Eye defects - Myopia | Don't Memorise
TLDRThis video script explores the human eye's structure and light propagation, focusing on the cornea and lens's roles in vision. It explains the concept of accommodation power and introduces myopia, or nearsightedness, where distant objects appear blurry due to the elongated eyeball causing light to converge in front of the retina. The script suggests using a concave lens to correct myopia by diverging light so it focuses on the retina. The video concludes with a teaser about hyperopia and presbyopia for the next lesson.
Takeaways
- 👁️ The human eye is structured to propagate light through its various layers, with the cornea playing a significant role in refraction.
- 🔍 The lens of the eye, being biconvex, primarily focuses on forming images on the retina by adjusting its shape to control light direction.
- 🌀 Accommodation power is the ability of the eye's lens to change its focal length, which is crucial for focusing on objects at varying distances.
- 🧐 Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a common eye defect where nearby objects are clear, but distant ones appear blurry.
- 🌌 In a myopic eye, light from distant objects converges in front of the retina due to the elongated eyeball, causing the blurriness.
- 🔍 The larger size of the eyeball in myopia increases the distance between the lens and the retina, leading to the formation of the image in front of the retina.
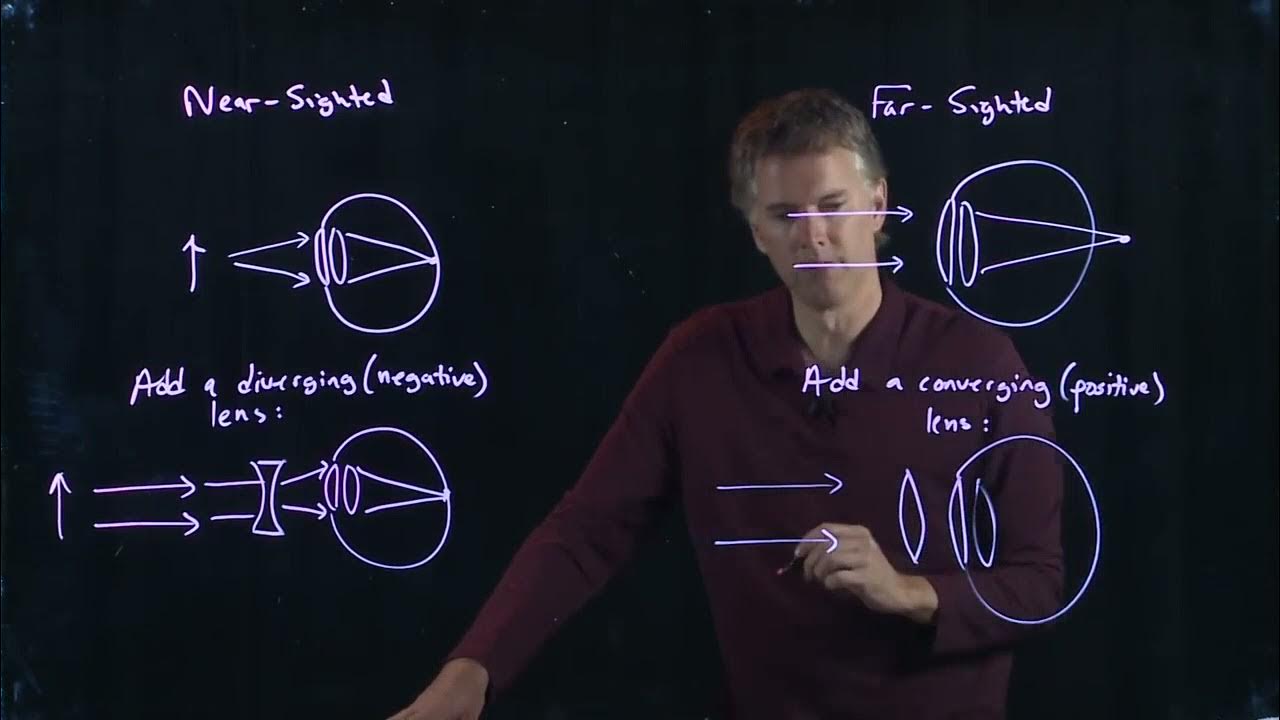
- 👓 Myopia can be corrected using a concave lens, which diverges light so that it refracts and converges on the retina, not in front of it.
- 🔄 The lens in a myopic eye still functions properly but forms the image at a different position than normal.
- 👀 The script briefly mentions hyperopia and presbyopia as other common eye defects to be discussed in the next lesson.
- 📚 The video script serves as an educational resource, explaining the function of the eye's lens and the nature of myopia.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the cornea in the human eye?
-The cornea is the outer front layer of the eye that primarily refracts the light that enters the eye.
What is the main role of the biconvex lens in the eye?
-The main role of the biconvex lens is to ensure that the image is formed on the retina only, by changing its shape to control the direction of light propagation.
What is Accommodation Power in the context of the eye?
-Accommodation Power refers to the ability of the lens to change its focal length, allowing it to focus light on the retina regardless of the distance of the object being viewed.
What is Myopia, and what is another term for it?
-Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a common eye defect where nearby objects are seen clearly, but distant objects appear blurry.
Why do distant objects appear blurry to someone with Myopia?
-In a myopic eye, light rays from distant objects converge in front of the retina instead of on it, causing the distant objects to appear blurry.
What causes the light to converge in front of the retina in a myopic eye?
-The larger size of the eyeball, specifically an elongated shape, results in a greater distance between the lens and the retina, causing the light to converge in front of the retina.
How does the lens function in a myopic eye?
-In a myopic eye, the lens functions as it should, but due to the elongated eyeball, the image is formed at a different position, in front of the retina.
How can Myopia be corrected?
-Myopia can be corrected by using a concave lens, which diverges the light so that the refracted rays converge on the retina instead of in front of it.
What is the purpose of placing a concave lens in front of a myopic eye?
-A concave lens is used to diverge the light rays so that when they pass through the eye's lens, they refract and converge on the retina, correcting the vision for distant objects.
What are the two main points to remember about Myopia from the script?
-The two main points are that people with myopia can see nearby objects clearly but not distant ones, and that a concave lens helps correct this by ensuring light rays converge on the retina.
What other eye defects are mentioned in the script for further discussion?
-The script mentions Hyperopia and Presbyopia as other eye defects that will be discussed in the next lesson.
Outlines
👀 Understanding the Human Eye and Myopia
This paragraph delves into the structure of the human eye, focusing on the cornea's role in refraction and the lens's function in image formation on the retina. It introduces the concept of accommodation power, which is the eye's ability to change its focal length. The main topic of the paragraph is myopia, or nearsightedness, where distant objects appear blurry due to the light converging in front of the retina. This condition is often caused by an elongated eyeball, which increases the distance between the lens and the retina. The paragraph concludes with a discussion on how a concave lens can correct myopia by diverging light so that it converges on the retina, thus improving distant vision.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Refraction
💡Biconvex Lens
💡Accommodation Power
💡Myopia
💡Nearby Objects
💡Distant Objects
💡Elucidated Eyeball
💡Lens Function
💡Concave Lens
💡Hyperopia
💡Presbyopia
Highlights
The human eye's structure and the propagation of light through it were studied in previous videos.
Most light entering the eye is refracted by the cornea, the outer front layer.
The biconvex lens in the eye refracts light and ensures image formation on the retina.
The lens can change its shape to control light direction, a process known as accommodation power.
This video discusses common eye defects, starting with Myopia or nearsightedness.
Myopia allows clear vision of nearby objects but not distant ones.
In a myopic eye, distant light rays converge in front of the retina, causing blurriness.
An elongated eyeball size is a common cause of myopia.
The lens in a myopic eye functions normally, but the image forms at a different position.
Myopia can be corrected using a concave lens that diverges light to focus on the retina.
A concave lens corrects myopia by refracting light so it converges on the retina.
A quick review of myopia highlights its effect on distant vision and the use of a concave lens for correction.
Hyperopia, another common eye defect, will be discussed in the next lesson.
Presbyopia, a condition related to age, is also mentioned as a topic for the next lesson.
The video provides an understanding of the eye's accommodation power and its role in vision defects.
The importance of the lens's shape in determining where the image is formed in the eye is emphasized.
The video concludes with an introduction to further lessons on hyperopia and presbyopia.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Difference Between Myopia and Hyperopia | Near and Farsightedness | Physics | Letstute

Optical Instruments - Your Eyeballs | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-01
Near Sighted vs Far Sighted | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-02

Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (1 of 5) Introduction

Structure of the Human eye | Human eye and the colorful world | Physics | Infinity Learn NEET

Human Eye - Passage of light through it | Don't Memorise
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: