what are degrees of freedom?
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of degrees of freedom, a fundamental yet complex idea in statistics that influences the interpretation of statistical tests and calculations like standard deviation. It explains degrees of freedom as the number of independent pieces of information required for a calculation, contrasting it with sample size and illustrating it with examples like coin tosses and traffic light colors. The script clarifies that degrees of freedom differ based on the calculation and prior knowledge, emphasizing its significance in statistical tests where p-values and test statistics are context-dependent on the degrees of freedom. The explanation aims to provide context for students, even though a deep understanding of the concept is not required for their assessment.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Degrees of freedom is a concept used in statistics, often required when presenting results of statistical tests or calculating certain estimates like the standard deviation of a sample.
- 🤔 Understanding the exact meaning of degrees of freedom is not crucial for this module, but it's important to know how it's used in calculations and assessments.
- 🔢 Degrees of freedom refers to the number of independent pieces of information needed to calculate a statistic, and it can vary depending on the calculation and what is already known.
- 🎰 An example of degrees of freedom is a coin toss, which has one degree of freedom because knowing one outcome (heads) automatically determines the other (tails).
- 🚦 In a system with categories, such as a traffic light, degrees of freedom is usually the number of categories minus one.
- 📊 When calculating the mean of a sample, each value in the sample is independent and affects the mean, so the degrees of freedom is equal to the sample size.
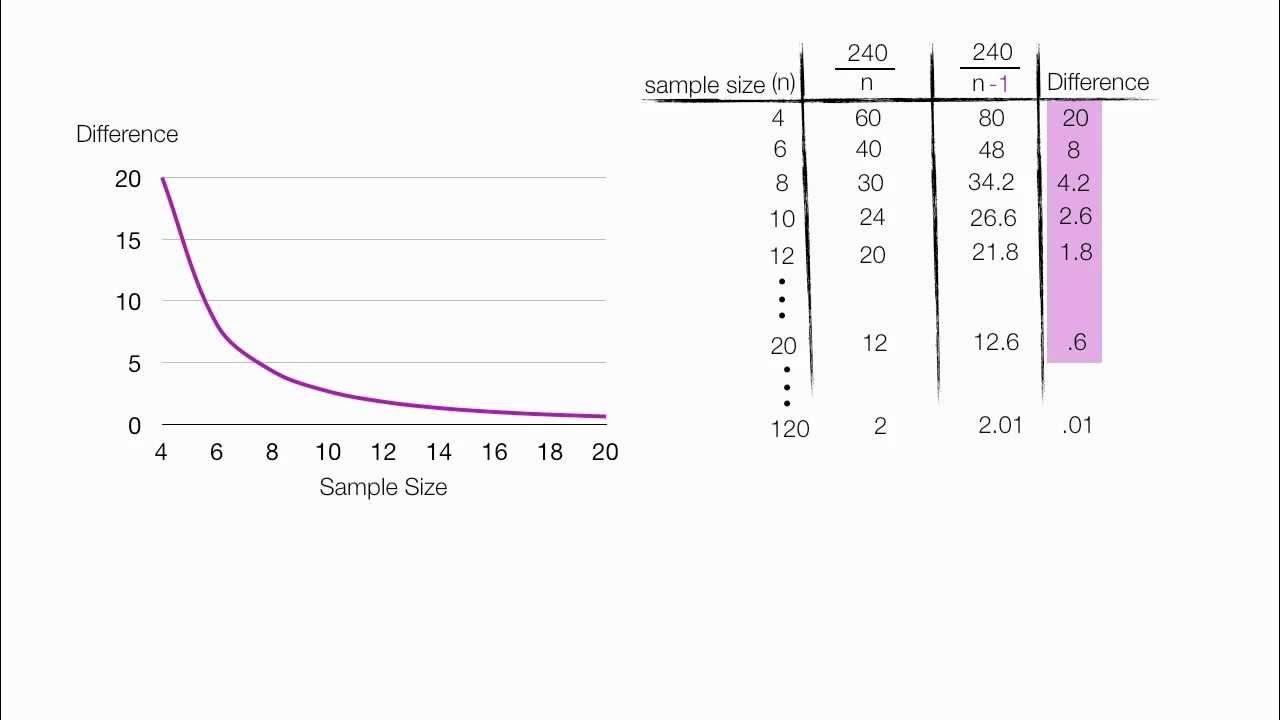
- 📉 For standard deviation, once the mean is known, the degrees of freedom is the sample size minus one, as the mean determines one piece of information, leaving n-1 independent pieces of information.
- 🔍 In statistical tests, the degrees of freedom depends on the number of independent pieces of information calculated in advance, such as means or totals.
- 📉 For a one-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom is n (sample size) minus 1, because the mean is already known.
- 📈 For a two-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom is the combined sample size minus 2, as the means of both samples are known.
- ⚖️ The interpretation of a test statistic, including the p-value, depends on the degrees of freedom, which provides context to the significance of the result.
- 💡 Degrees of freedom is a complex concept, and while not everyone may fully grasp it by the end of the course, it's essential for understanding statistical calculations and their implications.
Q & A
What is the concept of degrees of freedom in statistics?
-Degrees of freedom is a concept in statistics that refers to the number of independent pieces of information needed to calculate a statistic, such as a mean or standard deviation. It is not the same as the sample size and can vary depending on the specific calculation being made.
Why is understanding the concept of degrees of freedom important in statistical tests?
-Understanding degrees of freedom is important because it affects the interpretation of statistical test results, including the calculation of p-values. The significance of a test statistic can change based on the degrees of freedom associated with it.
How does the concept of degrees of freedom relate to the sample size?
-While degrees of freedom and sample size are related, they are not the same. Degrees of freedom depend on the sample size and the specific calculation being made, but they represent the number of independent pieces of information needed for that calculation, not the total number of observations.
Can you give an example of a situation with one degree of freedom?
-An example of a situation with one degree of freedom is a coin toss. Since there are only two possible outcomes (heads or tails), knowing one outcome automatically determines the other, thus requiring only one piece of information.
What is the relationship between degrees of freedom and the number of categories in categorical data?
-In cases where data are categorical, the degrees of freedom is usually the number of categories minus one. This is because knowing the total number of categories allows you to deduce the remaining category once one is known.
How does the calculation of the mean affect the degrees of freedom?
-When calculating the mean of a sample, the degrees of freedom are equal to the sample size, as each value in the sample contributes independently to the mean.
Why is the degrees of freedom for calculating the standard deviation of a sample n-1?
-The degrees of freedom for calculating the standard deviation is n-1 because once the mean is known, it determines the last value in the sample. Therefore, the standard deviation calculation only depends on n-1 independent pieces of information.
How does the number of pieces of information needed affect the degrees of freedom in a statistical test?
-The more pieces of information (like means, totals, and variances) that need to be calculated in advance for a statistical test, the fewer the degrees of freedom. This is because each piece of information reduces the number of independent data points available for the calculation.
What is the degrees of freedom for a one-sample t-test?
-For a one-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom is n-1, where n is the sample size. This is because only the mean of the sample needs to be known to calculate the t-statistic.
How does the degrees of freedom change for a two-sample t-test?
-For a two-sample t-test, the degrees of freedom is the combined sample size minus 2, as both means of the two samples need to be known to calculate the t-statistic.
Outlines
📊 Understanding Degrees of Freedom in Statistics
The first paragraph introduces the concept of degrees of freedom, emphasizing its frequent appearance in statistical tests and calculations. It explains that while degrees of freedom are often mentioned in assessments, a deep understanding of the term is not required for this module. Degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent pieces of information needed for a calculation. The paragraph clarifies that this is not equivalent to sample size and varies based on the specific calculation and prior knowledge. It uses examples such as a coin toss and a traffic light to illustrate degrees of freedom, showing how the concept applies to categorical data and measurements. The mean of a sample is highlighted as an example where each value in the sample affects the outcome, contrasting with the standard deviation, which is dependent on the mean and thus has fewer degrees of freedom.
📉 Degrees of Freedom in Standard Deviation and Statistical Tests
The second paragraph delves into the calculation of the standard deviation, where knowing the mean of a sample reduces the degrees of freedom to n-1, as the last value is determined by the mean and the other values. This is crucial for accurately calculating the standard deviation, especially in small samples. The paragraph further explains that calculating a test statistic involves preliminary calculations that reduce the degrees of freedom. For instance, a one-sample t-test has degrees of freedom equal to n-1, while a two-sample t-test has degrees of freedom equal to the combined sample size minus two. The interpretation of a test statistic, including the p-value, is dependent on the degrees of freedom. The paragraph concludes by acknowledging the complexity of the concept and reassuring that students will not be assessed on their understanding of degrees of freedom.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Degrees of Freedom
💡Statistical Tests
💡Sample Size
💡Mean
💡Standard Deviation
💡Test Statistic
💡Null Hypothesis
💡P-Value
💡One Sample T-Test
💡Two Sample T-Test
Highlights
Degrees of freedom is a fundamental concept in statistics that is often used in statistical tests and when calculating certain estimates like standard deviation.
Calculating the mean of a sample does not require knowledge of degrees of freedom, unlike other calculations.
Degrees of freedom refers to the number of independent pieces of information needed to make a calculation.
The degrees of freedom is not the same as the sample size and will vary depending on the specific calculation being made.
In a coin toss, there is one degree of freedom since knowing the outcome of one toss automatically determines the outcome of the other.
In a system with two degrees of freedom, like a traffic light with three colors, two pieces of information are needed to determine the unknown outcome.
The degrees of freedom for categorical data is typically the number of categories minus one.
When calculating the mean of a sample, the value of the mean depends on each individual value in the sample.
Calculating the standard deviation involves knowing the mean first, which reduces the degrees of freedom to n-1 since the last value can be determined from the others.
For small samples, using the full sample size when calculating standard deviation would include redundant data points, leading to an underestimate.
The degrees of freedom for a one sample t-test is n-1, while for a two sample t-test it is the combined sample size minus 2.
The interpretation of a test statistic and its corresponding p-value depends on the degrees of freedom.
A chi-squared statistic of 4 is significant with one degree of freedom but not with two degrees of freedom, illustrating the importance of considering degrees of freedom.
The concept of degrees of freedom is tricky and not essential to fully understand for this module, but provides important context for statistical calculations.
Understanding degrees of freedom helps to explore and interpret statistical results more effectively.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Degrees Of Freedom in a Chi-Squared Test

Degrees of Freedom and Effect Sizes: Crash Course Statistics #28

What are degrees of freedom?!? Seriously.

Statistical degrees of freedom - What are they REALLY?

What is Degrees Of Freedom in Statistics? Degrees of freedom in Statistics Explained!
Why are degrees of freedom (n-1) used in Variance and Standard Deviation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: