Vector Field
TLDRIn this informative video, Mr. Andersen explores the concept of vector fields, using the gravitational pull between the Earth and the Moon as an introduction. He explains how vectors differ from scalars by including both magnitude and direction, and illustrates this with the analogy of playing Angry Birds. The video delves into how vector fields can be used to represent gravitational attraction in Physics 1 and electromagnetism in Physics 2, demonstrating the principles through interactive examples and emphasizing the importance of vector addition in understanding these fields. The engaging content is designed to help viewers grasp the fundamentals of vector fields and their applications in physics.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Vector fields represent gravitational forces with arrows showing the direction and magnitude of the force.
- 🪐 The Moon orbits the Earth due to its velocity counteracting the gravitational pull, preventing it from crashing into the Earth.
- 🔢 Vectors differ from scalars as they include both magnitude and direction, which is crucial in physics for understanding forces and velocities.
- 🎯 In Physics 1, vector fields are used to understand gravitational attraction, while in Physics 2, they pertain to electromagnetism.
- 🔋 Understanding vector addition is essential for analyzing forces between charged particles, such as in the attraction between a positive and negative charge.
- 🎮 The concept of vector addition can be visualized using the analogy of playing Angry Birds, where the force's direction and magnitude can be adjusted.
- 🏹 Mapping vector fields helps in visualizing the forces acting on objects, such as the attraction or repulsion between charged particles or magnetic poles.
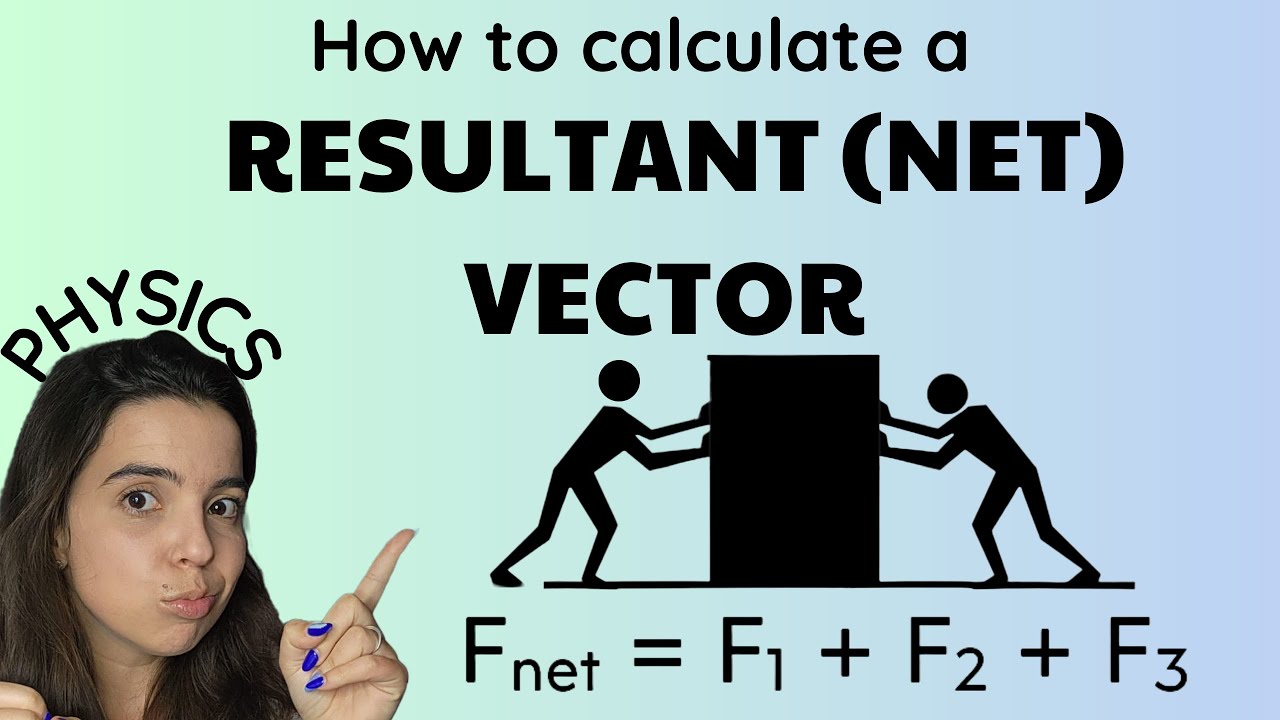
- 🤝 Vector addition involves lining up vectors tail to tip to find the resultant force, which is useful in determining the net force acting on an object.
- 🧲 The repulsion and attraction between charges can be demonstrated and understood through the mapping of vector fields, showing the direction and strength of the forces.
- 🔍 Given a vector field, one can determine the location and relative size of the source by observing where the arrows point towards or away from.
- 💡 The use of vector fields is not only theoretical but can be applied in practical scenarios like mapping the forces in an electric field hockey game.
Q & A
What is a vector field and how is it represented?
-A vector field is a visual representation of a force in two or three dimensions, using arrows to indicate both the direction and the magnitude of the force at various points in space.
How does the gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon illustrate the concept of a vector field?
-The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon can be represented by a vector field where arrows point towards the Earth, indicating the direction of the force, and the size of the circles near the Moon indicates the increasing magnitude of the force as the Moon gets closer to Earth.
What is the difference between vectors and scalars?
-Vectors have both magnitude and direction, whereas scalars have only magnitude without direction. Vectors are used to represent physical quantities like force and velocity, which have both size and direction components.
How does the game Angry Birds relate to the concept of vectors?
-In Angry Birds, when you pull back the slingshot, you are essentially applying a vector force to the bird. The force has a magnitude, indicated by how far you pull back, and a direction, indicated by the angle at which you release the bird.
What is vector addition and how is it used in physics?
-Vector addition is the process of combining two or more vectors to find their resultant vector. It is used in physics to determine the overall effect of multiple forces acting on an object, by adding the vectors representing each force tail to tip to find the combined force.
How can you determine the location and size of charges using a vector field?
-By observing where the arrows in a vector field point towards or away from, you can determine the location of charges. The density of the arrows indicates the relative size of the charges; denser arrows suggest a larger charge.
What is the significance of the direction of the arrows in a vector field?
-The direction of the arrows in a vector field indicates the direction of the force. Arrows pointing towards a point indicate attraction, while arrows pointing away indicate repulsion. This helps in understanding the nature of the interaction between objects or charges.
How does the concept of vector fields apply to electromagnetism?
-In electromagnetism, vector fields represent the forces between electric charges or magnetic poles. Positive and negative charges create fields of attraction, while like charges or like poles create fields of repulsion.
What is a phet simulation and how does it relate to vector fields?
-A phet simulation is an interactive computer simulation that allows users to visualize and explore scientific concepts. In the context of vector fields, a phet simulation like 'Electric Field Hockey' helps users understand how charges interact and how vector fields are formed and influenced by these interactions.
How can you use a compass to map magnetic fields?
-A compass can be used to map magnetic fields by placing it near a magnet. The needle of the compass will align itself with the magnetic field lines, showing the direction of the force. By moving the compass around, you can trace out the pattern of the magnetic field.
What is the practical application of understanding vector fields in physics?
-Understanding vector fields is crucial in physics for predicting the motion of objects under various forces, designing systems like electric motors and generators, and analyzing phenomena in electromagnetism and gravitational interactions.
Outlines
🌙 Introduction to Vector Fields and Gravitational Force
This paragraph introduces the concept of vector fields, specifically in the context of gravitational force. Mr. Andersen explains how the gravitational force pulling the moon towards the Earth can be visually represented by a vector field, a set of arrows indicating the direction of the force. He emphasizes that the moon doesn't crash into the Earth due to its velocity, which allows it to continually 'miss' the Earth. The paragraph also distinguishes between vectors and scalars, noting that vectors have both magnitude and direction. The importance of understanding vector fields is highlighted in both Physics 1, where it relates to gravitational attraction, and Physics 2, where it involves electromagnetism. The analogy of playing Angry Birds is used to illustrate the concept of vectors, showing how changing the direction and magnitude of the force applied affects the trajectory of the bird.
🎮 Vector Fields in Physics: Attraction and Repulsion
In this paragraph, the discussion continues with the application of vector fields in physics, focusing on the attraction between two charges and the repulsion between like charges or poles. The analogy of an 'electric field hockey' game is introduced, where the puck represents a positively charged object and the goal represents a negatively charged source. The paragraph explains how the vector fields can be mapped by observing the repulsion or attraction between charges, and how these fields change with distance and the presence of multiple charges. The importance of vector addition is reiterated, as it is crucial for determining the resultant force in scenarios involving multiple sources of attraction or repulsion. The paragraph concludes with a practical exercise for the viewer to identify the number and relative sizes of charges based on the density and direction of the arrows in the vector fields presented.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Vector Field
💡Gravitational Force
💡Velocity
💡Scalars vs Vectors
💡Electromagnetism
💡Vector Addition
💡Charges
💡Attraction and Repulsion
💡Sources
💡PhET Simulations
💡Vector Sum
Highlights
The concept of a vector field is introduced, which represents the gravitational force pulling the moon towards the Earth.
Vector fields are depicted as a set of arrows showing the direction and magnitude of forces.
The moon's velocity allows it to orbit the Earth instead of crashing into it, demonstrating the importance of vector quantities in physics.
Vectors are distinguished from scalars by having both magnitude and direction.
The application of vector fields in Physics 1 involves understanding gravitational attraction, while in Physics 2 it extends to electromagnetism.
The concept of vector addition is crucial for combining forces in physics, illustrated with the analogy of playing Angry Birds.
The use of vector addition to determine the resultant force is demonstrated with the tail-to-tip method.
The analogy of a multiplayer Angry Birds game is used to explain the interaction of multiple forces.
The mapping of vector fields is explored using the example of like charges repelling each other.
The process of mapping vector fields with opposite charges (positive and negative) is detailed.
The importance of understanding vector fields for determining the location and size of sources is emphasized.
The use of a compass to visualize magnetic fields is suggested as a practical application of vector fields.
The phet simulation game 'electric field hockey' is mentioned as a fun way to explore vector fields.
The impact of adding multiple charges on the complexity and curvature of vector fields is discussed.
The ability to deduce the number and relative size of charges from a given vector field is highlighted.
The video aims to educate viewers on how gravitational and electromagnetic sources affect vector fields.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: