Which Bond Is More Polar?
TLDRThe transcript explains the concept of bond polarity by comparing the electronegativity differences between various bonds such as carbon-hydrogen, carbon-oxygen, and hydrogen-oxygen. It illustrates how to determine bond polarity using electronegativity values and the periodic table, emphasizing that bonds with greater electronegativity differences are more polar. The transcript also covers the ranking of bonds from least to most polar and how to identify nonpolar bonds, providing examples and step-by-step calculations to clarify the concepts.
Takeaways
- 📊 The carbon-oxygen bond is more polar than the carbon-hydrogen bond due to a greater electronegativity difference.
- 📚 Electronegativity values: Carbon (2.5), Hydrogen (2.1), Oxygen (3.5), Fluorine (4.0), Nitrogen (3.0).
- 🔍 A bond with a higher electronegativity difference is more polar.
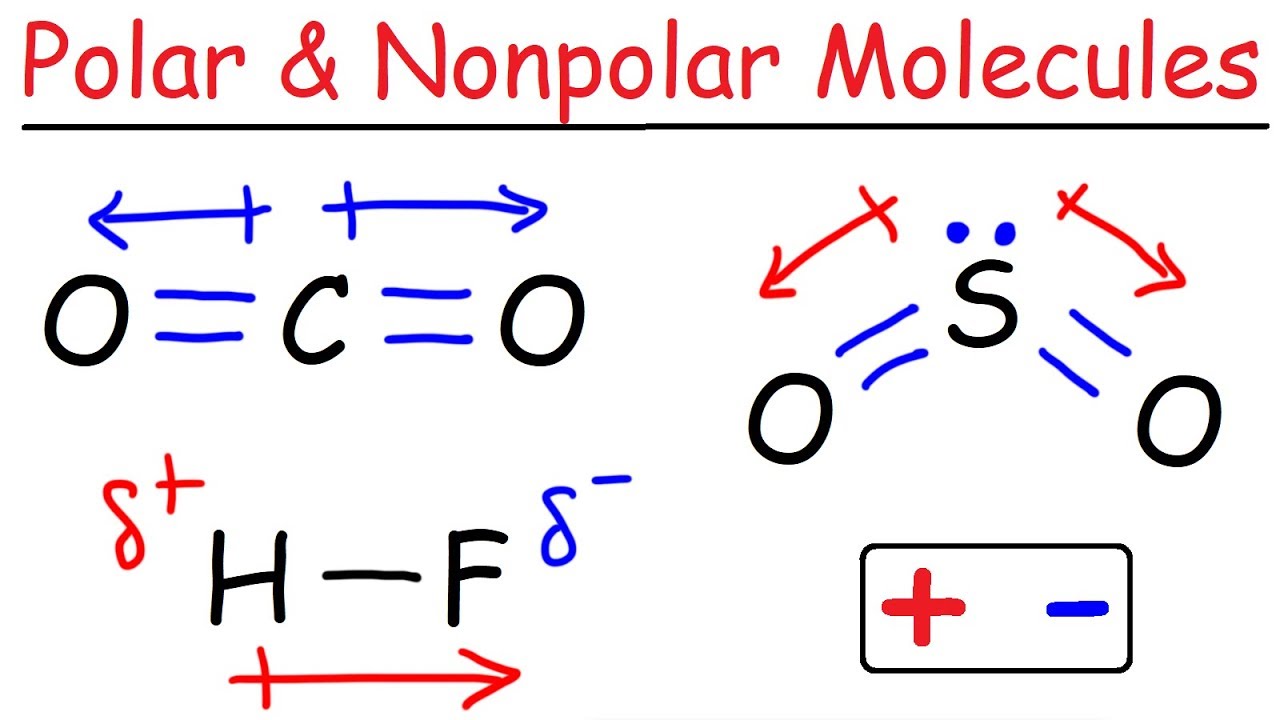
- ⚖️ The OH bond has an electronegativity difference of 1.4, while the HF bond has a difference of 1.9, making the HF bond more polar.
- 📈 Hydrogen bonds occur when hydrogen is attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, forming highly polar covalent bonds.
- ➡️ The direction of polarity is indicated by an arrow pointing towards the more electronegative element.
- 📝 If you don't know the electronegativity values, use the periodic table: electronegativity increases to the right and upwards.
- 🔍 The carbon-oxygen bond is more polar than the carbon-nitrogen bond because oxygen and carbon are further apart on the periodic table.
- 📊 Ranking bonds from least to most polar based on halogens: CI, CBr, CCl, CF, with CF being the most polar due to fluorine's high electronegativity.
- 📉 Carbon-carbon bonds are nonpolar with zero electronegativity difference, while carbon-nitrogen bonds are more polar than carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Q & A
Which bond is more polar: the carbon-hydrogen bond or the carbon-oxygen bond?
-The carbon-oxygen bond is more polar because it has a higher electronegativity difference of 1.0 compared to the carbon-hydrogen bond's difference of 0.4.
How do you determine the polarity of a bond?
-To determine the polarity of a bond, you need to look at the electronegativity values of the atoms involved and calculate the difference. A greater electronegativity difference indicates a more polar bond.
What are the electronegativity values for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen?
-Carbon has an electronegativity value of 2.5, hydrogen is 2.1, and oxygen is 3.5.
What is the electronegativity difference for the H-O bond and the H-F bond?
-The electronegativity difference for the H-O bond is 1.4, and for the H-F bond, it is 1.9.
Which bond is more polar: the H-O bond or the H-F bond?
-The H-F bond is more polar because it has a higher electronegativity difference of 1.9 compared to the H-O bond's difference of 1.4.
What is a special characteristic of hydrogen bonds?
-Hydrogen bonds occur when hydrogen is attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, creating a special case of strong dipole-dipole attraction.
How do you indicate the direction of polarity in a bond?
-The direction of polarity is indicated by pointing an arrow towards the more electronegative element, with the arrow's tail at the less electronegative element.
What can you do if you don't remember the electronegativity values during a test?
-If you don't remember the electronegativity values, you can use the periodic table to estimate the differences. Electronegativity increases as you move to the right and up across the periodic table.
Which bond is more polar: the carbon-nitrogen bond or the carbon-oxygen bond?
-The carbon-oxygen bond is more polar because the electronegativity difference is 1.0 compared to the carbon-nitrogen bond's difference of 0.5.
How do the positions of elements on the periodic table help in estimating bond polarity?
-Elements further apart on the same row of the periodic table have a greater electronegativity difference and therefore form more polar bonds.
List the carbon-halogen bonds in order from least polar to most polar.
-The order from least polar to most polar is: C-I (carbon-iodine), C-Br (carbon-bromine), C-Cl (carbon-chlorine), and C-F (carbon-fluorine).
What are the electronegativity values for carbon, iodine, bromine, chlorine, and fluorine?
-Carbon is 2.5, iodine is 2.5, bromine is 2.8, chlorine is 3.0, and fluorine is 4.0.
Which carbon-halogen bond is considered highly polar?
-The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is considered highly polar with an electronegativity difference of 1.5.
Rank the following bonds from most polar to least polar: carbon-nitrogen, carbon-hydrogen, and carbon-carbon.
-From most polar to least polar: carbon-nitrogen (0.5), carbon-hydrogen (0.4), and carbon-carbon (0.0).
Which bond is completely nonpolar among carbon-nitrogen, carbon-hydrogen, and carbon-carbon?
-The carbon-carbon bond is completely nonpolar with an electronegativity difference of 0.0.
Outlines
🔬 Memahami Polarisasi Ikatan Karbon
Pertimbangkan ikatan antara karbon dan hidrogen serta antara karbon dan oksigen. Mana yang lebih polar? Untuk menentukannya, kita perlu melihat nilai elektronegativitas dari unsur-unsur ini. Karbon memiliki nilai 2,5, hidrogen 2,1, dan oksigen 3,5. Perbedaan EN untuk ikatan karbon-hidrogen adalah 0,4 (nonpolar), sedangkan untuk ikatan karbon-oksigen adalah 1,0 (polar). Jadi, ikatan karbon-oksigen lebih polar. Contoh lain termasuk ikatan H-O dan H-F, di mana ikatan H-F lebih polar karena perbedaan EN yang lebih besar (1,9 vs 1,4). Penting untuk mengetahui arah polaritas, dengan elektron cenderung ke arah unsur yang lebih elektronegatif.
🔍 Menentukan Polarisasi Berdasarkan Tabel Periodik
Jika Anda tidak tahu nilai elektronegativitas, Anda bisa menggunakan letak unsur di tabel periodik. Misalnya, ikatan karbon-nitrogen dibandingkan dengan ikatan karbon-oksigen, di mana oksigen lebih jauh dari karbon di tabel periodik, menunjukkan perbedaan EN yang lebih besar dan lebih polar. Urutan dari yang paling tidak polar hingga paling polar untuk ikatan C-I, C-Br, C-Cl, dan C-F bisa ditentukan dengan melihat nilai elektronegativitas unsur-unsur ini di tabel periodik. Fluorin memiliki nilai tertinggi, diikuti oleh klorin, bromin, dan iodin. Dengan cara ini, ikatan C-F paling polar, dan C-I paling tidak polar.
🧪 Mengurutkan Ikatan Berdasarkan Polarisasi
Contoh terakhir membahas perbandingan antara ikatan karbon-nitrogen, karbon-hidrogen, dan karbon-karbon. Ikatan ini diurutkan dari yang paling polar hingga paling tidak polar. Karbon-nitrogen paling polar dengan perbedaan EN 0,5, diikuti karbon-hidrogen (0,4), dan karbon-karbon (0). Ikatan karbon-karbon dianggap nonpolar karena terdiri dari atom yang sama. Pemahaman ini membantu mengurutkan ikatan berdasarkan polaritas mereka, yang penting untuk berbagai aplikasi kimia.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electronegativity
💡Polar Covalent Bond
💡Nonpolar Covalent Bond
💡Dipole Moment
💡Periodic Table
💡Hydrogen Bonding
💡Fluorine
💡Bond Polarity
💡Electronegativity Difference
💡Hydrogen
Highlights
The concept of bond polarity is discussed, focusing on carbon-hydrogen and carbon-oxygen bonds.
Electronegativity values are key to determining bond polarity.
Carbon has an electronegativity value of 2.5, hydrogen 2.1, and oxygen 3.5.
Carbon-hydrogen bonds are nonpolar covalent bonds due to a small electronegativity difference of 0.4.
Carbon-oxygen bonds are polar covalent bonds with an electronegativity difference of 1.0.
The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond.
Hydrogen-oxygen and hydrogen-fluorine bonds are compared for polarity.
Fluorine is the most electronegative element with an electronegativity value of 4.0.
Hydrogen-fluorine bonds are more polar than hydrogen-oxygen bonds due to a higher electronegativity difference.
Direction of polarity is indicated by the partial charges on hydrogen and the more electronegative element.
A method to determine bond polarity without knowing electronegativity values is introduced.
Carbon-nitrogen and carbon-oxygen bonds are compared using their positions on the periodic table.
Electronegativity increases from left to right and top to bottom on the periodic table.
Carbon-oxygen bonds are more polar than carbon-nitrogen bonds based on their positions.
A ranking of carbon-halogen bonds from least to most polar is attempted without specific electronegativity values.
Carbon-fluorine bonds are identified as the most polar among the carbon-halogen bonds.
Electronegativity differences are calculated to confirm the polarity ranking of carbon-halogen bonds.
Carbon-carbon bonds are nonpolar due to identical electronegativity values.
A ranking of carbon-nitrogen, carbon-hydrogen, and carbon-carbon bonds is provided from most to least polar.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: