What Really Happens To Your Body When You're Electrocuted?
TLDRThe video script from Life Noggin discusses the dangers and benefits of electricity in our lives. It highlights the risks of electrocution, explaining how voltage and current affect the human body, and the potential for severe injury or death. The script also emphasizes the importance of safety guidelines, especially when skin is wet. On a positive note, it describes how defibrillators use controlled electrical shocks to save lives during cardiac emergencies, showcasing the dual nature of electricity as both a hazard and a life-saving tool.
Takeaways
- ⚡️ Electricity, while beneficial, can be hazardous and result in fatal electrocutions.
- 📈 Electrocution is defined as death or shock caused by electric current.
- 🔋 Understanding electricity involves measuring volts and amperes, with amperes being particularly relevant to harm.
- 💧 The flow of electrons can damage tissues and disrupt vital electrical signals like heartbeats.
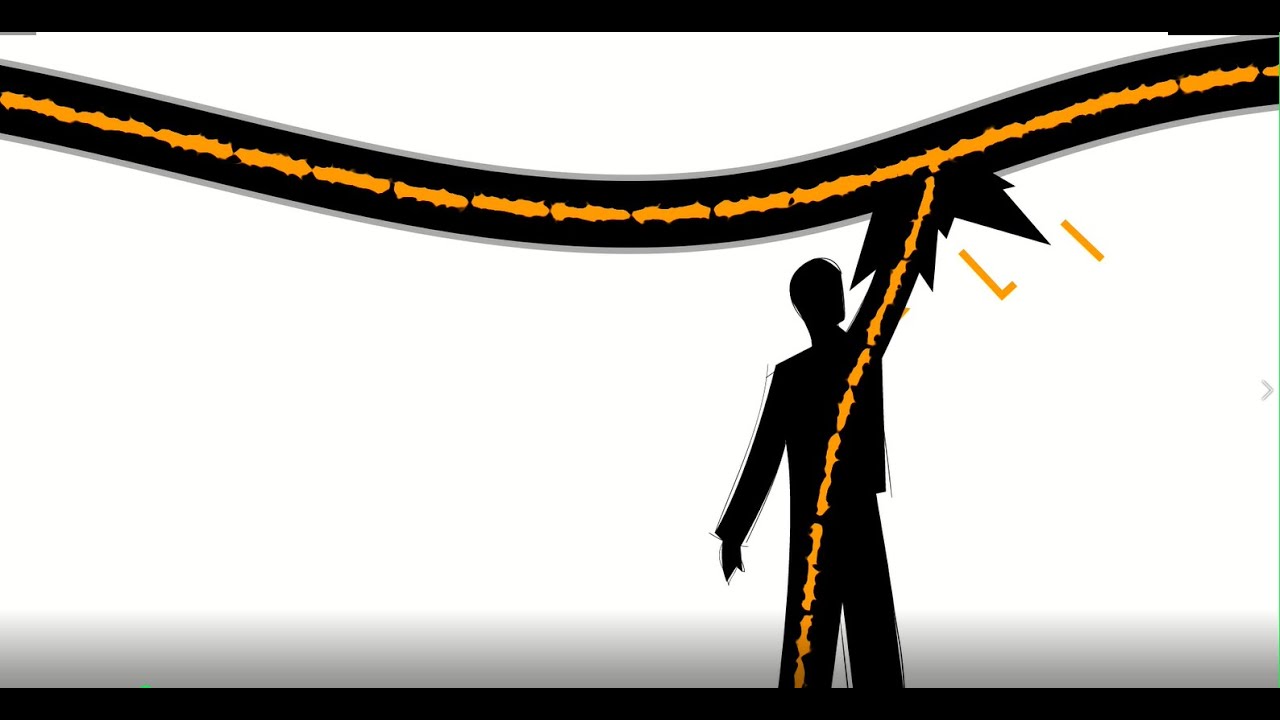
- 🏋️ High current can cause muscle tension, potentially preventing release from the electrical source.
- 🚨 OSHA provides guidelines on the dangers of various amperages to human health.
- 💓 Even small currents can be lethal if they pass through critical parts like the heart.
- ⚡️ The severity of electrocution depends on factors beyond amperage, including the path of current through the body.
- 🌩️ Lightning can cause varying degrees of harm, sometimes only resulting in skin burns.
- 💧 Wet skin increases the risk of electrocution due to its lower resistance compared to dry skin.
- 🩺 Defibrillators are life-saving devices that use controlled electrical shocks to treat cardiac arrest.
Q & A
What is the main danger associated with electricity in the context of the video?
-The main danger associated with electricity, as discussed in the video, is the risk of electrocution, which can lead to severe injuries or death. This can occur both in the workplace and through consumer products.
How many people are killed by electrocution in the United States each year?
-According to the video, approximately 100 people are killed at work due to electrocution each year in the United States, with another 60 or so electrocutions occurring from consumer products.
What does electrocution mean?
-Electrocution is defined as the death or shock of a person or animal caused by electricity.
What are the units used to measure electricity and what do they represent?
-The units used to measure electricity are volts and amperes (or amps). Volts measure the electrical potential difference, while amperes measure the current flow, which is the amount of electric charge passing through a point per unit of time.
What harm can the flow of electrons cause to the human body?
-The flow of electrons through the human body can cause damage to tissues or the nervous system. It can lead to burning of bodily tissues and interference with essential electrical signals, such as those that regulate the heartbeat.
What is the role of a person's muscles in the context of an electric shock?
-Under certain conditions, a person's muscles may tense and clench due to an electric shock, which can sometimes prevent the individual from releasing the source of the current.
What are the guidelines provided by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration regarding the danger of different amperages?
-The video mentions that currents around 1 mA can cause tingling sensations, while currents above 75 mA can potentially cause ventricular fibrillation, leading to death. Severe tissue and organ burns typically begin at currents above 1500 mA.
How does the path of the electric current through the body affect the severity of the injury?
-The path of the electric current through the body significantly impacts the severity of the injury. For instance, a small current flowing through one hand, directly through the heart, and out the other hand can be fatal, whereas a large current from a lightning bolt may only cause burns if it travels through the skin without penetrating deeper into the body.
Why are certain body parts more susceptible to electric damage than others?
-Certain body parts are more susceptible to electric damage because of the varying resistance levels. Inner organs have less resistance than the outer skin, making them more vulnerable to damage from electric current.
How does the state of the skin (wet or dry) influence the risk of electrocution?
-Wet skin has much less resistance than dry skin, which significantly increases the risk of electrocution when water is involved.
How can electricity, despite its dangers, be beneficial in certain medical situations?
-Despite its potential dangers, electricity can be beneficial in medical situations, such as when used in defibrillators. Defibrillators deliver a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the heart to treat conditions like sudden cardiac arrest, which can be life-saving.
What is the primary cause of sudden cardiac arrest?
-The primary cause of sudden cardiac arrest, as mentioned in the video, is usually ventricular fibrillation, a condition where the heart abruptly stops beating.
Outlines
💡 Understanding the Dangers of Electricity
This paragraph introduces the topic of electricity and its potential dangers. It highlights that in the United States, nearly 100 deaths occur annually due to electrocution in the workplace, with another 60 related to consumer products. Electrocution is defined as the death or shock caused by electricity. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of understanding how electricity can harm humans by discussing the measurement of electricity through volts and amperes. It explains that amperes measure the flow of electric charge, which can damage tissues or the nervous system when it flows abnormally through the body. The paragraph also mentions that the Occupational Safety and Health Administration provides guidelines on the dangers of different amperages, detailing the effects of currents from 1 mA to 1500 mA and above. It concludes by discussing the varying susceptibility of the human body to electric damage, noting that wet skin has less resistance than dry skin, increasing the risk of electrocution in the presence of water.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electrocution
💡Volts and Amperes
💡Current Flow
💡Tissue Damage
💡Ventricular Fibrillation
💡Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
💡Defibrillator
💡Sudden Cardiac Arrest
💡Inner Organs
💡Wet Skin
💡Electrical Resistance
Highlights
Electricity has enabled significant advancements but also poses dangers, with about 100 deaths in the United States yearly due to electrocution in the workforce.
An additional 60 electrocutions occur from consumer products like power tools and lighting equipment.
Electrocution is defined as the death of a person or animal caused by electricity or an electric shock.
Understanding how electricity hurts requires knowledge of how it is measured, primarily through volts and amperes.
Amperes measure the current flow, which is the amount of electric charge passing through a point per unit of time.
Electron flow is responsible for harm to a person, causing tissue or nervous system damage.
Electric current can cause internal damage when it flows through the body in unintended ways.
Certain conditions can cause muscle tension and clenching from electric current, potentially preventing the individual from releasing the source.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration provides guidelines on the dangers of different amperages.
Currents as low as 1 mA can cause tingling, while currents above 75 mA can potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation and death.
Severe tissue and organ burns typically begin at currents above 1500 mA.
The path of the current through the body significantly affects the degree of harm, with some paths being more dangerous than others.
Inner organs have less resistance than the skin, making them more susceptible to electric damage.
Wet skin has lower resistance than dry skin, increasing the risk of electrocution in the presence of water.
Despite the dangers, electricity can be used for life-saving purposes, such as in defibrillators.
Defibrillators deliver a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to treat conditions like sudden cardiac arrest.
Sudden cardiac arrest, often caused by ventricular fibrillation, can be fatal without intervention like CPR and a defibrillator.
Electricity, while dangerous, has the potential to save lives through modern medical devices.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

How to use a Multimeter for beginners: Part 1 - Voltage measurement / Multimeter tutorial

फेज, न्यूट्रल और अर्थ में अंतर Phase, Neutral And Earthing Wire | Khan GS Research Centre

Current Vs Voltage: How Much Current Can Kill You?
The four shock factors

How to identify a person in cardiac arrest and administer potentially lifesaving CPR

Do Volts or Amps Kill You? Voltage, Current and Resistance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: