Ionic Bonds, Polar Covalent Bonds, and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
TLDRThis lesson explains the differences between ionic and covalent bonds, focusing on polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. It highlights that bonds between identical atoms, like H2, are nonpolar covalent due to equal electron sharing. Polar covalent bonds, such as between carbon and oxygen, have unequal sharing due to differing electronegativities. The lesson covers how ionic bonds, like NaCl, form through electron transfer between metals and nonmetals. Examples include H2, CH4, and H2O, demonstrating different bond types and properties.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Anytime you have a bond between two atoms of the same element, it's always going to be a nonpolar covalent bond.
- ⚖️ In a covalent bond, electrons are shared equally if the atoms have the same electronegativity.
- 📊 If the electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms is 0.5 or more, the bond is considered polar covalent.
- 🌟 A carbon-oxygen bond is a polar covalent bond because the electronegativity difference is 1 (3.5 for oxygen and 2.5 for carbon).
- 🔄 In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, creating ions that attract each other.
- 🔋 Sodium (a metal) and chlorine (a nonmetal) form an ionic bond, where sodium becomes positively charged and chlorine becomes negatively charged.
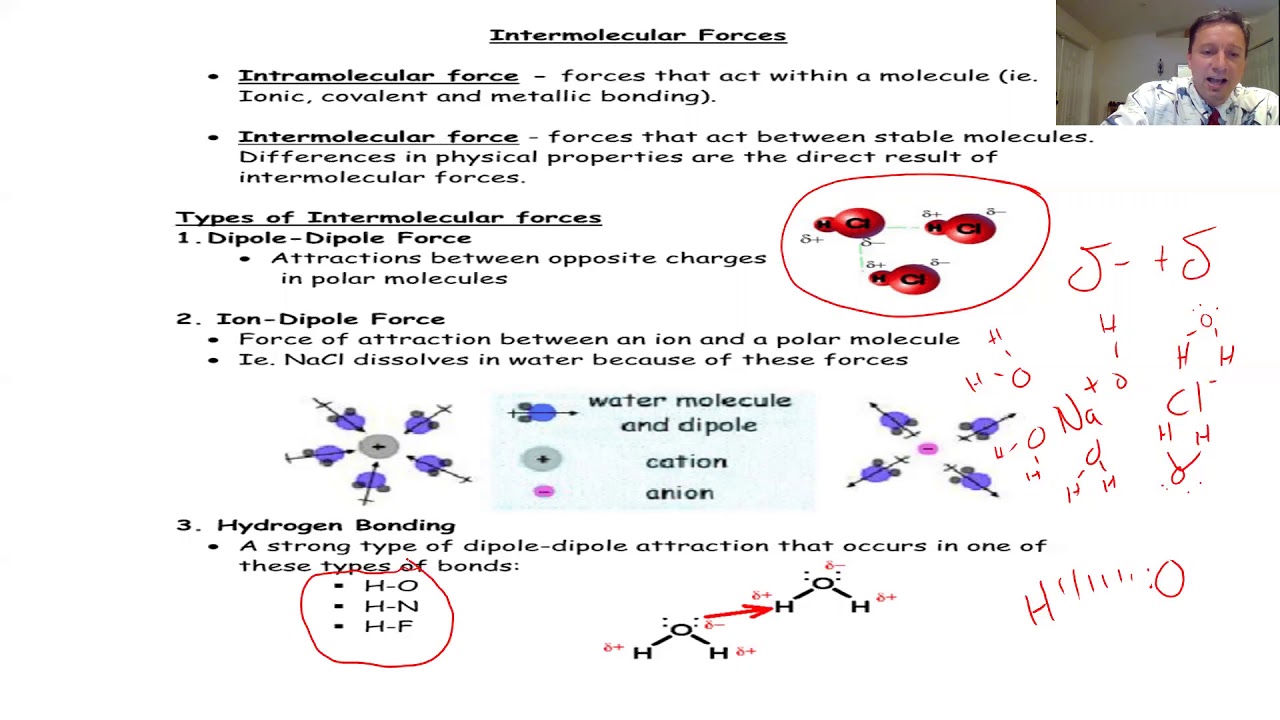
- 💧 A hydrogen bond is a special type of polar covalent bond that occurs when hydrogen is directly attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
- 🌊 Hydrogen bonds lead to higher boiling points in substances like water due to strong intermolecular forces.
- 🛠️ The carbon-hydrogen bond is nonpolar because the electronegativity difference is 0.4 (2.5 for carbon and 2.1 for hydrogen).
- 🔍 When determining bond types, if you have a metal and a nonmetal, it's typically an ionic bond, while bonds between nonmetals are covalent.
Q & A
What type of bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms?
-The bond formed between two hydrogen atoms is a nonpolar covalent bond.
Why is the bond between two hydrogen atoms considered nonpolar covalent?
-The bond is considered nonpolar covalent because the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms, which have the same electronegativity.
How can you determine if a bond between two nonmetals is polar or nonpolar covalent?
-To determine if a bond between two nonmetals is polar or nonpolar covalent, you need to look at the electronegativity values of the elements. If the difference is 0.5 or more, the bond is polar covalent. If the difference is 0.4 or less, the bond is nonpolar covalent.
What is the electronegativity difference that makes the carbon-oxygen bond polar covalent?
-The electronegativity difference between carbon (2.5) and oxygen (3.5) is 1.0, making the bond polar covalent.
How do you indicate the bond polarity and dipole moment in a polar bond?
-To indicate bond polarity and dipole moment, draw an arrow pointing towards the more electronegative element.
What type of bond is formed between sodium and chlorine?
-The bond formed between sodium and chlorine is an ionic bond.
What happens to the electrons in an ionic bond?
-In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
What type of bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen in a molecule like methane?
-The bond formed between carbon and hydrogen in methane is a nonpolar covalent bond.
What makes the O-H bond in water special compared to other polar covalent bonds?
-The O-H bond in water is special because it involves hydrogen bonding, a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that significantly increases the boiling point of water.
How can you identify an ionic bond based on the types of elements involved?
-You can identify an ionic bond if it involves a metal and a nonmetal, as this typically leads to the transfer of electrons and the formation of ions.
Outlines
🔬 Understanding Different Types of Bonds
This lesson introduces the concepts of ionic bonds, covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds, and nonpolar covalent bonds. A bond between two hydrogen atoms is described as nonpolar covalent because the electrons are shared equally due to identical electronegativity. The carbon-oxygen bond is identified as polar covalent due to a significant difference in electronegativity values, with oxygen being more electronegative, resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and a partial positive charge on carbon. The sodium-chlorine bond is categorized as ionic, involving a metal and a nonmetal, leading to electron transfer and the formation of ions held together by electrostatic forces.
🔍 Exploring Bond Characteristics with Examples
This section continues with more examples to illustrate the differences between ionic and covalent bonds. It explains the electron transfer in the sodium-chlorine bond, forming positive and negative ions. The hydrogen-hydrogen bond in H2 is explained as nonpolar covalent, with shared electrons. The carbon-hydrogen bond is also nonpolar covalent due to a small difference in electronegativity. Additionally, the text describes carbon-carbon bonds as nonpolar covalent because they involve atoms of the same element. The section ends with a discussion on hydrogen bonds, particularly in water, explaining their significant impact on boiling points.
⚛️ Identifying Ionic Bonds in Various Elements
This final section focuses on identifying ionic bonds in compounds involving metals and nonmetals. The lithium-fluorine bond is highlighted as ionic, with lithium being a positively charged cation and fluorine a negatively charged anion. The significant electronegativity difference between metals and nonmetals typically results in ionic interactions. The section emphasizes that recognizing the types of elements involved can help predict the nature of the bond, reinforcing the key characteristics of ionic and covalent bonds discussed throughout the lesson.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Ionic Bonds
💡Covalent Bonds
💡Polar Covalent Bonds
💡Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
💡Electronegativity
💡Dipole Moment
💡Hydrogen Bonding
💡Cations
💡Anions
💡Electron Transfer
💡Methane
Highlights
Introduction to ionic, covalent, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds.
Bond between two hydrogen atoms is always a nonpolar covalent bond due to equal sharing of electrons.
Electronegativity difference determines if a covalent bond is polar or nonpolar.
Carbon-oxygen bond is a polar covalent bond due to the significant electronegativity difference.
In a polar covalent bond, electrons are shared unequally, resulting in partial charges.
Metal and nonmetal bonds are typically ionic, such as sodium chloride.
Difference between ionic and covalent bonds: Ionic involves transfer of electrons, covalent involves sharing.
Carbon-hydrogen bond is nonpolar due to a small electronegativity difference.
Molecules with only carbon and hydrogen are nonpolar, such as methane and hexane.
Bonds between identical atoms are always nonpolar.
OH bond is highly polar and exhibits hydrogen bonding, leading to high boiling points.
Drawing arrows towards more electronegative elements indicates bond polarity and dipole moments.
Lithium-fluorine bond is ionic due to the large electronegativity difference and metal-nonmetal combination.
Positively charged ions are called cations, and negatively charged ions are called anions.
Hydrogen bonding significantly affects the physical properties of molecules.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Atomic Hook-Ups - Types of Chemical Bonds: Crash Course Chemistry #22

Types of Chemical Bonds - AP Chem Unit 2, Topic 1

ATI TEAS 7 I Chemical Bonds I Chemistry I

Introduction to Ionic Bonding and Covalent Bonding

Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds | Chemical bonds | Chemistry | Khan Academy
AP Chemistry Unit 2 Review
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: