Why Are There Stones Along Railway Tracks?
TLDRThe video script delves into the ubiquitous yet overlooked crushed stones known as track ballast that line the world's railway tracks. These stones, despite their seemingly simple appearance, play a critical role in the railway system's stability and safety. They form the trackbed for sleepers, interlock to maintain their position, distribute the immense load of trains, dampen vibrations for passenger comfort, facilitate drainage to prevent rust, inhibit vegetation growth, absorb noise, and minimize heat expansion. The importance of regular maintenance and cleaning of track ballast is highlighted, emphasizing its indispensable contribution to the global railway industry.
Takeaways
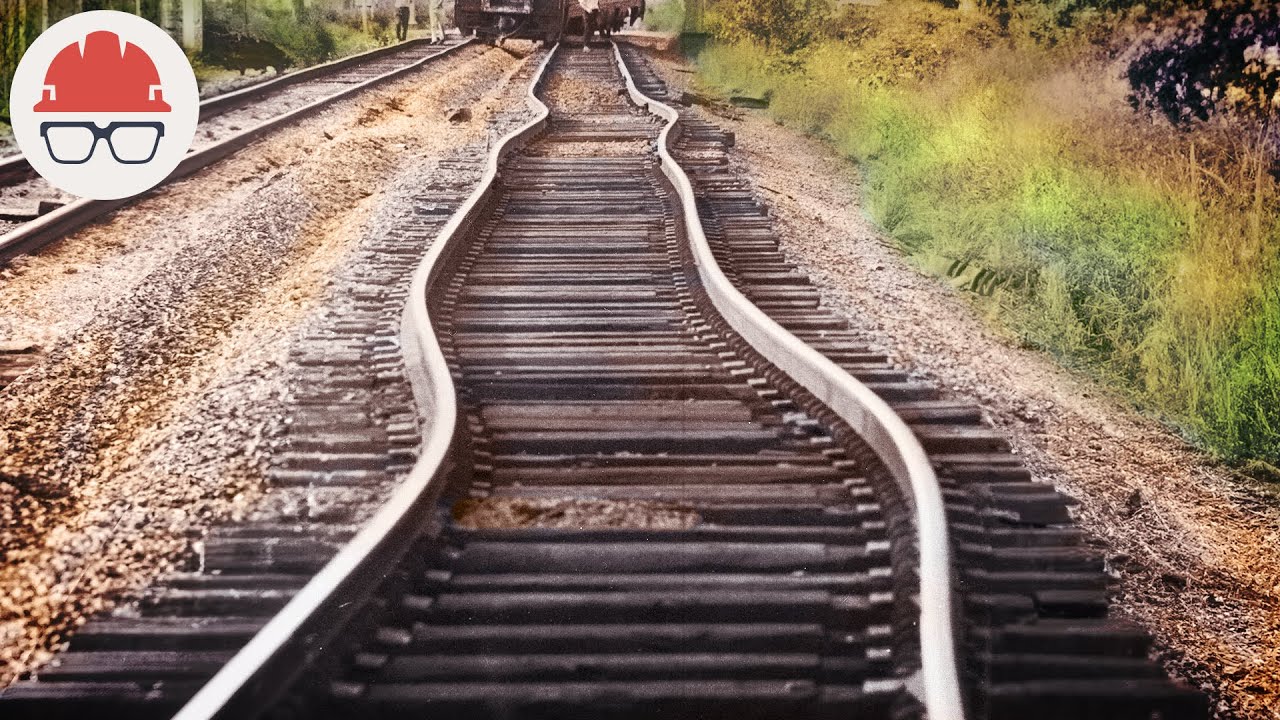
- 🚂 The crushed stones alongside railway tracks are known as track ballast, which forms the trackbed for the sleepers or railroad ties.
- 🔍 Track ballast is universally similar in shape and texture across the globe, regardless of the country, due to its specific requirements.
- 🧱 The stones used in track ballast have jagged edges and interlock with each other to provide stability and prevent movement of the sleepers.
- 🛤️ Track ballast serves to protect the railway tracks by holding sleepers in place, distributing load, dampening vibrations, aiding drainage, preventing vegetation growth, and absorbing noise.
- 💪 The track ballast evenly distributes the immense pressure exerted by heavy trains, ensuring the tracks can withstand the stress.
- 🌊 It prevents waterlogging and accumulation around the sleepers, which could lead to rapid rusting of the metallic parts of the tracks.
- 🌱 The jagged stones in the track ballast help in preventing the growth of vegetation that could compromise the track's structure and strength.
- 🔇 The larger surface area of the crushed stones in the track ballast facilitates noise absorption, making trains quieter for those outside.
- 🌡️ Track ballast minimizes heat expansion during the summer, ensuring the efficacy and safety of the railway tracks.
- 🧹 Regular maintenance and cleaning of track ballast are essential to its effectiveness, which may include replacing stones or using ballast cleaners.
- 🌟 The track ballast, though appearing as a random set of stones, is crucial to the railway industry and impacts millions of lives worldwide.
Q & A
What is the term used to describe the crushed stones that line railroad tracks?
-The crushed stones that line railroad tracks are collectively called track ballast.
What is the primary purpose of track ballast?
-The primary purpose of track ballast is to protect the railway track by holding the sleepers in place, distributing load, dampening vibrations, ensuring proper drainage, preventing vegetation growth around the tracks, absorbing noise, and minimizing heat expansion.
Why is the shape and texture of the stones in track ballast important?
-The shape and texture of the stones are important because their jagged edges and irregular surfaces allow them to interlock with each other, which helps to keep the stones in place and maintain the strength of the track ballast.
What are some alternative materials that can be used for track ballast in certain situations?
-In some cases, less suitable alternatives like burnt clay are used for track ballast when crushed rocks or stones are not available or appropriate.
How does track ballast help in preventing the growth of vegetation around the tracks?
-The stones in the track ballast help keep out vegetation by creating an environment that is inhospitable for grass, weeds, or plants to grow, thus preserving the structure and strength of the track.
What is the typical thickness of track ballast?
-The thickness of the track ballast usually ranges between 25-30 cm, although it can vary depending on certain conditions pertaining to the geographical location of the railway track.
How does track ballast contribute to the comfort of train passengers?
-Track ballast contributes to the comfort of passengers by absorbing vibrations caused by a moving train, providing a cushioning effect that reduces the jostling experienced during the journey.
Why is regular maintenance and cleaning of track ballast necessary?
-Regular maintenance and cleaning of track ballast is necessary to ensure its effectiveness. Accumulation of dirt or mud can negatively impact its draining ability and the interlocking of stones, which is crucial for the stability and protection of the railway track.
How does track ballast help in noise reduction for trains?
-Track ballast helps in noise reduction by offering a larger surface area than a flat plane, which facilitates noise absorption. This makes trains noticeably quieter when moving on tracks with track ballast.
What are the potential consequences if track ballast is replaced with smooth or circular rocks?
-If track ballast is replaced with smooth or circular rocks, they would slide over each other instead of interlocking, which would compromise the strength and stability of the track ballast and could lead to catastrophic results for the railway track.
What is the role of track ballast in preventing water-related issues on railway tracks?
-Track ballast plays a crucial role in preventing water clogging or accumulation on or around the sleepers, which helps to avoid rapid rusting of the metallic parts of the railway tracks and ensures proper drainage during rains.
What specialized machines are used to clean track ballast?
-There are machines called ballast cleaners that are used to clean track ballast, reducing the amount of manual labor required and maintaining the effectiveness of the track ballast.
Outlines
🚂 The Role of Track Ballast in Railway Infrastructure
This paragraph explains the importance of crushed stones, known as track ballast, which are universally used along railway tracks worldwide. The track ballast forms the trackbed for sleepers or railroad ties and serves multiple purposes: it holds the sleepers in place, distributes the load of heavy trains, dampens vibrations for passenger comfort, ensures proper drainage to prevent rusting, prevents vegetation growth that could weaken the track, absorbs noise, and minimizes heat expansion. The stones' jagged shape and texture allow them to interlock, providing stability and strength. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and sometimes replacement, is necessary to keep the track ballast effective.
🧹 The Use of Ballast Cleaners in Railway Maintenance
The second paragraph discusses the maintenance of track ballast, highlighting the use of specialized machines called ballast cleaners. These machines reduce the need for manual labor in the cleaning process. The paragraph emphasizes the significance of the track ballast, which despite appearing as a random set of stones, is crucial to the railway industry that impacts millions of people globally.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Track Ballast
💡Sleepers
💡Load Distribution
💡Vibration Dampening
💡Drainage
💡Vegetation Prevention
💡Noise Absorption
💡Heat Expansion
💡Corrosion and Rusting
💡Maintenance and Cleaning
💡Interlocking Stones
Highlights
Track ballast is the crushed stones that line railroad tracks and constitute the trackbed upon which sleepers or railroad ties are laid.
The shape and texture of track ballast stones are almost always the same across the globe.
Track ballast stones have a characteristic shape, size, and texture with jagged edges to interlock with each other and stay in place.
Replacing track ballast stones with circular or smooth rocks would compromise the strength of the track.
Track ballast serves to protect railway tracks by holding sleepers in place, distributing load, dampening vibrations, ensuring drainage, preventing vegetation, and absorbing noise.
Track ballast holds sleepers in place to prevent movement under the pressure of passing trains.
The jagged stones in track ballast interlock to distribute the immense load on sleepers and tracks evenly.
Track ballast absorbs vibrations from moving trains, enhancing passenger comfort.
Track ballast prevents water clogging or accumulation on or around sleepers to avoid rapid rusting of metallic parts.
The stones in track ballast help keep out vegetation that could compromise the track structure and strength.
Track ballast offers a larger surface area than a flat plane, facilitating noise absorption and reducing train noise levels.
Track ballast minimizes heat expansion in railway tracks during summer, ensuring track efficacy and safety.
Track ballast requires regular maintenance and cleaning, with machines like ballast cleaners reducing manual labor.
If track ballast is covered in too much dirt or mud, it can negatively impact its effectiveness and draining ability.
Sometimes track ballast stones are replaced with a new set of crushed stones to maintain their functionality.
The seemingly random set of stones in track ballast actually constitutes the backbone of an industry affecting millions of lives worldwide.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: