Near Sighted vs Far Sighted | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-02
TLDRThis script explains the concepts of nearsightedness and farsightedness, using the analogy of lens power and the eye's ability to focus light. It describes how nearsighted individuals see nearby objects clearly due to diverging light rays, which are corrected with a negative, or diverging, lens. Conversely, farsighted individuals need a positive, or converging, lens to focus distant light rays properly on the retina. The script also touches on identifying lens types by their effect on the perceived size of objects and astigmatism, which is indicated by lens distortion when rotated.
Takeaways
- 👀 Nearsightedness allows clear vision of nearby objects due to the eyes' lens focusing diverging light rays onto the retina.
- 🔍 For distant vision, nearsighted individuals require a diverging (negative) lens to correct the focus and make parallel light rays converge on the retina.
- 🌟 Farsightedness affects the ability to see distant objects clearly because the light rays do not focus correctly on the retina.
- 🛠️ Farsighted individuals need a converging (positive) lens to adjust the focus, bringing the light rays to a point on the retina for clear distant vision.
- 👓 Reading glasses, often used with age, have a positive value and are converging lenses, indicating the user is farsighted and needs assistance for close-up vision.
- 🔬 To determine if a lens is converging or diverging, observe the effect on the appearance of objects or the size of the eyes when looking through the lens.
- 🔍 A positive lens will make objects appear larger and the eyes look bigger when viewed through it, while a negative lens will have the opposite effect.
- 📏 Astigmatism is indicated by a lens that is not perfectly spherical but has a slight cylindrical shape, causing distortion that changes with the lens's rotation.
- 🔥 In a survival situation, a positive (farsighted) lens would be more useful for focusing sunlight to a point to start a fire, as a negative (nearsighted) lens would diverge the light.
- 👁️ The presence of astigmatism in glasses can be identified by the varying degrees of image distortion in each lens when rotated.
- 📐 Understanding the properties of lenses and the conditions they correct is crucial for proper vision care and can have practical implications in everyday life.
Q & A
What is the condition of being nearsighted?
-Nearsightedness, or myopia, is a condition where a person can see objects that are near clearly, but objects at a distance appear blurry. It occurs when the eyeball is longer than normal or the cornea has too much curvature, causing light rays from distant objects to focus in front of the retina instead of on it.
How does the eye focus light rays in a nearsighted person?
-In a nearsighted person, the light rays from nearby objects are diverging, and the lens of the eye can focus them onto the retina without issue. However, for distant objects, the light rays are almost parallel, and the eye cannot focus them correctly due to the eyeball's size or the cornea's focusing power being different from normal.
What type of lens is used to correct nearsightedness?
-To correct nearsightedness, a diverging or negative lens is used. This lens causes the parallel rays from distant objects to diverge, which helps them to focus on the retina, thus correcting the vision for distance.
What is the difference between a converging and a diverging lens?
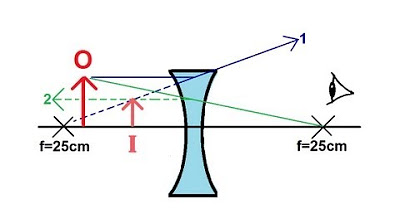
-A converging lens, also known as a positive lens, bends light rays inward to focus them on the retina, which is used to correct farsightedness. A diverging lens, or a negative lens, spreads light rays outward, which is used to correct nearsightedness.
How can you tell if a lens is converging or diverging by looking through it?
-If you look through a lens and the outside world appears to get larger, it is a converging lens. If the world appears smaller, it is a diverging lens. This is because a positive lens magnifies while a negative lens minifies the view.
What is astigmatism and how can it be identified in glasses?
-Astigmatism is a condition where the eye does not focus light evenly on the retina, often due to an irregularly shaped cornea. In glasses, it can be identified by looking through the lens and rotating it; if the image changes from being squished one way to another, it indicates astigmatism.
Why would a farsighted person need a positive lens?
-A farsighted person needs a positive lens because it helps to converge the parallel rays coming from distant objects so that they focus on the retina. Without the lens, the rays would focus behind the retina, making close objects appear blurry.
How can you determine if someone is nearsighted or farsighted by looking at their glasses?
-You can determine if someone is nearsighted or farsighted by observing the type of lens in their glasses. If the glasses have a negative, or diverging, lens, the person is likely nearsighted. If they have a positive, or converging, lens, they are likely farsighted.
What is the practical implication of having a positive lens if you're trying to start a fire with sunlight?
-A positive lens can focus sunlight to a single point, which can be used to start a fire. If you're farsighted and have a positive lens, it can help concentrate the sunlight's energy to ignite a fire, which wouldn't be possible with a negative lens used by a nearsighted person.
Why does the speaker mention that nearsightedness wouldn't help in starting a fire with sunlight?
-The speaker mentions this because a nearsighted person has a diverging lens, which spreads out the light rays and cannot focus them to a single point. This is necessary for starting a fire, as the sunlight needs to be concentrated, which a positive lens in a farsighted person's glasses can achieve.
How does the speaker demonstrate the effect of a positive lens on the camera?
-The speaker demonstrates the effect of a positive lens by looking through his reading glasses at the camera. As he moves the glasses away from his eyes, his eyeballs appear larger to the camera, indicating the magnifying effect of the positive lens.
Outlines
👓 Understanding Nearsightedness and Corrective Lenses
This paragraph explains the concept of nearsightedness, where an individual can see objects clearly only when they are close. It describes how the eye's lens focuses diverging light rays from nearby objects onto the retina. The speaker also discusses the use of diverging or negative lenses to correct nearsightedness by causing parallel rays from distant objects to diverge, thus focusing them correctly on the retina. The paragraph concludes with a practical demonstration of how to identify the type of lens—converging or diverging—by observing the effect on the appearance of the eyes when looking through them.
🔍 Farsightedness, Astigmatism, and Practical Applications of Lenses
The second paragraph delves into farsightedness, where the eye can focus on distant objects but struggles with nearby ones. It explains that a converging or positive lens is used to correct this by bending parallel rays to focus on the retina. The paragraph also touches on astigmatism, a condition where the eye's lens is not perfectly spherical, causing distortion when looking through glasses. The speaker demonstrates how to identify astigmatism by rotating glasses and observing image distortion. Lastly, the paragraph discusses the practical application of lenses in focusing sunlight to a point, emphasizing that a positive lens is necessary for this purpose, as a negative lens would not be effective.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Nearsightedness
💡Lens Power
💡Diverging Lens
💡Farsightedness
💡Converging Lens
💡Astigmatism
💡Reading Glasses
💡Positive Lens
💡Negative Lens
💡Retinal Focus
💡Spherical Lens
Highlights
Nearsightedness allows clear vision of nearby objects due to the diverging nature of light rays.
The lens power in nearsighted eyes can focus diverging rays onto the retina without issue.
Nearsighted individuals struggle to see distant objects clearly due to the inability to focus parallel rays properly.
A diverging lens, or negative lens, is used to correct nearsightedness by making parallel rays diverge more.
Farsightedness is characterized by difficulty focusing parallel rays from distant objects onto the retina.
A converging lens, or positive lens, is required to correct farsightedness by bringing the focus closer to the retina.
The presence of reading glasses with a positive value indicates farsightedness and the need for assistance in reading close objects.
A positive lens makes the world appear larger when looked through, indicating a converging lens.
A negative lens makes the world appear smaller and can be identified by the apparent reduction in size of the eyes through the lens.
Astigmatism is suggested by a lens that distorts the image when rotated, indicating a cylindrical shape rather than spherical.
The degree of astigmatism can be observed by the varying image distortion in each lens of a pair of glasses.
A positive lens can focus light to a point, which is useful in practical applications like starting a fire with sunlight.
A negative lens, characteristic of nearsightedness, would not be helpful in focusing sunlight to a point.
Understanding the type of lens by its effect on the appearance of the eyes or the world can help in practical scenarios.
The transcript provides a clear explanation of how different types of lenses correct vision problems in nearsighted and farsighted individuals.
The practical application of lens types in everyday life, such as reading and starting fires, is discussed.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (1 of 5) Introduction

Eye defects - Myopia | Don't Memorise

Near Point and Far Point | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-06

Physics - Optics: Vision Correction (4 of 5) Farsighted

Optical Instruments - Your Eyeballs | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M28-01
Physics - Optics: Lenses (2 of 2) Diverging Lens
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: