This Is What's Causing Your Back Pain
TLDRThe video delves into the common issue of back pain, exploring its potential causes and the anatomy of the spine. It discusses the five regions of the spine, the functions and demands placed on it, and how these contribute to back pain. The script also covers various sources of back pain, including issues with intervertebral discs, spinal nerves, facet joints, and muscular strain. It emphasizes the importance of proper spinal care and suggests various treatments and therapies for alleviating back pain.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Back pain is a common issue affecting many people at some point in their lives, with varying degrees of severity and causes.
- 🏠 The spine, or vertebral column, is made up of individual bones called vertebrae, divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal.
- 💡 The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions are mobile parts of the spine, allowing for movement but also increasing the risk of injury and pain.
- 🛡️ The primary functions of the spine include protecting the spinal cord, transmitting forces and weight, and facilitating movement in all three planes of space.
- 🧽 Intervertebral discs act as shock-absorbing pads between the vertebrae, but they can also be a source of back pain due to degeneration or injury.
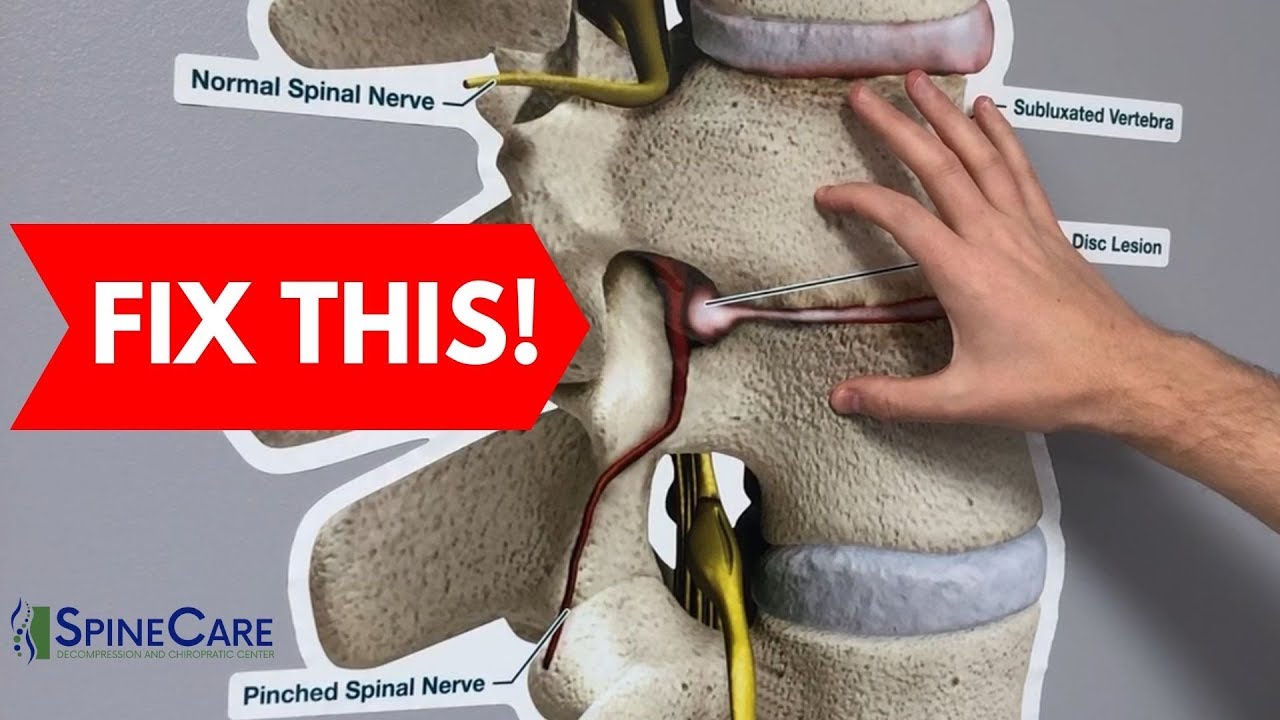
- 🔧 Herniated or bulging discs can cause pain by compressing or irritating nearby spinal nerves, leading to symptoms like sharp shooting pain, numbness, and tingling.
- 🦴 Facet joints, found throughout the spine, can develop osteoarthritis due to the breakdown of cartilage, causing localized back pain.
- 💪 Muscular back pain can result from strains or spasms in the muscles that support and move the spine, often described as feeling 'thrown out'.
- 🛌 Proper support, such as a good mattress, can help alleviate back pain, and companies like Helix Sleep offer customizable mattresses to meet individual needs.
- 🩺 Treatment options for back pain range from conservative therapies like heat, massage, and exercise to more invasive procedures like injections and surgery.
Q & A
What are the five regions of the spine and what are their functions?
-The five regions of the spine are the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. The cervical region consists of 7 vertebrae and is associated with the neck, allowing for head movement. The thoracic region has 12 vertebrae and is linked to the ribcage and chest anatomy. The lumbar region contains 5 vertebrae and is responsible for bearing body weight and facilitating movement. The sacral region is a single solid bone formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae, providing support and protection to the spinal cord. The coccygeal region, also known as the tailbone, is made up of 3-5 fused coccygeal bones and provides attachment for muscles and ligaments.
What is the role of the intervertebral discs in the spine?
-Intervertebral discs are located between each vertebra and serve as shock-absorbing pads that cushion the spine, allowing for smooth and flexible movement. They also help to maintain the spacing between vertebrae, which is crucial for spinal health and preventing degeneration.
What are the potential causes of back pain related to the intervertebral discs?
-Back pain related to the intervertebral discs can be caused by degeneration or aging of the discs, leading to a narrowing of the disc space. Injuries or improper lifting can result in a herniated or bulging disc, which can press on spinal nerves and cause pain. Regular activities that involve twisting or heavy lifting may also lead to disc damage.
How can spinal nerves contribute to back pain?
-Spinal nerves can contribute to back pain if they are irritated, compressed, or damaged. This can occur when the spaces between vertebrae, known as intervertebral foramina, become narrowed due to degeneration of the vertebrae or discs. The compressed nerves can cause sharp, shooting pain along the nerve pathway, numbness, tingling, and even muscle weakness.
What is the sciatic nerve and how is it related to lower back pain?
-The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body, originating from five spinal nerves (L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3) in the lower lumbar region. It runs down the back of the thigh, through the lower leg, and into the foot. Herniated or bulging discs in the lower lumbar region can compress or irritate the sciatic nerve, leading to a condition known as sciatica, which is characterized by shooting pain down the leg and into the foot, as well as numbness and tingling.
How does osteoarthritis affect the spine and cause back pain?
-Osteoarthritis is a form of arthritis that occurs when the cartilage covering the ends of bones in a joint breaks down over time. In the spine, this can affect the facet joints, which are small joints between the vertebrae. When the cartilage in these joints degenerates, it can lead to pain and stiffness in the affected area of the spine.
What are the main muscles involved in muscular back pain and how can they be affected?
-Muscular back pain often involves the deep back muscles such as the Erector Spinae group, which includes the iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis muscles. These muscles can be strained or pulled, leading to muscle fiber tears and pain. Additionally, muscles can go into spasm or tension, causing a feeling of tightness and discomfort that can be exacerbated by movement.
What are some conservative therapies for managing back pain?
-Conservative therapies for managing back pain include applying heat, massage, regular exercise, and physical therapy. Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen (NZs) and topical lidocaine patches can help manage pain. In cases of muscle spasms, muscle relaxers may be prescribed. These approaches aim to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the back muscles to prevent future injuries.
What are some advanced treatment options for back pain that doesn't respond to conservative therapies?
-Advanced treatment options for back pain include injections of anti-inflammatory medications around inflamed nerves or facet joints, radio frequency ablation which creates a heat lesion to block pain signals from a specific nerve, and surgical procedures to create more space around compressed nerves or to address issues with a ruptured or bulging disc.
How does a good mattress contribute to spinal health and potentially alleviate back pain?
-A good mattress provides the right level of support and comfort for the spine, helping to maintain its natural alignment while sleeping. This can reduce pressure on the intervertebral discs and nerves, potentially alleviating back pain. A customized mattress that fits an individual's body type and sleep preferences can further enhance spinal support and comfort.
What are some preventive measures to take for avoiding back pain?
-Preventive measures for back pain include using proper lifting techniques, regularly mobilizing the spine, and strengthening the surrounding muscles. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and proper posture, can also help to prevent back pain and promote overall spinal health.
Outlines
🧘♂️ Understanding Back Pain
The video begins by addressing the common experience of back pain, varying in severity and cause. It introduces an exploration of the spinal anatomy, including vertebrae, nerves, discs, and muscles, to better comprehend potential sources of back pain. The spine is divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal, each with specific functions and vulnerabilities. The cervical region consists of seven vertebrae, the thoracic region has twelve, and the lumbar region comprises five vertebrae, all of which are mobile and thus more prone to injury. The sacral and coccygeal regions are fused bones, contributing to the less mobile part of the spine. The video emphasizes the spine's role in protecting the spinal cord, transmitting forces and weight, and facilitating movement, while also highlighting the increased risk of injury due to mobility.
🛌 The Impact of Mattresses on Back Health
The second paragraph discusses specific causes of back pain, such as the intervertebral disc, and introduces Helix Sleep as a sponsor providing customized mattresses to alleviate disc pressure. The speaker shares their personal experience with the Helix Midnight Luxe mattress, noting its comfort and the company's sleep quiz that caters to individual preferences. The benefits of a good mattress for spinal health are emphasized, and the video provides a link for a special discount on Helix mattresses. The discussion then returns to spinal health, focusing on the importance of the intervertebral discs, their degeneration, and the resulting pain from disc issues or injury, such as herniated or bulging discs. The potential irritation or damage to nearby structures, particularly spinal nerves, is also highlighted as a source of back pain.
🏥 Disc and Nerve-related Back Pain
This section delves deeper into the anatomy of intervertebral discs and their degeneration, as well as the impact on spinal nerves. The video uses a cadaver dissection to illustrate the narrowing of discs and the resulting effects on the vertebral bodies. It explains how the degeneration of the intervertebral foramen can compress and irritate nerves, leading to sharp, shooting pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. The concept of sciatica and its relation to herniated lumbar discs and the sciatic nerve is introduced, emphasizing the widespread effects of lower back disc issues on the leg and foot.
🦴 Arthritis and Muscular Back Pain
The fourth paragraph discusses two additional causes of back pain: osteoarthritis and muscular back pain. Osteoarthritis involves the degeneration of cartilage in facet joints throughout the spine, leading to pain and stiffness. Factors contributing to arthritis include injury, wear and tear, improper mechanics, and aging. Muscular back pain, often associated with the phrase 'throwing out one's back,' involves strains or spasms in the deep back muscles, such as the Erector Spinae and multifidus. The video explains that these issues can occur simultaneously with other spinal problems, exacerbating pain and discomfort.
💆♂️ Managing and Preventing Back Pain
The final paragraph wraps up the discussion on back pain by acknowledging that not all types of back pain were covered in the video but focuses on the mechanical forms originating from the spine and related structures. The video suggests various supportive therapies for managing back pain, such as heat application, massage, exercise, physical therapy, and medication. It also mentions more advanced treatments like injections and surgical procedures for cases that do not improve with conservative approaches. The video concludes with advice on proper lifting techniques, spine mobilization, and muscle strengthening to prevent back pain, inviting viewers to suggest topics for future videos and promoting a healthy lifestyle for spinal health.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Back Pain
💡Spinal Bones
💡Intervertebral Discs
💡Spinal Nerves
💡Facet Joints
💡Muscular Back Pain
💡Sciatica
💡Osteoarthritis
💡Helix Sleep
💡Physical Therapy
Highlights
Back pain is a common experience affecting nearly everyone at some point in their lives, varying in severity and duration.
The spine, or vertebral column, is composed of multiple individual bones called vertebrae, which can be a source of potential problems and pain.
The spine is divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal, each with a specific function and potential for different pain-related issues.
The cervical region consists of seven vertebrae, abbreviated from C1 to C7, and is responsible for neck movement and supporting the head.
The thoracic region has 12 vertebrae, associated with the ribcage and chest anatomy, providing protection and support.
The lumbar region comprises five vertebrae, known as L1 to L5, and is the region where most people experience back pain due to its role in supporting the body's weight and movement.
The sacral and coccygeal regions are less mobile and consist of fused bones, reducing the risk of injury but still capable of causing pain due to various factors.
The spinal cord is protected by the vertebral foramen, a hole in each vertebra that forms a canal when stacked.
The vertebral body is designed to transmit forces and weight, while the intervertebral discs act as shock-absorbing pads between the vertebrae.
The spine's ability to move in all three planes of space is facilitated by various processes, such as the transverse and spinous processes, which are attachment sites for muscles.
Degenerative disc disease is a common cause of back pain, resulting from the aging process and wear and tear on the spine.
Herniated or bulging discs can cause pain by damaging the disc itself or by compressing and irritating nearby nerves.
Nerve pain, or neuropathic pain, can manifest as sharp, shooting pain, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness along the nerve's pathway.
Sciatica, a specific type of nerve pain, is caused by irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, which can result from a herniated disc in the lower lumbar region.
Osteoarthritis, a form of arthritis affecting the facet joints in the spine, can lead to back pain due to the degeneration of cartilage.
Muscular back pain can result from muscle strains or spasms, often occurring when someone 'throws out their back'.
Many types of back pain can improve with time and supportive therapies, such as heat application, massage, exercise, and physical therapy.
More severe or persistent back pain may require interventions like injections, radio frequency ablation, or surgical procedures to alleviate symptoms.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
How to Fix a Bulging Disc in Your Lower Back | RELIEF IN SECONDS!

BEST sleeping position to FIX Neck Hump, Hunchback, or Forward Head Posture | Dr. Jon Saunders

2 Sleeping Positions You Must Avoid.

How To FIX Low Back Pain In 90 Seconds - (So Simple)

5 Best Stretches For Low Back Pain In Bed. Do Daily.

STOP Back Pain Without Exercises: For Older Adults
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: