Applied Chemistry_ Polar & Non-Polar Bond_ Class 11 for all Polytechnic Boards
TLDRThe video script discusses various concepts related to chemistry, particularly focusing on the properties of nonpolar and polar compounds, intermolecular forces, and the behavior of substances in different states of matter. It delves into the specifics of chemical bonding, including polar and nonpolar bonds, and explores the characteristics and examples of such compounds. The script also touches on the application of these concepts in real-world scenarios, emphasizing the importance of understanding these principles for further studies in the field of chemistry.
Takeaways
- 🎯 The concept of polar and nonpolar bonds was discussed, emphasizing the difference in electronegativity between bonded atoms.
- 📚 The role of electronegativity in forming polar and nonpolar bonds was explained, highlighting how differences in electronegativity lead to polarity.
- 🔬 The script touched on the idea of VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory and how it relates to the shape of molecules.
- 🌟 The importance of understanding molecular geometry and bond angles was stressed for predicting the properties of compounds.
- 💡 The difference between polarizability and dipole moments was clarified, with examples provided to illustrate these concepts.
- 📈 The impact of bond length on bond strength and polarity was discussed, noting how shorter bonds can affect molecular properties.
- 🔋 The concept of electric potential and its relation to chemical bonding was introduced, with an explanation of how it influences molecular behavior.
- 🌿 The script mentioned the relevance of understanding these concepts for fields like organic chemistry and biochemistry, where bond types are crucial.
- 📊 The importance of practice and revision was emphasized for grasping these topics, suggesting that revisiting examples and properties is key to mastering the material.
- 🎓 The role of online resources and channels was highlighted as valuable tools for learning and revising the concepts discussed in the script.
- 📝 The necessity of understanding the practical applications of these concepts, such as predicting solubility and reactivity in chemical reactions, was mentioned.
Q & A
What is the significance of understanding the concept of polar and nonpolar bonds in the context of the provided script?
-Understanding polar and nonpolar bonds is crucial as it helps in predicting the properties of molecules and compounds. In the script, the discussion around water's polarity and its effects on solubility and chemical reactions emphasizes the importance of these concepts in chemistry and their real-world applications.
How does the script explain the formation of a covalent bond between two nonmetal atoms?
-The script explains that a covalent bond between two nonmetal atoms is formed by the sharing of electrons. This sharing occurs because each atom attempts to achieve a stable electron configuration by filling its valence shell, resulting in the formation of a bond that holds the atoms together in a molecule.
What is the role of electronegativity in determining the polarity of a bond?
-Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. In the script, it is mentioned that a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms leads to a polar bond, where the more electronegative atom pulls the electrons towards itself, creating a partial negative charge on one end and a partial positive charge on the other.
How does the script relate the concept of bond polarity to real-world phenomena such as solubility in water?
-The script connects bond polarity to solubility by explaining that polar molecules, such as water, can dissolve other polar or ionic compounds due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds or other intermolecular forces. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, do not interact as effectively with polar solvents like water, leading to lower solubility.
What is the significance of understanding the difference between polar and nonpolar bonds in the context of chemical reactions?
-Understanding the difference between polar and nonpolar bonds is essential for predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions. The script implies that the polarity of bonds can influence reaction rates, product formation, and the overall energy changes associated with a reaction, as different types of bonds require different amounts of energy to break and form.
How does the script illustrate the concept of a nonpolar covalent bond?
-The script describes a nonpolar covalent bond as one where the electrons are shared equally between two atoms with the same or similar electronegativities. This equal sharing results in no separation of charge, and thus, the molecule does not have a positive or negative end, remaining nonpolar.
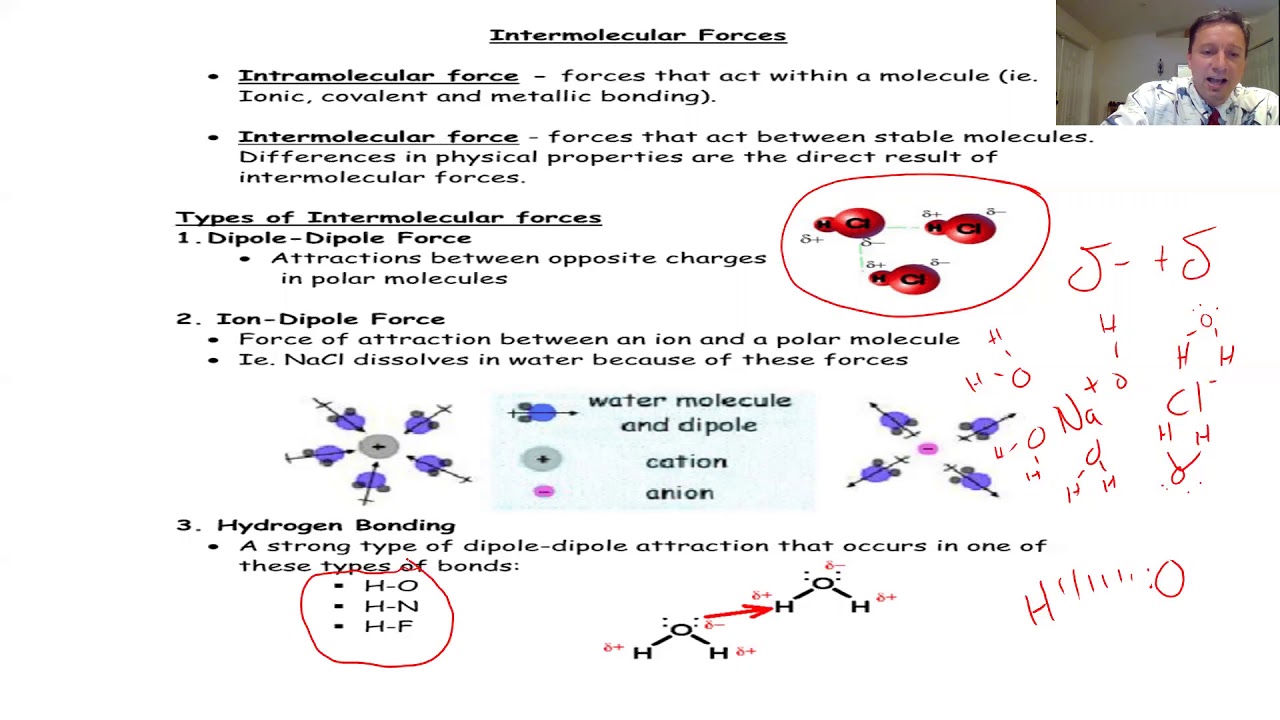
What is the role of intermolecular forces in the context of the script, and how do they relate to bond polarity?
-Intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonds and dipole-dipole interactions, play a significant role in the properties of substances, as discussed in the script. These forces are stronger between polar molecules and can lead to higher boiling points, increased solubility, and the formation of liquids or solids. Nonpolar molecules, lacking significant intermolecular forces, often exist as gases or oily liquids at room temperature.
How does the script explain the concept of a polar bond in the context of a water molecule?
-The script explains that a water molecule is an example of a polar molecule due to its bent molecular geometry, which results from the difference in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen atoms. The oxygen atom is more electronegative and pulls the electrons closer, creating a partial negative charge on one side and a partial positive charge on the other, leading to its polar nature.
What is the importance of understanding the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules in the study of chemistry?
-Understanding the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules is fundamental in chemistry as it affects a wide range of properties, including solubility, melting and boiling points, and reactivity. The script highlights this by discussing how polar molecules like water can dissolve many substances due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, a property not seen in nonpolar molecules.
How does the script relate the concept of electron sharing to the formation of chemical compounds?
-The script relates the concept of electron sharing to the formation of chemical compounds by explaining that compounds are formed when atoms share electrons to achieve stability. This sharing is the basis of covalent bonding, which can result in the formation of molecules with various properties depending on whether the bond is polar or nonpolar.
What is the significance of the melting and boiling points of a substance as discussed in the script?
-The script implies that the melting and boiling points of a substance are related to the strength of the intermolecular forces present. Polar molecules with strong hydrogen bonding, like water, have higher melting and boiling points due to the significant energy required to overcome these forces. Nonpolar molecules, with weaker intermolecular forces, generally have lower melting and boiling points.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Applied Chemistry and Bonding
The paragraph introduces the topic of applied chemistry, focusing on the understanding of chemical bonding. It mentions the continuation of previous discussions on chemical mastering and the importance of comprehending the properties of compounds. The speaker, Arke Singh, emphasizes the significance of learning about various types of bonds and their applications in different conditions, including the concept of turning on and how it relates to the properties of elements and compounds.
🔬 Exploring Electronegativity and Bond Polarity
This section delves into the concepts of electronegativity and bond polarity, explaining how they affect the properties of elements and compounds. The speaker discusses non-metal elements, their tendencies, and how these influence the formation of bonds. The paragraph also touches on the idea of electron sharing and the resulting bond strength, highlighting the importance of understanding these concepts to grasp the behavior of molecules and their interactions.
🧪 Chemical Bonding and the Formation of Molecules
The paragraph discusses the process of chemical bonding and the formation of molecules, focusing on the balance of charges and the resulting stability. It explains how certain elements, due to their electronegativity, form bonds with others and how these bonds can be either polar or nonpolar. The speaker also mentions the concept of ionic bonding and the role of electronegativity in determining the type of bond formed.
🌟 Understanding the Properties of Ionic Compounds
This section provides insights into the properties of ionic compounds, emphasizing the importance of understanding their formation and characteristics. The speaker talks about the role of electron transfer in the formation of ionic bonds and how this affects the overall charge and stability of the compound. The paragraph also touches on the concept of lattice energy and its significance in the stability of ionic compounds.
🔄 The Dynamics of Polarity in Chemical Bonds
The paragraph explores the dynamics of polarity in chemical bonds, discussing how the distribution of electrons and the resulting charges influence bond properties. It explains the concept of positive and negative charges within a bond and how these contribute to the overall polarity of a molecule. The speaker also talks about the implications of bond polarity on the physical and chemical behavior of compounds.
📈 Charting the Path of Nonpolar Compounds
This section focuses on nonpolar compounds, explaining their formation and characteristics. The speaker discusses the absence of a significant electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, leading to an even distribution of electron density and the lack of polarity. The paragraph also highlights the importance of understanding nonpolar compounds in the context of chemical reactions and their applications in various fields.
🌐 The Impact of Polarity on Solubility and Reactivity
The paragraph discusses the impact of polarity on the solubility and reactivity of compounds. It explains how polar compounds interact with each other and with solvents, leading to solubility or precipitation. The speaker also talks about the role of hydrogen bonding in enhancing solubility and the factors that influence the reactivity of polar and nonpolar compounds.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Polar Compounds
💡Nonpolar Compounds
💡Dipole Moment
💡Electronegativity
💡Chemical Bonding
💡Polar Bonds
💡Solubility
💡Molecular Structure
💡Chemical Properties
💡Physical Properties
Highlights
The discussion begins with an introduction to the applied chemistry chapter, emphasizing the importance of understanding chemical bonding and molecular structure.
The concept of chemical bonding is explored, particularly focusing on the role of valence electrons in forming bonds between atoms.
The lecture delves into the specifics of polar and nonpolar bonds, explaining how the distribution of electrons affects the properties of a molecule.
The impact of intermolecular forces on physical properties such as boiling points and solubility is discussed, providing a deeper understanding of phase behavior.
The role of hydrogen bonding in stabilizing molecular structures is highlighted, with examples demonstrating its significance in various compounds.
The lecture introduces the concept of hybridization, explaining how atomic orbitals mix to form hybrid orbitals which influence the geometry of molecules.
The concept of valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) is discussed, offering a model for predicting the shapes of molecules.
The discussion touches on the importance of understanding molecular polarity and its implications for the physical properties of substances.
The lecture provides insights into the types of chemical reactions, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding, and their respective characteristics.
The role of catalysts in chemical reactions is explored, emphasizing their ability to increase the rate of reactions without being consumed.
The lecture introduces the concept of chemical equilibrium, explaining how dynamic balance in reactions is achieved and the factors that affect it.
The discussion includes the application of Le Chatelier's principle, demonstrating how changes in conditions can shift the position of equilibrium.
The lecture emphasizes the importance of understanding the properties of functional groups in organic chemistry and their impact on molecular behavior.
The concept of isomerism in organic compounds is introduced, highlighting the different structural arrangements of atoms that can lead to different properties.
The lecture concludes with a focus on the practical applications of chemical knowledge, emphasizing the relevance of chemistry in everyday life and industrial processes.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: