How to Compare Pure Substances and Mixtures - HSC Chemistry
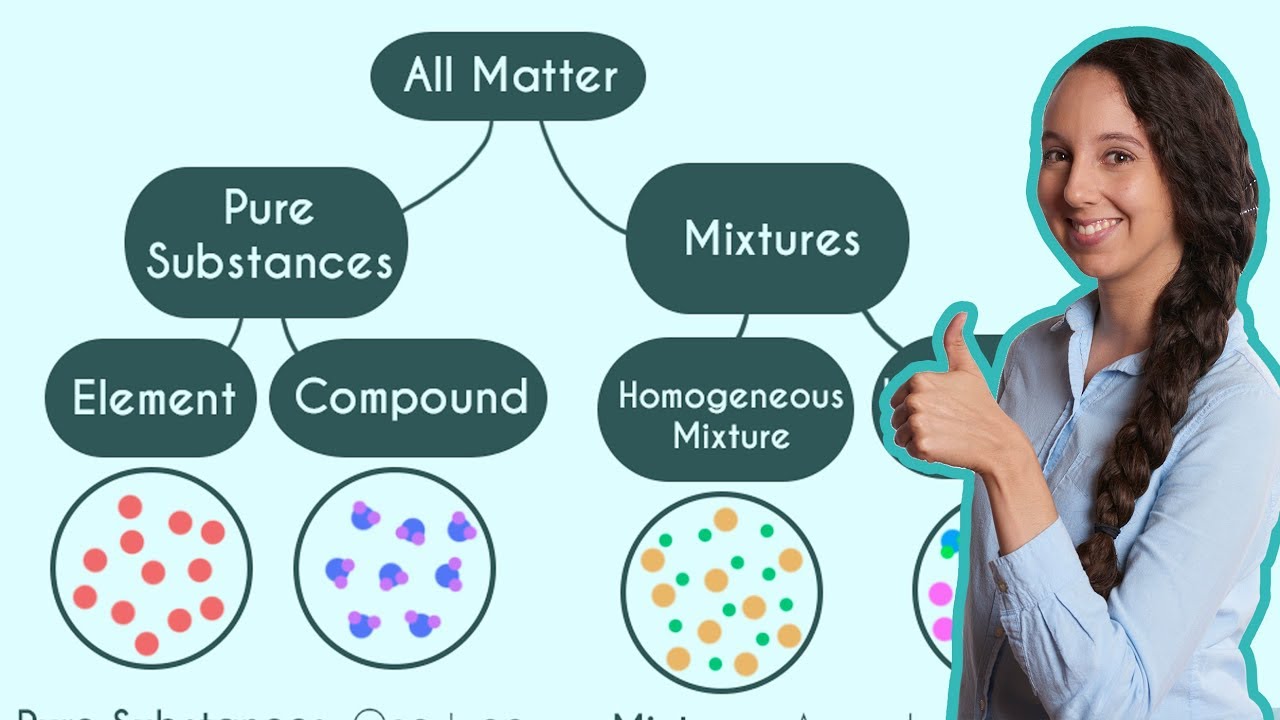
TLDRThis video script delves into the chemistry of matter, distinguishing between pure substances and mixtures. It explains that pure substances, which include elements and compounds, have a uniform particle distribution and fixed composition. Mixtures, on the other hand, are physical combinations of substances without chemical bonds, like the example of gold coins and sand. The script emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for both academic and practical applications, such as in experiments or separating materials like the pirate Blackbeard's treasure.
Takeaways
- 📚 Matter is defined as a substance with mass and a given volume.
- 🌊 Pure substances consist of the same type and distribution of particles throughout and have a fixed composition.
- 🔬 Pure substances can be broken down into elements (single elements from the periodic table) or compounds (chemically combined elements).
- 🏆 Gold coins are an example of pure substances because they are made of a single element, gold, and can be physically separated into identical products.
- 🏖️ Sand, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, is also a pure substance with a definite fixed composition.
- 💰 Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are physically, but not chemically, combined and can be separated through physical means.
- 🗝️ A pirate's buried treasure of gold coins and sand exemplifies a mixture, where the two pure substances are physically combined but not chemically bonded.
- 🔎 Sieving is a separation technique where particles are separated by size, useful for separating mixtures like gold coins and sand.
- 🧪 Practical applications of mixtures knowledge extend beyond pirates to scientific experiments conducted at school or home.
- 📝 In the HSC chemistry course, students are often required to classify different types of matter, emphasizing the importance of understanding definitions and distinctions between pure substances and mixtures.
Q & A
What is the definition of matter in chemistry?
-Matter is a substance that has mass and occupies a given volume.
What are the two main types of matter discussed in the video?
-The two main types of matter discussed are pure substances and mixtures.
What are pure substances further broken down into?
-Pure substances can be broken down into elements and compounds.
How can a pure substance be identified?
-A pure substance consists of the same type and distribution of particles throughout and has a definite, fixed composition.
What is an example of a pure substance that is an element?
-Gold coins are an example of a pure substance that is an element, as they are made entirely of a single element, gold.
What is an example of a pure substance that is a compound?
-Sand, which usually consists of silicon dioxide, is an example of a pure substance that is a compound made from silicon and oxygen atoms chemically bonded together.
How are mixtures defined in the context of chemistry?
-Mixtures are defined as two or more substances that have been physically, not chemically, combined, meaning there are no chemical bonds linking the pure substances in a mixture.
Can mixtures be separated? If so, how?
-Yes, mixtures can be separated through physical means, such as sieving, which separates particles by size.
What is an example of a mixture from the video?
-A mixture of gold coins and sand buried by a pirate, where two pure substances of different sizes are physically combined.
How can the gold coins and sand mixture be separated?
-The gold coins and sand mixture can be separated by sieving, using a sieve with holes smaller than the gold coins but bigger than the sand particles, allowing the gold coins to be collected while the sand falls through.
What are the key points to remember when classifying pure substances and mixtures?
-The key points are that matter has mass and volume, pure substances have a uniform type and distribution of particles with a fixed composition and can be either elements or compounds, and mixtures consist of physically combined substances that can be separated through physical means.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Matter: Pure Substances and Mixtures
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of matter in chemistry, focusing on pure substances and mixtures. It explains that matter has mass and occupies volume, using the analogy of a pirate ship to illustrate the concept. The distinction between pure substances, which have a uniform composition and can be elements or compounds, and mixtures, which are physically combined without chemical bonding, is clarified. The examples of gold coins and sand as pure substances, and their combination as a mixture, are used to demonstrate these concepts. The importance of understanding these classifications is emphasized for both academic and practical applications.
🧪 Separation Techniques and Classification of Matter
The second paragraph delves into the practical applications of understanding matter, specifically the separation techniques for mixtures and the classification of substances. It describes how a sieve can be used to separate gold coins from sand based on particle size. The paragraph also provides examples of real-world items that are mixtures, such as white vinegar, sodium bicarbonate, fresh air, and a lava lamp, and emphasizes the need to identify each component in a mixture. The summary reinforces the definitions of matter, pure substances, and mixtures, and encourages viewers to apply this knowledge in their studies and experiments. The video concludes by promoting further learning on the topic of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Pure Substances
💡Elements
💡Compounds
💡Mixtures
💡Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
💡Physical and Chemical Combination
💡Separation Techniques
💡Silicon Dioxide
💡Mass and Volume
💡HSC Chemistry
Highlights
Chemistry explores the properties of different types of matter.
Matter is defined as a substance with mass and occupying a given volume.
Pure substances can be broken down into elements and compounds.
Mixtures are classified as either homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Pure substances have the same type and distribution of particles throughout with a definite fixed composition.
Pure substances can be physically broken up into identical products.
A pure substance can be composed of a single element or a compound of chemically combined elements.
Gold coins are an example of pure substances made of a single element.
Sand is considered a pure substance as it consists of chemically bonded silicon and oxygen atoms.
Mixtures are defined as two or more substances physically combined without chemical bonds.
Mixtures can contain combinations of gases, liquids, and solids separable by physical means.
An example of a mixture is a combination of gold coins and sand.
Mixtures can be physically separated, for instance, by sieving.
White vinegar is a mixture containing liquid water and aqueous acetic acid.
Sodium bicarbonate is a pure substance, a solid compound made from chemically combined elements.
Fresh air is a mixture of different gases including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
A lava lamp contains a mixture of two liquids, water and melted wax.
In the HSC chemistry course, students are often asked to classify different types of matter.
Understanding matter, both pure substances and mixtures, is essential in chemistry.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: