Characteristics of Light | Source, Speed, Intensity, Color | Science 7 Quarter 3 Module 4 Week 5
TLDRThis educational video delves into the characteristics of light, explaining its nature as an electromagnetic wave that doesn't require a medium to propagate. It highlights light's speed, its journey from the sun to Earth, and its dual particle-wave behavior. The video also explores the electromagnetic spectrum, visible light's role in enabling sight, and the concepts of light intensity and color, including the visible spectrum's dispersion into colors like red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. It concludes with the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and color, and a teaser for the next lesson on heat.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Light is an electromagnetic wave that does not need a medium to propagate and travels in a straight line in a vacuum.
- 🔢 The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
- ☀️ The Sun is our main natural source of light and is considered a luminous body, capable of producing its own light.
- 💡 Artificial sources of light include lamps, bulbs, and candles, which are examples of non-luminous bodies that emit light.
- 🤓 Historical scientists like Newton, Huygens, de Broglie, and Maxwell contributed to our understanding of light's dual nature as both a particle and a wave.
- 🌈 The electromagnetic spectrum arranges waves by frequency, with radio waves having the lowest and gamma rays the highest.
- 👀 The visible light spectrum, also known as white light, is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye.
- 📏 Visible light has wavelengths ranging from 400 nanometers to 750 nanometers, with colors from red to violet.
- 🌈 Dispersion is the phenomenon where a prism separates white light into its component colors—red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
- 💡 Light intensity, or brightness, is the power of light illuminating a surface and is measured in terms of luminous intensity (candela).
- 🎨 The color of light depends on its frequency or wavelength, with red having the longest wavelength and lowest frequency, and violet the shortest wavelength and highest frequency.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the characteristics of light.
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
-The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
How long does it take for light to travel from the sun to the Earth?
-It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light to travel from the sun to the Earth.
What is the smallest unit of visible light?
-The smallest unit of visible light is called a photon.
What is a luminous body according to the video?
-A luminous body is an object capable of producing its own light, such as the sun.
What is the dual nature of light as described in the video?
-Light has a dual nature; it behaves as tiny particles called photons and also as a wave.
What is the visible light spectrum?
-The visible light spectrum is the only frequency of electromagnetic waves that is visible to the human eye, also known as white light.
What is the phenomenon where a prism separates white light into component colors called?
-The phenomenon is called dispersion.
What are the properties of light that are related to its special characteristics?
-The properties of light that are related to its special characteristics are wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
What is the science of measuring the intensity or brightness of light called?
-The science of measuring the intensity or brightness of light is called photometry.
How does the brightness of light depend on the distance from the source?
-The brightness of light depends on how far you are from the source; the closer you are, the brighter the light appears, and the farther you are, the dimmer it appears.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in the context of visible light?
-As the wavelength of visible light increases, the frequency decreases, and vice versa. Red has the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency, while violet has the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency.
What does the color white represent in terms of visible light wavelengths?
-The color white represents the combination of all the wavelengths of visible light.
What does the color black represent in terms of visible light wavelengths?
-Black represents the absence of visible light wavelengths.
Outlines
🌞 Introduction to Light Characteristics
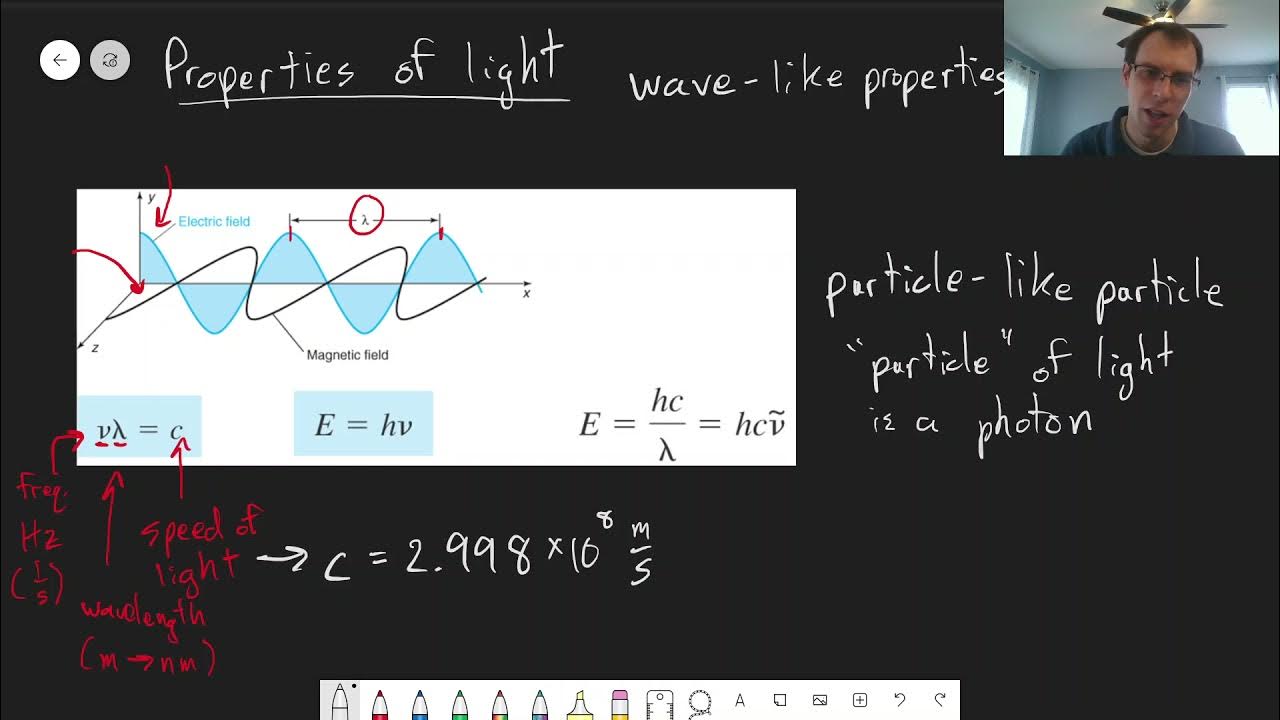
This paragraph introduces the concept of light as an electromagnetic wave and its fundamental properties. It explains that light doesn't require a medium to propagate and travels at a constant speed in a vacuum, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second. The video script highlights the dual nature of light, behaving both as particles (photons) and as a wave. The characteristics of light, such as intensity and color, are mentioned, setting the stage for a deeper exploration in the subsequent paragraphs. The importance of visible light in our ability to see is emphasized, and the role of the sun as a natural source of light is discussed. Historical perspectives from scientists like Newton, Huygens, de Broglie, and Maxwell on the nature of light are briefly touched upon, leading to the modern understanding of light's electromagnetic properties.
🌈 Exploring Light Intensity and Color
The second paragraph delves into the characteristics of light intensity and color. It defines light intensity as the power of light illuminating a surface, measured in terms of the number of photons passing a certain area, and related to the amplitude of the light wave. The script discusses how brightness, a qualitative measure of light intensity, is perceived differently by individuals and can be quantified using luminous intensity measured in candelas. The concept of dispersion is introduced, explaining how a prism separates white light into its component colors, which are arranged according to their frequency in the visible spectrum. The color of light is determined by its frequency or wavelength, with visible light ranging from 400 to 750 nanometers. The relationship between wavelength and frequency is clarified, with red having the longest wavelength and lowest frequency, and violet having the shortest wavelength and highest frequency. The paragraph concludes by differentiating between white and black in terms of the presence and absence of light wavelengths.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Visible Light
💡Electromagnetic Wave
💡Speed of Light
💡Photons
💡Luminous Body
💡Artificial Sources of Light
💡Dual Nature of Light
💡Electromagnetic Spectrum
💡Dispersion
💡Wavelength and Frequency
💡Intensity of Light
💡Color
Highlights
Introduction to the study of light characteristics using concepts from wave studies.
Visible light is essential for seeing objects around us.
Light is an electromagnetic wave that does not require a medium for propagation.
Speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
It takes about 8 minutes for light to travel from the sun to the Earth.
Light is a form of energy composed of photons, the smallest unit of visible light.
The sun is a natural source of light and considered a luminous body.
Artificial sources of light include lamps, bulbs, and candles.
Historical scientific debates on the nature of light, including Newton's particle theory and Huygens' wave theory.
De Broglie and Maxwell's contributions to the understanding of light's dual nature as both a particle and a wave.
Light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is arranged by increasing frequency.
Visible light spectrum is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye.
Dispersion is the phenomenon where a prism separates white light into its component colors.
The visible spectrum includes colors red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Light has properties such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude, affecting its characteristics like intensity and color.
Light intensity is the power of light, measured by the amount illuminating a surface, and is related to photometry.
Brightness is the visual perception of light intensity, measured in candela.
The brightness of light is dependent on the distance from the source and the amplitude of the wave.
Color of light is determined by its frequency or wavelength, with visible light ranging from 400 to 750 nanometers.
The relationship between frequency and wavelength: as wavelength increases, frequency decreases.
Red has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency, while violet has the shortest wavelength and highest frequency.
White represents the combination of all visible wavelengths, and black is the absence of light.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Introduction To Light | Properties of Light | Introduction to Light | properties of light | letstute
Chapter 18: Properties of Light | CHM 214 | 150

Visible Light Spectrum Explained - Wavelength Range / Color Chart Diagram - Chemistry

What Is Light?

Why do we see colour? Video

What Is Color? | Physics in Motion
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: