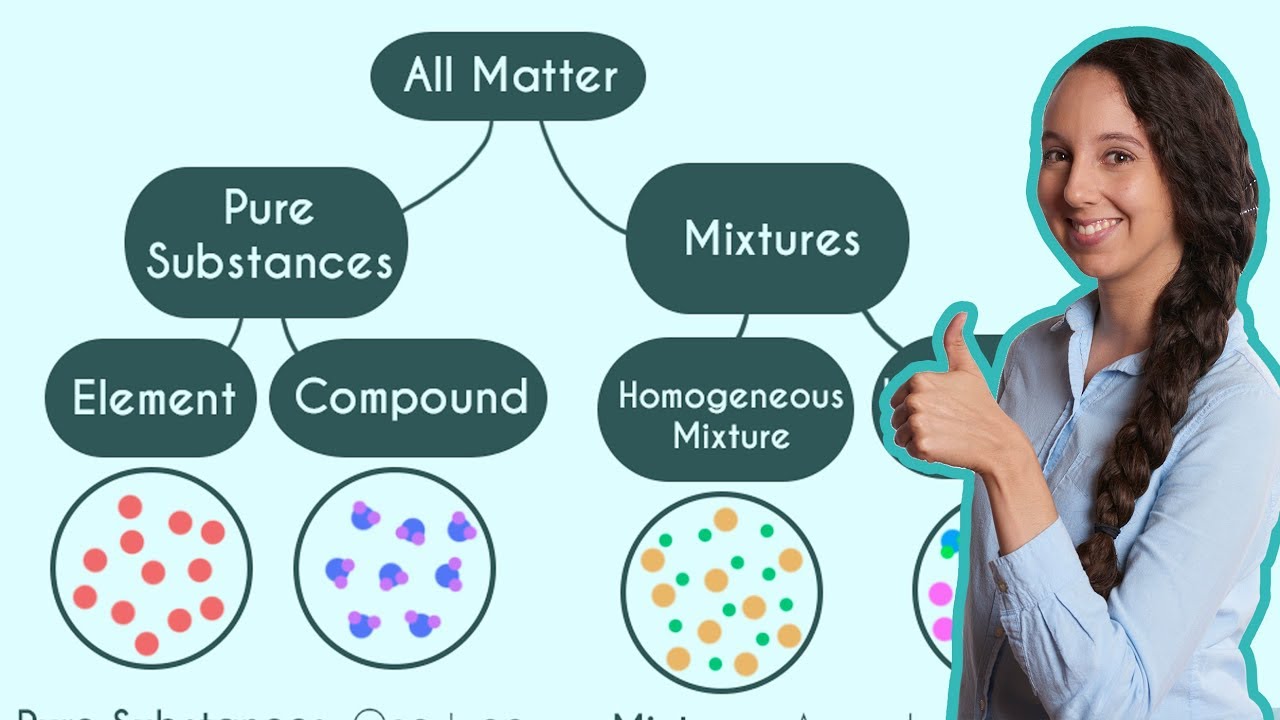
Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,
TLDRThe video script provides a clear explanation of the difference between pure substances and mixtures. A pure substance is characterized by a constant composition, which can be either an element made up of one type of atom or a compound consisting of two or more different atoms. Examples include helium, water (H2O), and hydrogen gas (H2). In contrast, a mixture is a combination of multiple pure substances with a variable composition, such as salt water, which is composed of water and salt. The script also describes how pure substances can be separated into their components through chemical processes, like electrolysis for water, while mixtures can be separated through physical processes, such as boiling to separate salt from water. The video concludes with a list of various materials, classifying each as a pure substance or a mixture, helping viewers to better understand these concepts.
Takeaways
- 🧪 A pure substance has a constant composition and can be either an element or a compound made up of a definite and constant composition.
- 🤔 A mixture is a combination of multiple pure substances and can have a variable composition.
- 🌟 Examples of pure substances include the element helium and the compound H2O (water), which is made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
- 💧 Hydrogen gas (H2) is a pure substance composed of molecules, but it's a pure element because it consists of only one type of atom.
- 🔍 Molecules are made up of multiple atoms, which can be the same type, like in hydrogen gas, or different types, like in water.
- 🧴 A mixture, such as salt water, is composed of different pure substances (e.g., water and salt) that are combined together.
- 📉 The composition of a pure substance is fixed and cannot be altered without creating a mixture.
- 🔄 Mixtures can be separated into their components through physical processes like evaporation, boiling, or filtration.
- ⚗️ Pure substances in the form of compounds can be broken down into their elements through chemical processes, such as electrolysis.
- 🧬 Alloys, like brass or sterling silver, are mixtures because they are composed of multiple metals.
- 🌐 Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, while heterogeneous mixtures do not.
- 🍇 Common examples of mixtures include soda, milk, and wine, which are composed of various substances mixed together.
Q & A
What is a pure substance?
-A pure substance is a material that has a constant and definite composition. It can be either an element, which is made up of only one type of atom, or a compound, which consists of two or more different types of atoms in a fixed ratio.
How does a mixture differ from a pure substance?
-A mixture differs from a pure substance in that it is a combination of multiple pure substances that are not chemically bonded together. The composition of a mixture can be variable, unlike the fixed composition of a pure substance.
Is helium considered a pure substance?
-Yes, helium is considered a pure substance because it is a pure element composed of single atoms of the same type.
What is the difference between water (H2O) and hydrogen gas (H2) in terms of their classification as pure substances?
-Water (H2O) is a compound because it is made up of two different types of atoms, hydrogen and oxygen, in a fixed ratio. Hydrogen gas (H2), on the other hand, is a pure element because it consists of molecules made up of the same type of atom, hydrogen.
How can you separate the components of a mixture?
-The components of a mixture can be separated by physical processes such as evaporation, boiling, decantation, filtration, centrifugation, and chromatography.
Can you separate the components of a pure substance?
-The components of a pure substance, if it is a compound, can be separated by a chemical process. An example of this is electrolysis, which can break down water into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Why does a mixture have a variable composition?
-A mixture has a variable composition because the proportion of its constituent pure substances can be altered. For instance, the amount of salt in a saltwater solution can be varied to create solutions of different concentrations.
What is the composition of a pure substance like, and can it be changed?
-The composition of a pure substance is constant and definite. It cannot be changed by physical means. The only way to alter the composition is to create a mixture by combining it with other substances.
What is an example of a pure substance that is also a molecule?
-An example of a pure substance that is also a molecule is water (H2O). It is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Is brass a pure substance or a mixture?
-Brass is a mixture. It is an alloy composed of copper and zinc, forming a solid solution of these two metals.
How can you identify if a substance is a pure substance or a mixture?
-A pure substance is typically a single element or a single compound with a constant composition. A mixture, on the other hand, consists of multiple substances that are not chemically bonded and can have a variable composition. Physical and chemical processes can be used to separate the components of a mixture or to break down a compound into its elements, respectively.
What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, such as air which is a mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. A heterogeneous mixture does not have a uniform composition and can have different compositions in different parts, such as a mixture of sand and water.
Outlines
🔬 Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures
The first paragraph introduces the topic of distinguishing pure substances from mixtures. It explains that a pure substance has a constant composition and can be either an element, like helium, or a compound, like water (H2O). The paragraph also clarifies that mixtures are combinations of multiple pure substances with variable compositions. Examples given include helium as a pure element, water as a compound, and hydrogen gas as a pure element composed of molecules. The difference between elements, compounds, and molecules is highlighted, with an emphasis on the constant composition of pure substances and the variable composition of mixtures.
🧪 Variable Composition in Mixtures and Separation Processes
The second paragraph delves into the variable composition of mixtures, contrasting it with the constant composition of pure substances. It illustrates how the composition of a mixture, such as salt water, can be altered by changing the proportions of its components. The paragraph also discusses the methods of separating the components of a mixture through physical processes like evaporation and boiling, and pure substances through chemical processes. An example of electrolysis is given to demonstrate how a compound like water can be broken down into its constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen, using electricity.
📚 Classifying Various Substances as Pure or Mixtures
The third paragraph provides a list of different substances and categorizes each as either a pure substance or a mixture. It covers a range of materials, including carbon dioxide (a compound and thus a pure substance), iron metal (a pure element), brass (an alloy and therefore a mixture), and air (a mixture of gases). The distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures is mentioned, and examples like sugar water and 24 karat gold are used to further clarify the concepts of pure substances and mixtures.
🌿 Further Classification of Substances into Mixtures
The fourth paragraph continues the classification of substances, focusing on those that are mixtures. It discusses rubbing alcohol, soda, milk, sterling silver, sea water, wood, soil, and wine, explaining why each is considered a mixture due to the combination of different substances. The paragraph reinforces the idea that pure substances are typically single elements or compounds, while mixtures consist of multiple substances combined together.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Pure Substance
💡Mixture
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Molecule
💡Constant Composition
💡Variable Composition
💡Physical Process
💡Chemical Process
💡Alloy
💡Heterogeneous Mixture
Highlights
A pure substance has a constant composition, while a mixture can have a variable composition.
Pure substances can be elements or compounds with a definite and constant composition.
A mixture is a combination of multiple pure substances.
Helium is a pure substance as it is a single element.
H2O (water) is a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, classifying it as a pure substance.
Hydrogen gas (H2) is a pure substance composed of molecules, but only one type of atom.
Molecules are made up of multiple atoms, which can be the same or different types.
Pure elements consist of only one type of atom, like helium or hydrogen gas.
A mixture, such as salt water, is composed of different substances like water and salt.
The composition of a pure substance cannot be altered without creating a mixture.
Mixtures can be separated into their components by physical processes, while compounds require chemical processes.
Electrolysis is a chemical process that can break down water (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Physical processes like evaporation, boiling, and filtration can separate components of a mixture.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and dry ice are pure substances as they are single compounds.
Iron metal is a pure element, making it a pure substance.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, classifying it as a mixture.
Air is a mixture of gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Pure substances like sugar (C12H22O11) and 24 karat gold are single elements or compounds.
Mixtures like soda, milk, and wine are composed of multiple substances.
Sterling silver is a mixture, being an alloy of silver and copper.
Sea water is a mixture, primarily of water and sodium chloride with other elements.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: