (an element), and oil and water (a heterogeneous mixture) are used to illustrate these concepts, aiming to deepen the viewer's understanding of matter classification.
Takeaways
- 📌 Matter can be categorized into two main groups: pure substances and mixtures.
- 🔍 Pure substances consist of a single type of matter and can be further divided into elements and compounds.
- 🌟 Elements are pure substances made up of only one kind of atom, such as oxygen gas, helium, and iron metal.
- 💠 Compounds are also pure substances but are composed of two or more different elements, like water (H2O) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
- 🥣 Mixtures are combinations of two or more pure substances and can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- 🔀 Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, examples include saltwater solution and brass (a metal alloy).
- 🌐 Heterogeneous mixtures lack uniformity; their components can be visually distinguished, like oil and water or sand and water.
- 🌬️ Air is an example of a homogeneous mixture, containing a blend of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and argon.
- 🔬 To understand the classification of matter, one can explore example problems and further content through linked resources.
- 📚 The script serves as an introduction to the types of matter and their classification in the field of chemistry.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of matter discussed in the video?
-The two main categories of matter discussed in the video are pure substances and mixtures.
What defines a pure substance?
-A pure substance is a material that is uniform in composition and consists of a single type of matter.
What are the two types of pure substances mentioned in the video?
-The two types of pure substances mentioned in the video are elements and compounds.
What is an element in the context of chemistry?
-An element is a pure substance that is made up of only one kind of atom. Examples include oxygen gas, helium, and iron metal.
How is a compound different from an element?
-A compound is a pure substance that is composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together, such as water (H2O) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
What are the two types of mixtures and how are they distinguished?
-The two types of mixtures are homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, while heterogeneous mixtures do not have a uniform composition and consist of distinct phases or separations.
Give an example of a homogeneous mixture mentioned in the video.
-Salt dissolved in water is an example of a homogeneous mixture, where the salt is uniformly distributed throughout the water.
How does a heterogeneous mixture differ in appearance from a homogeneous mixture?
-A heterogeneous mixture has a visible separation of its components, such as oil floating on top of water due to its lower density, whereas a homogeneous mixture appears as a single phase with no visible separation.
What is another example of a heterogeneous mixture given in the video?
-Sand mixed with water is an example of a heterogeneous mixture, where the sand particles are distinct and separate from the water.
How can you identify a compound versus an element in a pure substance?
-A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more different elements chemically combined, while an element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom.
What advice does the video offer for those who want to learn more about pure substances and mixtures?
-The video suggests that viewers who want to learn more about pure substances and mixtures should check out the additional video content and example problems provided in the description section below the video.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Matter: Pure Substances and Mixtures
This paragraph introduces the concept of matter and categorizes it into two main groups: pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are further divided into elements and compounds, with elements being made up of a single type of atom and compounds consisting of two or more different elements chemically bonded together. Mixtures, on the other hand, are composed of two or more pure substances that are not chemically bonded. They are classified into homogeneous mixtures, where the components are uniformly distributed, and heterogeneous mixtures, where the components are not uniformly distributed and can be physically separated. Examples provided include oxygen gas, helium, nitrogen gas, iron metal, zinc, elemental sulfur, water, sodium chloride, ethanol, and carbon dioxide.
🌐 Examples and Characteristics of Mixtures
This paragraph delves into the characteristics of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures are described as having a uniform composition throughout, with examples including saltwater solution and air, which is a mixture of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Heterogeneous mixtures are characterized by their non-uniform composition, where the different components can be physically separated, as seen in oil and water or sand and water mixtures. The paragraph emphasizes the distinction between the two types of mixtures and provides visual examples to aid in understanding.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Pure Substances
💡Elements
💡Compounds
💡Mixtures
💡Homogeneous Mixtures
💡Heterogeneous Mixtures
💡Density
💡Chemical Bonding
💡Physical Properties
💡Classification
Highlights
Matter can be categorized into two main types: pure substances and mixtures.
Pure substances consist of a single type of matter.
Mixtures are composed of two or more different pure substances.
Pure substances can be further divided into elements and compounds.
Elements are pure substances made up of only one kind of element, such as oxygen gas, helium, and iron metal.
Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more different elements, like water and sodium chloride.
Mixtures can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition, such as salt and water.
Heterogeneous mixtures lack uniform composition, an example being oil and water.
In a heterogeneous mixture, components can be visually distinguished, like oil floating on water.
Air is a homogeneous mixture of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, and carbon dioxide.
Sand and water form a heterogeneous mixture, with sand particles visibly separate from the water.
This video provides foundational knowledge for understanding the classification of matter in chemistry.
Additional video content and example problems on pure substances and mixtures are available in the description section.
The concepts discussed are essential for anyone studying or interested in chemistry.
Understanding the difference between elements and compounds is crucial for chemical analysis and experimentation.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9

What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?

Mixtures - Class 9 Tutorial

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,

Pure Substances and Mixtures | Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: