Data and the frequency distribution
TLDRThis video script introduces the concept of data and distributions in a three-part series. It explains that individual numbers are data points and the collection forms a distribution. Using a hypothetical survey example, the script illustrates how data is spread across a scale, highlighting the importance of summarizing data beyond raw numbers. It differentiates between nominal and ordinal/interval variables, emphasizing the need for better data summarization techniques like frequency distributions, which are explored in the script's subsequent parts.
Takeaways
- 📊 The script introduces a three-part series focused on data, distributions, and their significance in understanding data sets.
- 🔢 It defines individual numbers as 'data points' and a collection of these as 'data', emphasizing the importance of data in statistical analysis.
- 📈 An example is used to illustrate data collection, where people's agreement with a question is rated on a scale from one to five.
- 👥 The script mentions that in real-world scenarios, data sets can range from hundreds to millions of observations, making raw data analysis impractical.
- 📋 The concept of 'distribution' is introduced, explaining that data points are not clustered but spread along a number line.
- 🔄 The term 'univariate distribution' is explained, referring to the distribution of a single variable.
- 🎓 A brief review of measurement theory is suggested, differentiating between the nominal variable 'person' and the ordinal or interval variable 'agreement'.
- 📝 The script explains that 'person' is a nominal variable with no quantitative value, while 'agreement' can be treated as an ordinal or interval variable.
- 📉 The importance of summarizing data is highlighted, with the introduction of 'frequency' as a method to count how often each value appears in the data set.
- 📊 The concept of a 'frequency distribution' is introduced, which is a distribution of how frequently each data point occurs.
- 📚 The script outlines future topics, such as frequency histograms and grouped frequency distributions, to further analyze and visualize data patterns.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video series?
-The main topic of the video series is to explain data, distributions, and what they represent.
What is the difference between a datum and data?
-A datum is a single measured value, while data is the entire set of these values.
What is an example of a univariate distribution?
-A univariate distribution is a distribution involving a single variable. In the script's example, the agreement ratings on a scale from one to five represent a univariate distribution.
Why is it not practical to analyze large datasets by looking at raw numbers?
-Analyzing large datasets by looking at raw numbers is impractical because they typically contain hundreds to millions of observations, making it difficult to discern patterns or insights.
What is the difference between nominal and ordinal variables in the context of the video?
-Nominal variables, like 'person' in the script, categorize data without any inherent order, while ordinal variables, like 'agreement', have a clear order but no specific interval between the values.
What is the purpose of measuring agreement on a scale from one to five?
-The purpose is to capture the level of agreement with a statement or question, with one indicating strong disagreement and five indicating strong agreement.
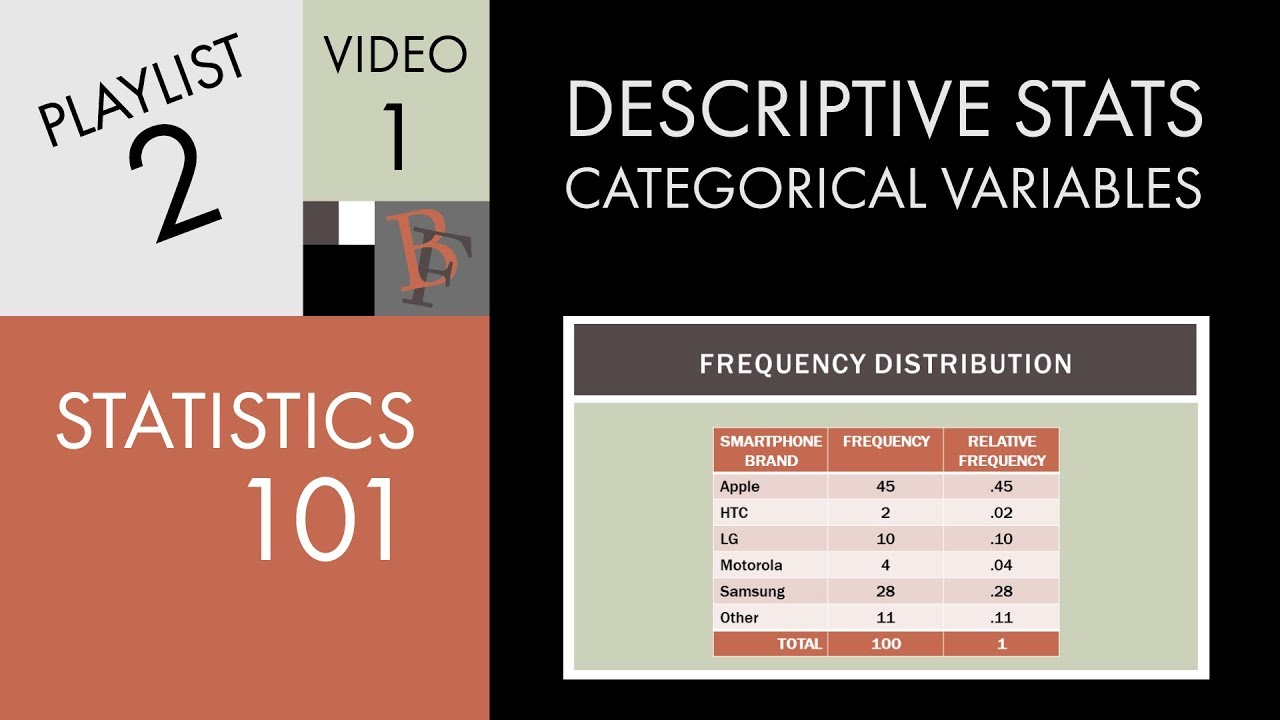
What is a frequency distribution?
-A frequency distribution is a set of numbers that shows how often each value occurs in a dataset.
How does the script illustrate the concept of a frequency distribution?
-The script illustrates the concept by counting how many times each agreement rating (from one to five) appears in the example dataset.
What tool will be introduced in the next video to visualize the frequency distribution?
-In the next video, a frequency histogram will be introduced as a tool to visualize the frequency distribution.
What is the significance of the term 'distribution' in the context of the script?
-In the context of the script, 'distribution' refers to the way data points are spread or arranged along a scale or number line, indicating the frequency or prevalence of certain values.
What is a grouped frequency distribution mentioned in the script?
-A grouped frequency distribution is a method of organizing data into intervals or groups, which will be covered in more detail in a subsequent video.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to Data Distributions
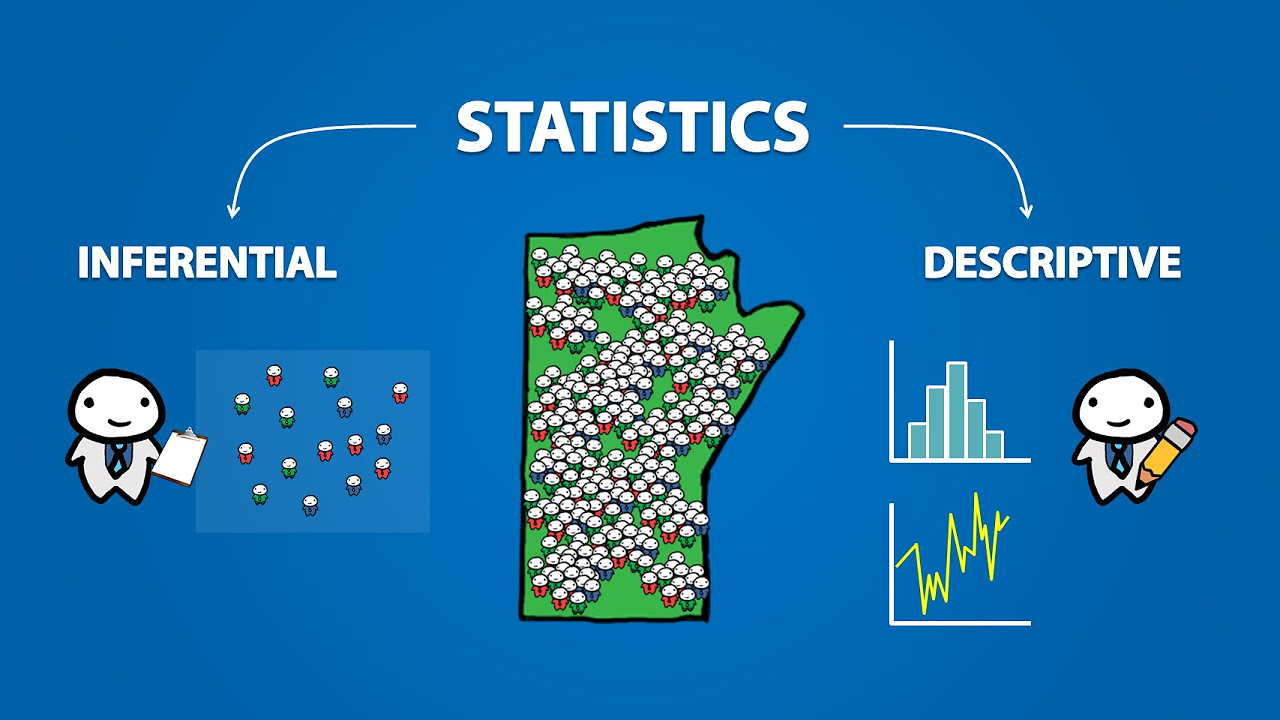
This paragraph introduces the concept of data and distributions, explaining the difference between individual data points ('atoms') and the entire set ('data'). The speaker uses a made-up example of a survey asking for agreement on a scale from one to five. The raw data is presented, and the speaker suggests that while it's possible to make sense of it in this simple case, real-world data often contains many more observations. The paragraph also touches on the importance of summarizing and illustrating data to identify patterns, and introduces the term 'univariate distribution' for a single variable measured.
🔢 Understanding Data through Frequency Distribution
The speaker delves into the concept of frequency distribution, illustrating how to count the occurrences of each value in the data set. This is demonstrated using the survey data example, where the frequency of each response (from one to five) is counted and presented as a new set of numbers. The paragraph explains that this method can be particularly useful for identifying patterns in real-world data, which often contains a large number of observations. The speaker also mentions the next steps, which include creating a frequency histogram and exploring grouped frequency distribution in subsequent videos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Data
💡Distribution
💡Univariate Distribution
💡Frequency
💡Frequency Distribution
💡Nominal Variable
💡Ordinal Variable
💡Interval Level Variable
💡Measurement Theory
💡Frequency Histogram
💡Grouped Frequency Distribution
Highlights
Introduction to a three-part series on data and distributions.
Explanation of the terms 'datum' and 'data'.
Use of a made-up example to illustrate data collection.
Description of a scale for measuring agreement with a question.
Observation that few people chose extreme values on the scale.
The concept of data distribution along a number line.
Introduction of the term 'univariate distribution'.
Brief review of measurement theory and its relevance.
Differentiation between nominal and ordinal variables.
Discussion on the treatment of rating scales as interval variables.
The necessity of summarizing data for better understanding.
Introduction of the concept of 'frequency' in data analysis.
Counting the frequency of each value in the data set.
Explanation of the frequency distribution.
Advantages of frequency distribution in pattern recognition.
Preview of the next video on frequency histograms.
Teaser for a future video on grouped frequency distribution.
Conclusion of the video with a summary of frequency distributions.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
The Mode – The Most Frequently Occurring Measure of Central Tendency (5-2)
Types of Data: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval/Ratio - Statistics Help
Variables and Types of Variables | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures
Classification of Variables and Types of Measurement Scales
Statistics 101: Describing a Categorical Variable
Introduction to Statistics (1.1)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: