Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
TLDRThis video script delves into the fundamental particles that constitute substances, focusing on the concepts of atoms, elements, compounds, and mixtures. It explains that atoms are the building blocks of all matter, whether living or nonliving. Elements, which are different types of atoms, are categorized in the periodic table, with around 100 known elements. The script illustrates how elements can combine to form compounds through chemical bonding, with sodium chloride (table salt) as an example. It also highlights the distinct properties of compounds compared to their constituent elements, using water (H2O) as a case study. Mixtures are defined as combinations of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded, with air as a prime example. The video also touches on molecules, which are formed by the bonding of two or more nonmetal atoms. The script concludes with a call to action for viewers to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Everything is made up of atoms, including living and nonliving objects.
- 🔍 Different types of atoms are known as elements, with around 100 elements displayed on the periodic table.
- 📚 Elements like oxygen, chlorine, iron, and gold are examples of substances made up of only one type of atom.
- 🔬 A compound is formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together, such as sodium chloride (table salt).
- 📈 Compounds have different properties than the elements that compose them, as seen with water made from hydrogen and oxygen.
- 🤝 In a compound model, you would see two or more different colors or shapes representing the bonded elements.
- 🤔 A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together, like the components of air.
- 🌬️ Air is a mixture containing nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, methane, and other elements and compounds.
- 💧 A molecule is defined as two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together, often found on the right side of the periodic table.
- ⚛️ Molecules can represent elements, like O2, or compounds, like H2O (water), where hydrogen bonds with oxygen.
- 📚 For more information and resources, visit GCSE revision monkey comm and Science surgery comm for educational packages.
Q & A
What are the basic particles that make up all substances?
-The basic particles that make up all substances are atoms.
How many types of elements are there, and where are they displayed?
-There are around 100 different types of elements, and they are displayed in the periodic table.
What is an element, and how is it represented in a particle model?
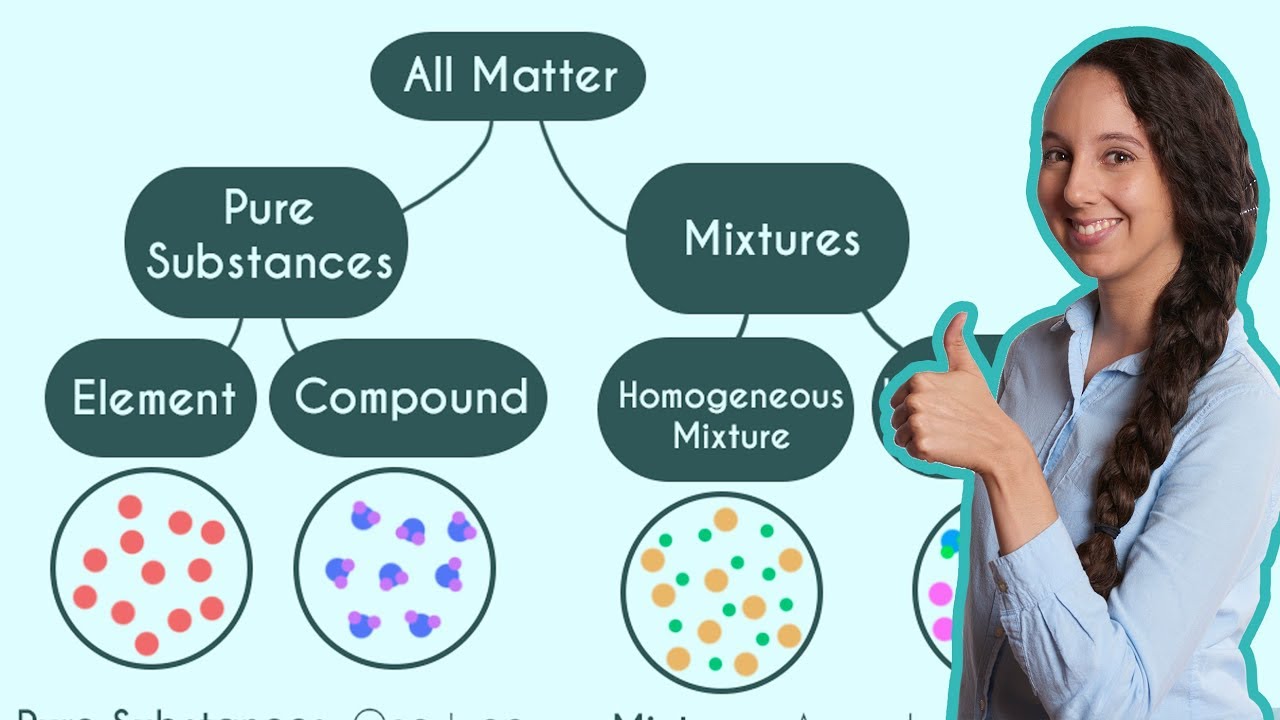
-An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom. In a particle model, it is represented by having only one colored circle.
What is a compound, and how does it differ from an element?
-A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. It differs from an element in that it consists of multiple elements chemically combined, rather than a single type of atom.
How is a compound represented in a particle model?
-In a particle model, a compound is represented by showing two or more different colors or shapes, indicating the different elements that are chemically bonded together.
What is the difference between the properties of a compound and the elements that make it up?
-The properties of a compound can be very different from the properties of the elements that compose it. For example, water, which is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, has a higher boiling point and is a liquid at room temperature, unlike its constituent elements.
What is a mixture, and how does it differ from a compound?
-A mixture is a combination of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together. It differs from a compound in that the components of a mixture are not chemically combined.
Give an example of a mixture and explain its composition.
-Air is an example of a mixture. It contains elements and compounds such as nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and methane, which are not chemically bonded to each other.
What is a molecule, and how is it defined in terms of atomic composition?
-A molecule is a group of two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together. Nonmetals are typically found on the right-hand side of the periodic table.
How does the representation of a molecule differ from that of an element in a particle model?
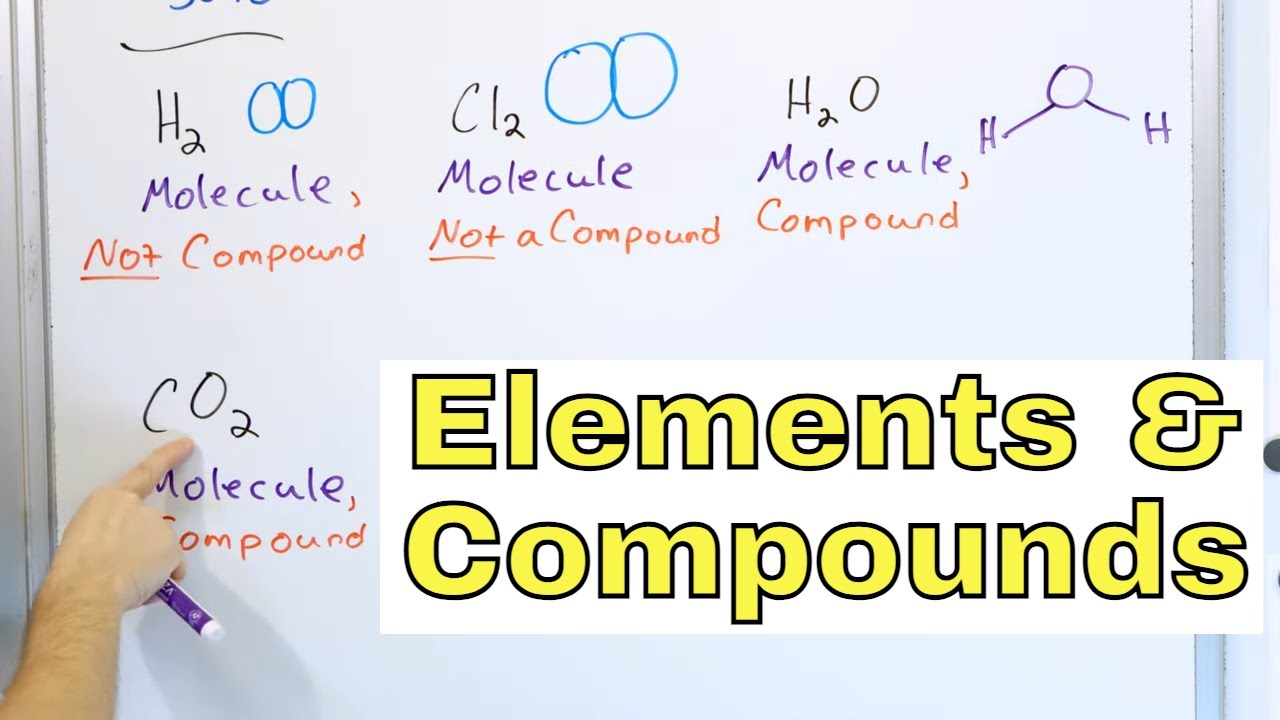
-In a particle model, a molecule can be represented by multiple atoms of the same nonmetal element bonded together, such as O2 for oxygen, or by atoms of different nonmetals bonded together, such as H2O for water.
What are some recognizable elements that might be found in the periodic table?
-Some recognizable elements include oxygen, chlorine, iron, copper, and gold.
How does the video script suggest one can enhance their understanding of these concepts?
-The video script suggests subscribing for more videos on the topic and visiting 'GCSE revision monkey comm' for a collection of videos and Key Stage 3 resources for further study.
Outlines
🌐 Understanding Basic Particles: Atoms, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
This paragraph introduces the fundamental particles that constitute all matter, including atoms, elements, compounds, and mixtures. It explains that atoms are the building blocks of everything, whether living or nonliving. Elements are different types of atoms, with around 100 known elements displayed on the periodic table. The paragraph also distinguishes between elements, which are made up of only one type of atom, and compounds, which are formed by two or more elements chemically bonded together. It provides examples of elements and compounds, such as gold and sodium chloride (table salt), and discusses how the properties of a compound can differ significantly from the properties of its constituent elements, using water (H2O) as an example. The concept of a mixture, which is a combination of two or more elements or compounds not chemically bonded, is also introduced, with air being a common example. Lastly, the paragraph touches on molecules, which are formed by two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together.
📚 Further Exploration of Molecules and Educational Resources
The second paragraph delves deeper into the concept of molecules, emphasizing that they are composed of two or more nonmetal atoms bonded together, typically found on the right-hand side of the periodic table. It uses oxygen (O2) as an example of a molecule, which consists of two oxygen atoms. The paragraph also mentions that hydrogen, despite being a nonmetal, can bond with oxygen to form a water molecule (H2O). In addition to the scientific content, the paragraph provides information on educational resources for further learning. It encourages viewers to subscribe for more content and directs them to the website 'GCSE revision monkey com' for a collection of videos and resources. It also mentions the 'Science surgery com' for a package containing all revision monkey videos and additional Key Stage 3 resources.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atom
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Mixture
💡Molecule
💡Periodic Table
💡Chemical Bond
💡Properties
💡Nonmetal
💡Diatonic Molecule
💡Substance
Highlights
Atoms make up everything, including living and nonliving objects.
Different types of atoms are known as elements.
There are around 100 elements, displayed in the periodic table.
Elements like oxygen, chlorine, and metals like iron and copper are examples of elements.
Gold is an element composed of only one type of atom.
A compound is formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together.
Sodium chloride, or salt, is an example of a compound made of sodium and chlorine.
Compounds can be represented by models showing two or more elements chemically bonded.
The properties of a compound can be very different from the properties of its constituent elements, as seen with water made of hydrogen and oxygen.
A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together.
Air is an example of a mixture, containing nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and methane.
Molecules are formed when two or more nonmetal atoms are bonded together.
Nonmetals are found on the right-hand side of the periodic table.
Oxygen exists as O2, an example of a molecule made of two oxygen atoms.
Hydrogen, a nonmetal, bonds with oxygen to form a water molecule (H2O).
A molecule can be an element, like O2, or a compound, like H2O.
The video provides educational content for GCSE revision and Key Stage 3 science.
Additional resources and videos are available at GCSE revision monkey and Science Surgery websites.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Element, Compound and Mixture | Chemsitry

What Distinguishes Compounds from Molecules?
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9
Intro to Elements, Compounds, & the Periodic Table - [1-1-3]

Elements, Atoms, Molecules, Ions, Ionic and Molecular Compounds, Cations vs Anions, Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: