Polar Coordinate System Example | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M3-08
TLDRIn this instructional video, Professor Anderson explores the conversion of Cartesian coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinates (r, θ) using the example of the point (1, √3). The professor guides the audience through a visual estimation, followed by a mathematical calculation to confirm the guesses. The point lies in the first quadrant, leading to an r-value of 2 and a θ-value of 60 degrees, deduced from the properties of a 30-60-90 triangle. The process emphasizes the importance of estimation and intuition in problem-solving, encouraging viewers to refine their approach if their initial guesses are significantly off.
Takeaways
- 📝 The discussion is about converting Cartesian coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinates (r, θ).
- 🎯 Given coordinates are x = 1 and y = √3, which are used to find corresponding r and θ values.
- 📐 The instructor initially guesses r to be 2 and θ to be 60 degrees based on a drawn Cartesian coordinate system.
- 🔢 The calculation for r involves taking the square root of the sum of the squares of x and y (r = √(x^2 + y^2)), resulting in r = 2.
- 📐 For θ, the instructor identifies the triangle as a 30-60-90 triangle, which helps in determining the angle.
- 📊 The tangent of θ (tan(θ)) is given as √3/1, which corresponds to an angle of 60 degrees in a 30-60-90 triangle.
- 🤔 The process of guessing and then verifying is emphasized as a useful problem-solving strategy.
- 👀 The instructor encourages visualizing the problem by drawing the Cartesian coordinate system and the point in question.
- 🧠 The importance of developing intuition about problems is highlighted, and adjusting it if the guess is significantly off.
- 📚 The example used is a well-known triangle (1, √3, 2), which is a special case that the class seems familiar with.
- 📞 The offer of additional help through office hours is provided for those who need further clarification.
Q & A
What is the Cartesian coordinate system mentioned in the script?
-The Cartesian coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a set of numerical coordinates, typically denoted as (x, y).
What are the given values for x and y in the polar coordinates example?
-The given values are x = 1 and y = √3.
How does the script suggest determining r in polar coordinates?
-The script suggests determining r by calculating the square root of the sum of the squares of the x and y components, which in this case is √(1^2 + (√3)^2) = √(1 + 3) = √4 = 2.
What is the significance of the 1-√3-2 triangle in the context of the script?
-The 1-√3-2 triangle is a special kind of triangle known as a 30-60-90 triangle, which has specific properties that make it useful in trigonometry and geometry.
What is the guessed value for theta in the script?
-The guessed value for theta is 60 degrees.
How is theta confirmed to be 60 degrees in the script?
-Theta is confirmed to be 60 degrees by using the tangent function, where tan(theta) = √3/1, and the arc tangent of √3 is 60 degrees.
What does the script advise when a guess is far off from the actual answer?
-If the guess is far off from the actual answer, the script advises to check if there was a mistake in the problem-solving process or if the initial intuition about the problem was incorrect, and to fix one of those aspects.
What is the role of guessing in solving problems according to the script?
-Guessing plays a role in providing a preliminary estimate that can be checked for accuracy. It helps in assessing whether the problem-solving approach is on the right track or if the intuition about the problem is correct.
What is the relationship between the x and y components and the polar coordinates r and theta?
-The x and y components are related to the polar coordinates r and theta through the equations r = √(x^2 + y^2) and theta = arctan(y/x) in the first quadrant.
How does the script emphasize the importance of understanding special triangles?
-The script emphasizes that understanding special triangles, like the 30-60-90 triangle, can greatly aid in problem-solving by providing quick insights and accurate guesses, as these triangles have well-known properties that can be easily applied.
What does the script suggest doing if the initial approach to a problem is unclear?
-If the initial approach to a problem is unclear, the script suggests seeking clarification through additional review or by consulting the professor during office hours.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Polar Coordinates
Professor Anderson begins by introducing a polar coordinates example, aiming to determine the values of r and theta given x=1 and y=√3. The professor suggests visualizing the problem using the Cartesian coordinate system and making educated guesses based on the drawn figure. The point (1, √3) is identified as being in the first quadrant, leading to the conclusion that r must be greater than 1 and that theta should be a positive number. The guess for r is 2, and for theta, it is 60 degrees.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Polar Coordinates
💡Cartesian Coordinate System
💡Guessing
💡Square Root
💡Theta
💡R
💡3-4-5 Triangle
💡Tangent
💡Arc Tangent
💡Office Hours
💡Pythagorean Theorem
Highlights
Professor Anderson begins a lesson on polar coordinates.
The example given involves the Cartesian coordinates (x=1, y=√3).
A guesswork approach is suggested to estimate r and θ values visually.
The value of x (1 unit) is used to determine the horizontal distance from the origin.
The value of y (√3) is recognized as being greater than 1, influencing the vertical distance.
An educated guess for r is made to be 2 based on the visual estimation.
An educated guess for θ is 60 degrees, considering the shape of the triangle formed.
The actual calculation of r confirms the guess, resulting in √4 or 2.
The triangle is identified as a 30-60-90 triangle, which helps in determining θ.
θ is calculated to be 60 degrees, which matches the guess.
The tangent function is used to verify the calculated value of θ.
The lesson emphasizes the importance of making educated guesses to check the accuracy of solutions.
The 1-√3-2 triangle is highlighted as a well-known figure in mathematics.
Office hours are mentioned as a resource for students seeking further clarification.
The process of visual estimation and verification is encouraged for problem-solving.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Polar coordinates 2 | Parametric equations and polar coordinates | Precalculus | Khan Academy

Polar coordinates 3 | Parametric equations and polar coordinates | Precalculus | Khan Academy
How to Convert From Polar Coordinates to Rectangular Coordinates (Precalculus - Trigonometry 37)
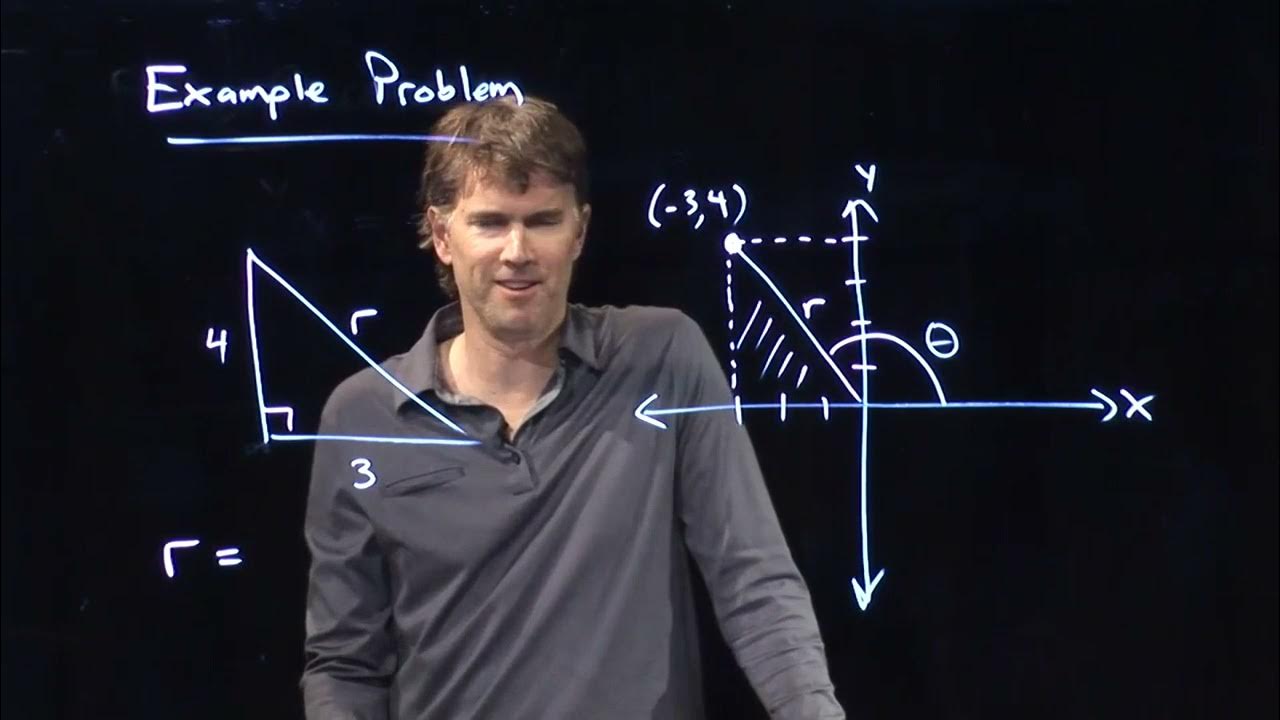

An Example Using Polar Coordinates | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M3-09

AP Precalculus Practice Exam Question 15
Polar Equations to Rectangular Equations, Precalculus, Examples and Practice Problems
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: