Pure Substances and Mixtures | Chemistry
TLDRThe video script discusses the classification of matter into pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances consist of identical particles, such as a sheet of iron made up of one type of atom, whereas mixtures are composed of non-identical particles, like a sugar solution. Elements and compounds, including ionic and covalent compounds, are categorized as pure substances due to their uniform composition and properties. Mixtures, on the other hand, have non-uniform compositions and can be separated by physical processes. Examples of mixtures include carbonated drinks, air, honey, and steel.
Takeaways
- 📚 Matter is classified into two categories: pure substances and mixtures.
- 🔬 A pure substance is composed of identical particles, such as a sheet of iron made up of the same type of atoms.
- 🥤 A mixture consists of non-identical particles, like a sugar solution which contains both sugar and water molecules of different sizes and properties.
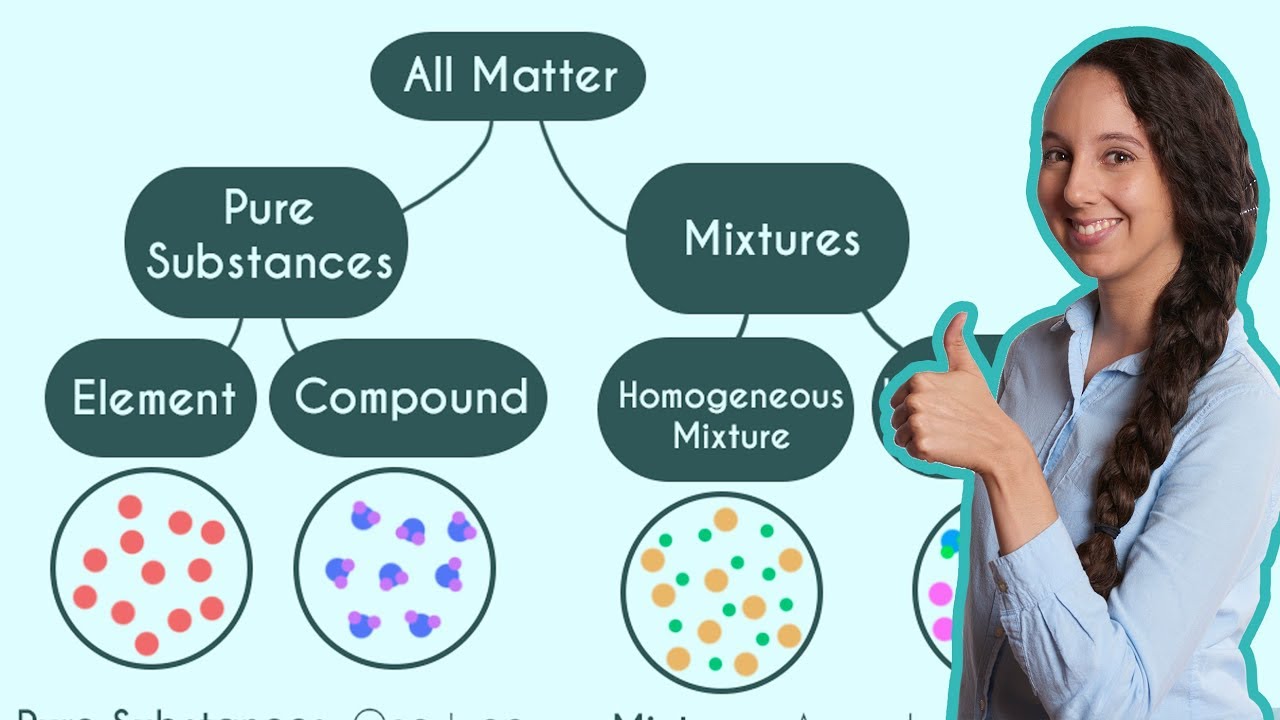
- 🌟 Elements like iron, gold, and copper are pure substances because they are made up of atoms of the same type with identical properties.
- 🧪 Compounds, whether ionic like table salt or covalent like water, are considered pure substances when they consist of identical units throughout.
- 🍯 Mixtures such as carbonated drinks, air, honey, and steel are composed of different substances physically combined and can be separated by physical processes.
- 🔍 In pure substances, particles are chemically bonded and have uniform composition and properties throughout.
- 🌈 Mixtures have non-uniform composition and the different particles possess different chemical and physical properties.
- ✂️ Pure substances cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical means, unlike mixtures which can be separated into their components.
- 🔄 The distinction between pure substances and mixtures lies in the type of particle combination (chemical vs. physical) and their uniformity in composition and properties.
Q & A
What is the fundamental difference between pure substances and mixtures?
-Pure substances are composed of identical particles, while mixtures are composed of non-identical particles.
Give an example of a pure substance and explain why it is considered pure.
-A sheet of iron is a pure substance because it is made up of only one type of atom, with all atoms having the same size, properties, and chemical composition.
What is a mixture and how does it differ from a pure substance in terms of particle composition?
-A mixture is a combination of different substances where the particles are not identical. For example, a sugar solution consists of sugar molecules and water molecules, which are different in size and properties.
What are the two categories of matter discussed in the script?
-The two categories of matter discussed are pure substances and mixtures.
Why are all elements considered pure substances?
-All elements are considered pure substances because they consist of the same type of atoms throughout, with identical properties and sizes.
What are the two types of compounds and how do they relate to pure substances?
-The two types of compounds are ionic and covalent compounds. Both are considered pure substances because ionic compounds consist of identical formula units and covalent compounds consist of identical molecules throughout.
How can you differentiate a pure substance from a mixture in terms of their composition?
-In pure substances, particles are chemically combined and have uniform composition throughout, whereas in mixtures, particles are physically combined and the composition is usually non-uniform.
Can pure substances be separated into simpler substances through physical processes?
-No, pure substances cannot be separated into simpler substances by any physical process.
Provide an example of a mixture and explain its composition.
-Air is a mixture composed of different gases like nitrogen and oxygen, which are physically combined but not chemically bonded.
What is the difference in the smallest unit of pure substances and mixtures?
-The smallest unit of an element is an atom, for ionic compounds it is a formula unit, and for covalent compounds, it is a molecule.
How can mixtures be separated?
-Mixtures can be separated by physical processes such as filtration, evaporation, or distillation.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of pure substances and mixtures. It explains that matter, which occupies space and has mass, is categorized into two groups: pure substances and mixtures. A pure substance is composed of identical particles, such as a sheet of iron made up of the same type of atoms. On the other hand, a mixture consists of non-identical particles, like a sugar solution containing different sugar and water molecules. The paragraph further clarifies that elements and compounds, including ionic and covalent compounds, are considered pure substances because they are made up of identical particles. Examples are provided to illustrate the difference between pure substances and mixtures, emphasizing that all solutions are mixtures.
🔍 Differentiating Pure Substances and Mixtures
This paragraph delves into the differences between pure substances and mixtures in terms of their composition and properties. It highlights that in pure substances, particles are chemically combined and share uniform chemical and physical properties throughout the mass. In contrast, mixtures have particles that are physically combined with varying chemical and physical properties. The paragraph also explains that pure substances have a uniform composition and cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical processes, whereas mixtures can be separated through physical means like filtration. The discussion concludes with examples of common mixtures such as carbonated drinks, air, honey, and steel, reinforcing the understanding of the concepts.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Pure Substances
💡Mixtures
💡Matter
💡Elements
💡Compounds
💡Chemically Combined
💡Physically Combined
💡Uniform Composition
💡Non-Uniform Composition
💡Separation by Physical Process
💡Alloys
Highlights
Matter is classified into two groups: pure substances and mixtures.
Pure substances are composed of identical particles.
A mixture consists of non-identical particles.
An example of a pure substance is a sheet of iron, made up of the same type of atoms.
A sugar solution is a mixture composed of sugar molecules and water molecules of different sizes and properties.
All elements like iron, gold, and sodium are pure substances due to their uniform atomic composition.
Compounds, both ionic and covalent, are considered pure substances.
The smallest unit of an ionic compound is the formula unit, which is identical throughout.
Covalent compounds like water have identical molecules with the same properties throughout.
Carbonated drinks are mixtures composed of sugar, water, and various colors.
Air is a mixture of different gases such as nitrogen and oxygen.
Honey is a mixture of water, sugar, and minerals.
Steel and coins are mixtures, specifically alloys, made up of elements like copper and zinc.
In pure substances, particles are chemically combined, whereas in mixtures, they are physically combined.
Pure substances have uniform composition, while mixtures have non-uniform composition.
Pure substances cannot be simplified into simpler substances by physical processes, unlike mixtures.
This lecture provides a clear distinction between pure substances and mixtures, emphasizing their composition and properties.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances

How to Compare Pure Substances and Mixtures - HSC Chemistry

Mixtures - Class 9 Tutorial

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: