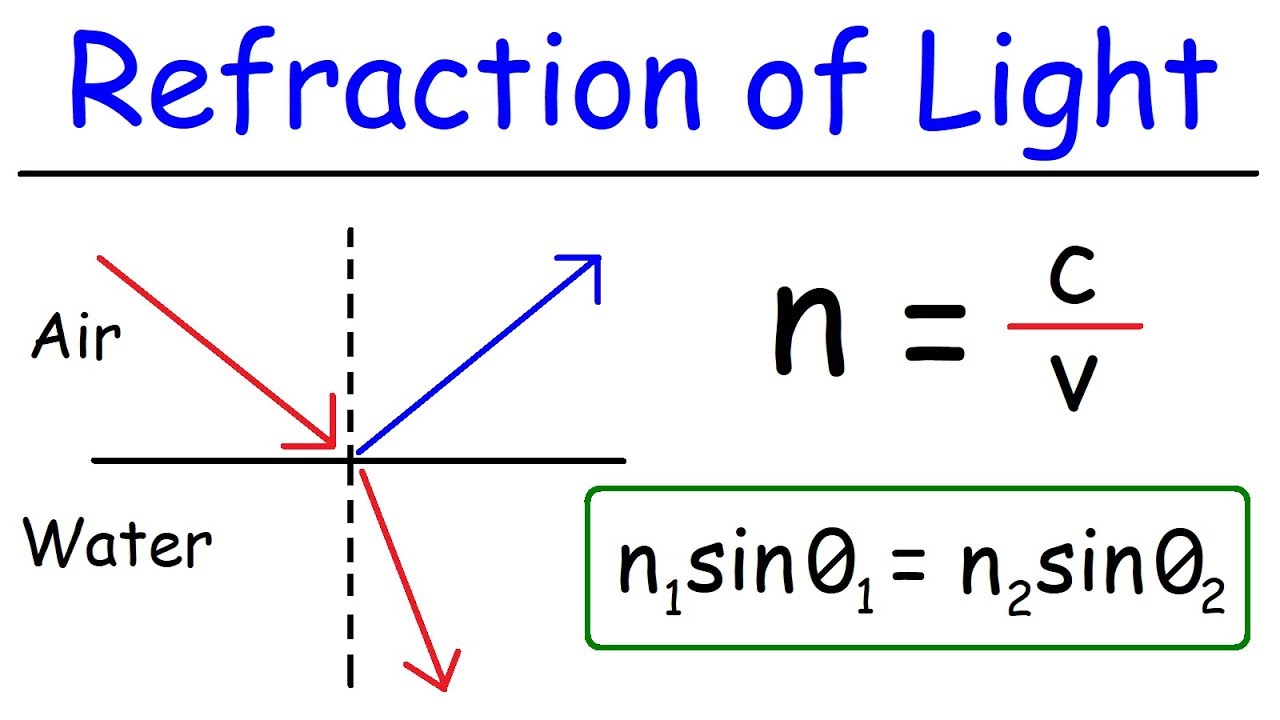Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle
TLDRThe script explains the concept of total internal reflection, focusing on how light behaves when transitioning between different media like glass and air. It covers critical angles and conditions necessary for total internal reflection, with practical examples from daily life and scientific applications. The script also touches on the significance of these principles in various contexts, such as optics and communication technologies.
Takeaways
- 🚨 The script discusses the concept of total internal reflection and its importance in various media, including glass and water.
- 🔍 It explains the phenomenon of light traveling from one medium to another, such as from air to glass, and the conditions that affect this process.
- 🌟 The critical angle is highlighted as a key factor in total internal reflection, beyond which light will not pass into the second medium and will instead reflect back into the first.
- 📚 The script mentions specific angles, such as 29 degrees and 43 degrees, which are significant in the context of light refraction and reflection.
- 💡 The importance of understanding total internal reflection for practical applications like optical fibers and lenses is emphasized.
- 🛠️ The script provides examples of how light behaves when it hits the interface between two different media, either being transmitted or reflected based on the angle of incidence.
- 🌈 The concept of light being 'trapped' within a medium due to total internal reflection is explained, which is crucial for fiber optics and other technologies.
- 🔬 The script touches on the technical aspects of light refraction, including terms like 'incident light', 'normal line', and 'medium'.
- 🌞 It also discusses the implications of light traveling through different types of media, such as the difference between light traveling through air and glass.
- 📐 The script mentions the impact of the angle of incidence on the behavior of light, particularly how it relates to the critical angle for total internal reflection.
- 🌊 The concept of light traveling through water and the effects of total internal reflection in aquatic environments is briefly mentioned.
Q & A
What is the concept of 'Total Internal Reflection' discussed in the script?
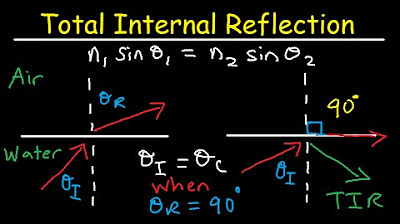
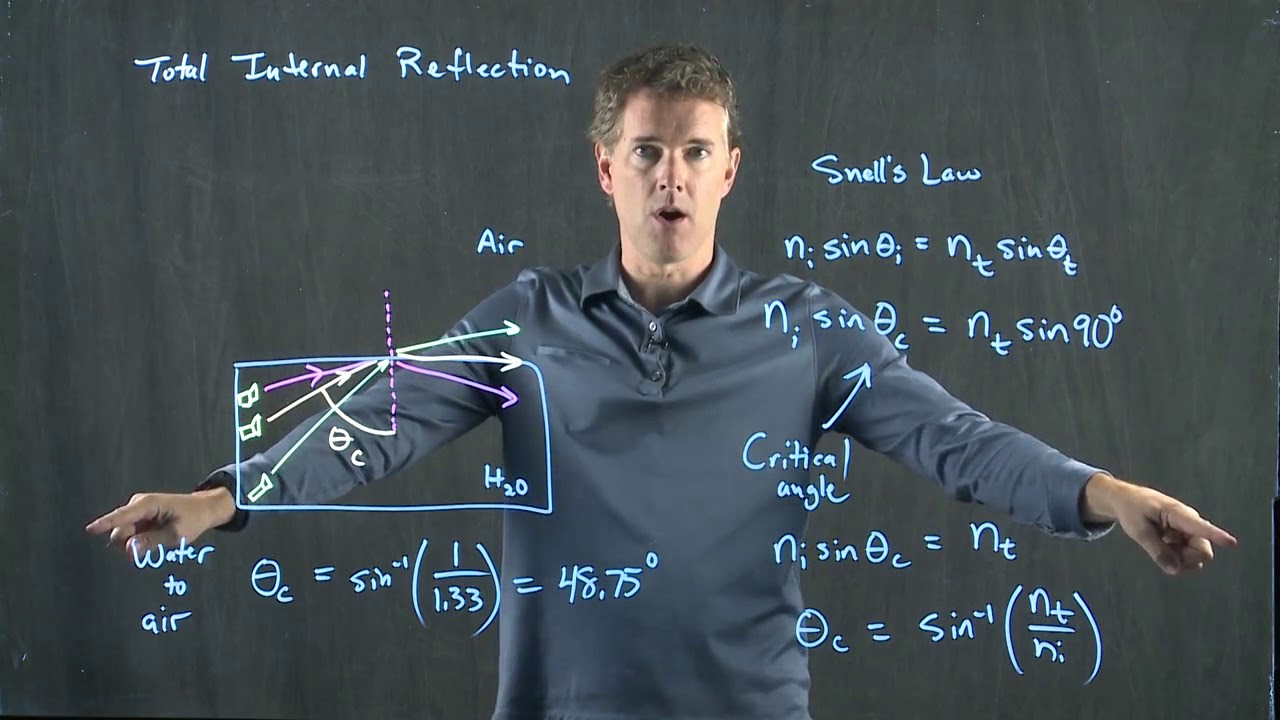
-Total Internal Reflection (TIR) is a phenomenon that occurs when a light wave traveling from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index hits the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing the light to be completely reflected back into the medium.
What is the significance of the critical angle in the context of the script?
-The critical angle is the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90 degrees, and it is the threshold for total internal reflection. If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, light will be totally internally reflected.
How does the script describe the transition of light from one medium to another?
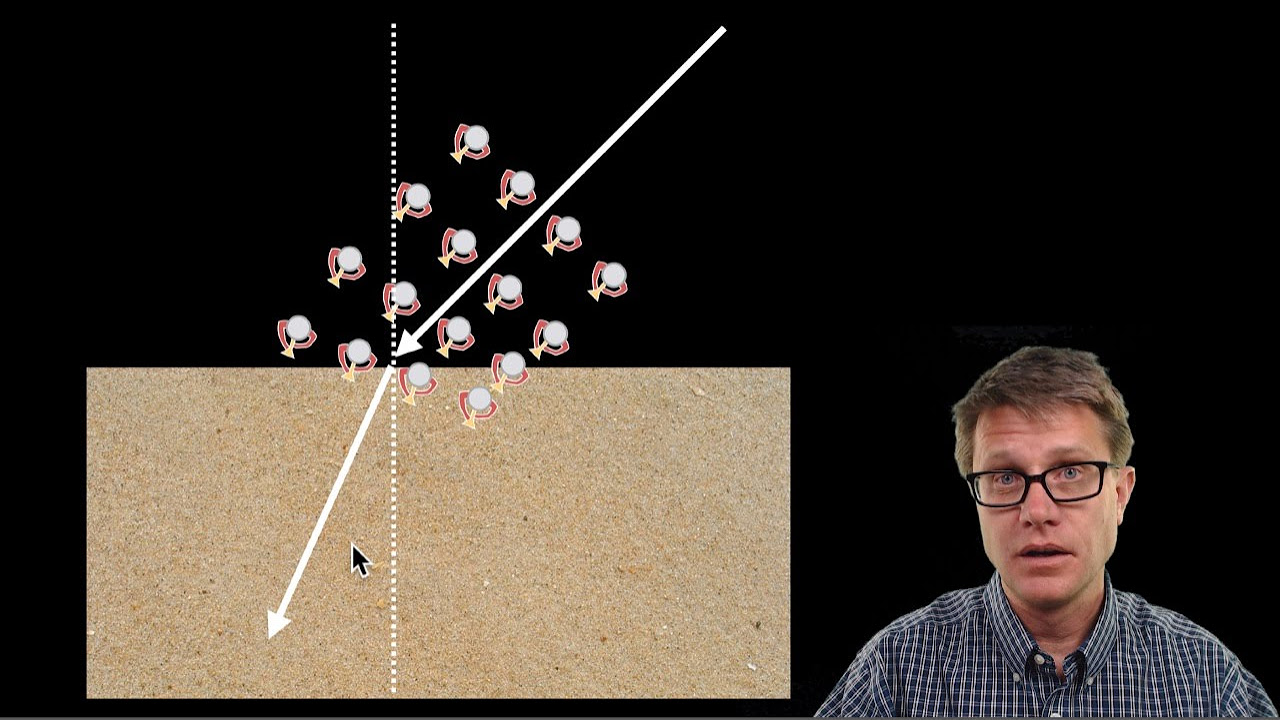
-The script discusses the transition of light traveling from one medium to another, such as from air to glass, and the effects of different angles of incidence on the behavior of light, including the possibility of total internal reflection.
What is the role of the incident angle in the process of light reflection?
-The incident angle is crucial in determining the path of light when it encounters the boundary between two media. If the angle is greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs, and the light does not pass into the second medium.
What is the impact of medium defects on light transmission as mentioned in the script?
-Medium defects, such as impurities or irregularities in the medium, can cause light to scatter or deviate from its path, potentially preventing total internal reflection and affecting the transmission of light.
How does the script relate the concept of total internal reflection to everyday life?
-The script does not explicitly relate total internal reflection to everyday life examples, but the concept is fundamental in various applications such as fiber optics, prisms, and other optical devices.
What are the conditions for total internal reflection to occur as per the script?
-Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index and the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
What is the significance of the refractive index in the script's discussion on light behavior?
-The refractive index is a measure of how much a medium can bend or slow down light. It plays a key role in determining the path of light, especially in the context of total internal reflection.
How does the script differentiate between normal and critical angles?
-The script implies that a normal angle refers to any angle of incidence that does not result in total internal reflection, whereas the critical angle is the specific angle at which total internal reflection begins to occur.
What is the importance of understanding total internal reflection in the field of optics?
-Understanding total internal reflection is essential in optics as it is a fundamental principle that underlies the functioning of many optical devices and systems, including fiber optic communication and laser systems.
How does the script address the concept of light traveling through different media?
-The script discusses the behavior of light as it travels from one medium to another, highlighting the changes in the path of light due to variations in the refractive index and the angle of incidence.
Outlines
😀 Light Reflection and Media Considerations
This paragraph discusses the concept of total internal reflection and its application in daily life. It mentions the importance of understanding the first angle of incidence and how light travels from one medium to another, such as from glass to air. The critical angle for total internal reflection is highlighted, along with the significance of this phenomenon in various situations, including the visibility of light in different media and the effects of the angle of incidence on light behavior.
😀 Critical Angles and Light Behavior
The second paragraph delves deeper into the critical angle and its implications for light behavior in different media. It emphasizes the importance of the critical angle in the context of light reflection and refraction, particularly in glass and water. The paragraph also touches on the impact of the critical angle on visibility and the total internal reflection phenomenon, suggesting that understanding these concepts is crucial for various applications, including safety and optical clarity.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Total Internal Reflection
💡Critical Angle
💡Refractive Index
💡Incident Light
💡Medium
💡Welding of Light
💡Optical Density
💡Incident Angle
💡Normal Line
💡Media Like Share and Glass
💡Degree of Incidence
Highlights
Total Internal Reflection is a critical concept for understanding light behavior in various media.
The concept operation involves a team discussing the principles of light traveling through different media.
Preparation for an exam involves considering cases of light traveling from one medium to another, such as from air to glass.
Incident light at a certain angle will result in total internal reflection when it hits the glass surface.
The critical angle for total internal reflection is essential for light traveling from glass to air.
The medium's refractive index plays a significant role in determining the behavior of light, including total internal reflection.
Different angles of incidence result in various light paths, affecting the total internal reflection.
The importance of the critical angle is reiterated for light traveling from a denser to a rarer medium.
The concept of light traveling through a medium like glass and the implications for visibility and clarity.
Exploration of light refraction and its impact on the direction of light when it enters a different medium.
Total internal reflection is used in various applications, such as fiber optics, for efficient light transmission.
The discussion of light's behavior in the presence of a medium defect and its implications for total internal reflection.
The importance of considering the angle of incidence for achieving total internal reflection in practical scenarios.
The impact of medium properties on the total internal reflection and the need for precise calculations.
The relationship between the incident angle and the critical angle for light traveling from glass to air.
The significance of total internal reflection in optical devices and its contribution to the field of optics.
The practical applications of total internal reflection in daily life, such as in prisms and lenses.
The theoretical contributions of total internal reflection to the understanding of light behavior in various media.
The innovative methods discussed for demonstrating total internal reflection and its effects on light paths.
The summary of the key points regarding total internal reflection and its importance in the study of optics.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: