What are Real and Virtual Images? | Reflection of Light | Infinity Learn
TLDRThis video script offers an engaging introduction to the concepts of virtual and real images, focusing on the role of light reflection in their formation. It explains that virtual images, like those seen in a plane mirror, appear to be behind the mirror but are not physically present. In contrast, real images, formed by concave mirrors, are inverted and converge at a point on the same side as the object. The script piques interest in the underlying principles of light reflection and promises further exploration in future videos.
Takeaways
- 🪞 The video aims to explain the concepts of virtual and real images using the example of mirrors.
- 🏠 A plane mirror is characterized by its flat reflecting surface, commonly found in bathrooms.
- 🔍 Spherical mirrors, specifically concave mirrors, are curved inwards and often used for shaving due to their reflective properties.
- 🤔 The reason for using a concave mirror for shaving will be explained in future videos.
- 💡 The visibility of our image in a mirror is due to the reflection of light rays from our body to the mirror and then to our eyes.
- 📐 The laws of reflection dictate how light rays bounce off a mirror's surface.
- 👉 The image seen in a plane mirror is virtual, appearing to be formed behind the mirror but not actually existing there.
- 🔑 Virtual images are formed when light rays diverge after reflection, creating the illusion of an image behind the mirror.
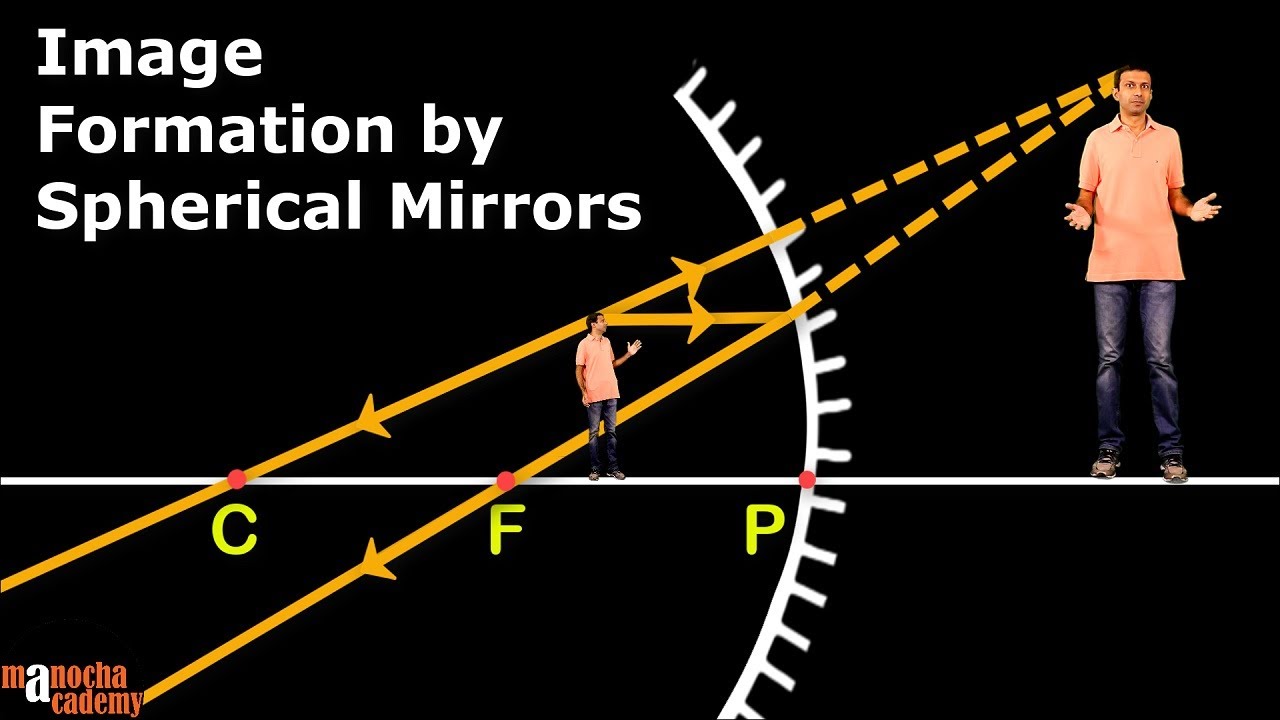
- 🌐 In contrast, real images are formed when light rays converge after reflection, creating an actual point where the image is located.
- 🔽 Real images formed by concave mirrors are always inverted and are located on the same side as the object.
- 📍 The formation of real or virtual images by concave mirrors depends on the object's distance from the mirror, a topic for future exploration.
Q & A
What is a plane mirror?
-A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat, smooth reflecting surface.
Where might you typically find a plane mirror?
-You might find a plane mirror on the stand of your bathroom or hung up on a wall.
What is a spherical concave mirror?
-A spherical concave mirror is a mirror that curves inward, often used for shaving.
Why do we use a concave mirror for shaving instead of a plane mirror?
-The video hints that this will be explained in future videos, but typically, concave mirrors magnify the image, making it easier to see details.
How is an image formed in a plane mirror?
-An image is formed in a plane mirror due to the reflection of light rays. Light rays bounce off an object, hit the mirror, reflect back, and reach our eyes, making us see the image.
What is a virtual image?
-A virtual image is an image that appears to be formed behind the mirror, but in reality, no light rays reach that point.
What is the main characteristic of images formed by plane mirrors?
-Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual and not real.
How are real images formed by concave mirrors?
-Real images are formed by concave mirrors when light rays converge after reflecting from the mirror's surface. These images are always inverted and formed on the same side of the mirror as the object.
What is the difference between virtual and real images?
-A virtual image appears to be formed behind the mirror without actual light rays reaching that point, while a real image is formed on the same side of the mirror as the object with light rays actually reaching that point.
Can concave mirrors form both real and virtual images?
-Yes, concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images, depending on the distance of the object from the mirror.
Outlines
🪞 Introduction to Virtual and Real Images
The video script introduces the concepts of virtual and real images, starting with a basic explanation of a plane mirror and its flat reflecting surface. It contrasts this with a spherical concave mirror, which is curved inward and commonly used for shaving. The script poses a question about why a concave mirror is preferred for shaving, promising an answer in a future video. The main focus is on the plane mirror and how it forms a virtual image through the reflection of light rays. The script simplifies the concept by using an arrow to represent a boy and explains how the virtual image appears to be formed behind the mirror, even though no light actually reaches that point. This is the first characteristic of images formed by plane mirrors: they are virtual and not real.
🔍 Understanding Real Images with Concave Mirrors
The second paragraph delves into the formation of real images using spherical concave mirrors. It explains that unlike plane mirrors, which cause light rays to diverge, concave mirrors cause the rays to intersect or converge at a point, forming a real image. The script emphasizes that real images are inverted and are always formed on the same side of the mirror as the object. It also clarifies that the perception of light rays diverging from a point in front of the mirror is real, as the light rays physically reach that point. The paragraph concludes by noting that the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror—whether real or virtual—depends on the object's distance from the mirror, with further details to be explored in future videos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Virtual Image
💡Real Image
💡Plane Mirror
💡Spherical Concave Mirror
💡Reflection
💡Light Rays
💡Diverging Rays
💡Converging Rays
💡Inverted Image
💡Law of Reflection
💡Perception
Highlights
Introduction to the concepts of virtual and real images in a long but interesting video.
Explanation of a plane mirror and its flat reflecting surface.
Introduction to spherical concave mirrors commonly used for shaving.
The reason for using concave mirrors for shaving will be explained in future videos.
Reflection of light and its role in forming images in a mirror.
Virtual images appear to be formed behind the mirror but are not actually present.
Virtual images are formed when light rays diverge after reflection from a plane mirror.
Characteristic of plane mirrors: they form virtual and not real images.
Introduction to spherical concave mirrors for forming real images.
Real images are formed when light rays converge after reflection from a concave mirror.
Real images formed by concave mirrors are always inverted.
Real images are formed on the same side of the mirror as the object.
Difference between virtual and real images: light rays' behavior after reflection.
Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images depending on the object's distance.
More characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors will be discussed in future videos.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

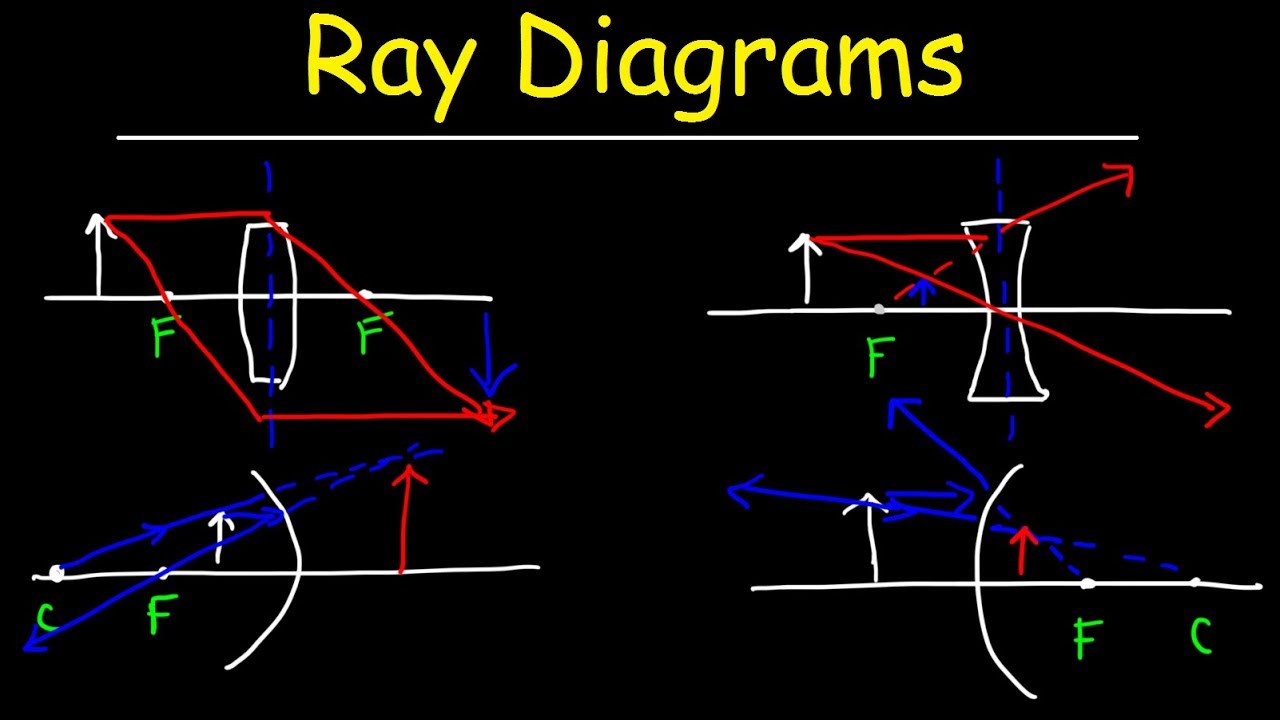
Ray Diagrams - Mirrors

The Difference Between Real & Virtual Images | Geometric Optics | Physics Demo

What are Real and Virtual Images? |Light Reflection in a Plane Mirror | Physics | Science | LetsTute

Concave Mirrors and Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram - Equations / Formulas & Practice Problems
Spherical Mirrors
Ray Diagrams
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: