Introduction To Light | Properties of Light | Introduction to Light | properties of light | letstute
TLDRThis enlightening session delves into the multifaceted nature of light, a phenomenon integral to life. It explores light's role in daily life, from the sun's life-giving rays to the invisible spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. The script explains the visible light's place within the broader electromagnetic spectrum, highlighting the differences among its types based on wavelength, frequency, and energy. It also touches on various applications of light, from the warmth of infrared to the penetrating power of gamma rays, all traveling at the universe's fastest speed. The session concludes with a teaser about light's interactions with matter, inviting viewers to engage further.
Takeaways
- 🌞 The sun is considered the primary source of light and life on Earth, crucial for processes like photosynthesis and the water cycle.
- 🌈 Light comes in many forms, with the visible spectrum being just a small part of the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
- 👀 Our eyes can detect visible light thanks to specialized cells called rods and cones, which are essential for color vision.
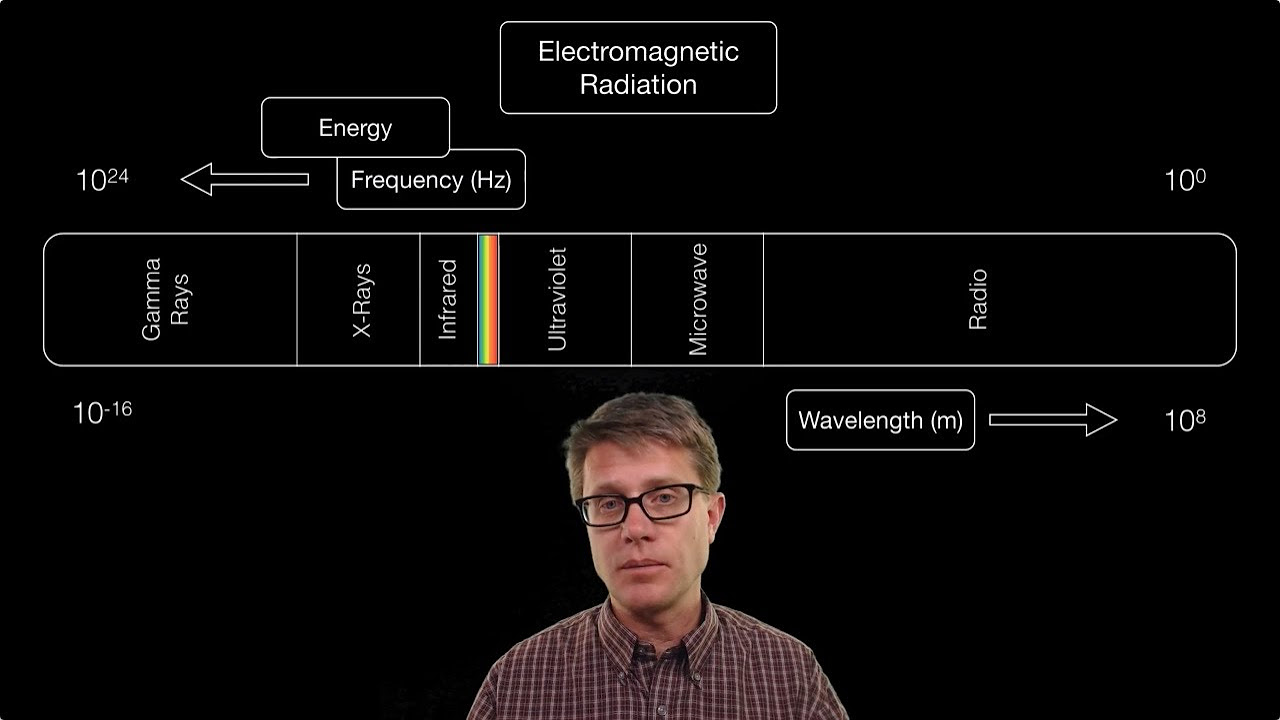
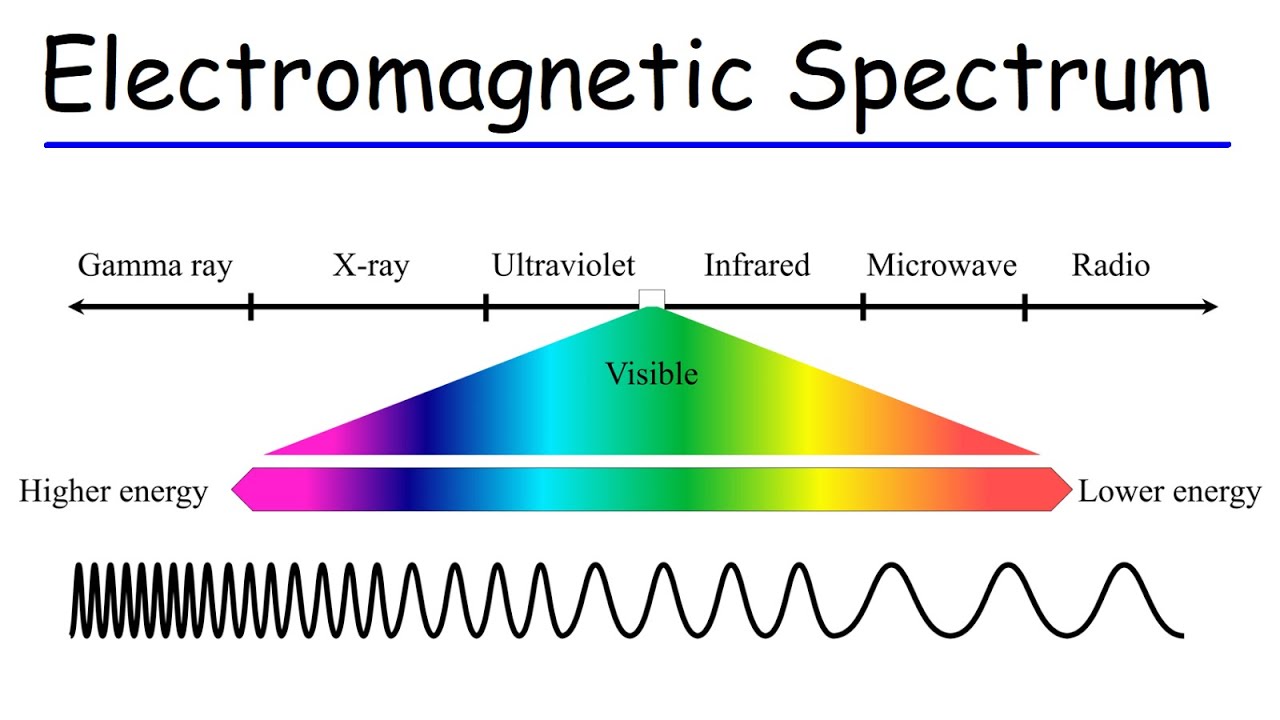
- 🌌 Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a broad term that includes all types of light, from radio waves to gamma rays, each with unique properties.
- 🔬 The characteristics of EMR are defined by wavelength, frequency, and energy, with shorter wavelengths corresponding to higher frequencies and energies.
- 📡 Radio waves, with the longest wavelengths, are used for broadcasting and telecommunications due to their ability to travel long distances.
- 🍲 Microwaves are used in appliances for heating and cooking food, as well as in wireless communication technologies.
- 🔥 Infrared radiation is associated with heat and is used in various heating applications and for its therapeutic properties.
- 🌈 Visible light is the portion of the EM spectrum that humans can see, adding color and visibility to our world.
- 🦠 Ultraviolet (UV) radiation has applications in sterilization, dentistry, and currency verification, and some organisms use it for vision.
- ⚕️ Higher energy radiations like X-rays and gamma rays are used in medical imaging and treatment, despite their potential dangers.
- 🌌 All types of EMR travel at the same speed, the speed of light, which is the fastest known speed in the universe.
Q & A
What is the main subject discussed in the video script?
-The main subject discussed in the video script is light, specifically electromagnetic radiation and its various forms within the electromagnetic spectrum.
Why is light important in our daily life?
-Light is important in our daily life because it separates day from night, brings hope in dark times, and is responsible for sight and the enjoyment of colors in the world around us.
What is the sun's role in relation to light and life on Earth?
-The sun is considered the giver of life on Earth, providing sunlight which is essential for food production in plants, maintaining the water cycle, and contributing to general health.
What is the scientific term for the type of radiation emitted by the sun?
-The scientific term for the type of radiation emitted by the sun is electromagnetic radiation or EMR.
What is the visible spectrum in the context of the electromagnetic spectrum?
-The visible spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that falls on the Earth and can be detected by human eyes, allowing us to perceive light and colors.
How are rods and cones in the eyes related to our perception of light?
-Rods and cones are specialized cells in the eyes that enable us to perceive light and distinguish between different colors.
What are the three factors that differentiate the types of electromagnetic radiation?
-The three factors that differentiate the types of electromagnetic radiation are wavelength, frequency, and energy.
What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy in electromagnetic radiation?
-As the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation shortens, the frequency increases and the energy also increases, and vice versa.
Why are radio waves suitable for broadcasting TV and radio signals?
-Radio waves are suitable for broadcasting TV and radio signals because they have long wavelengths, which allow them to cover greater distances through the atmosphere.
What are some applications of ultraviolet (UV) radiation in daily life?
-UV radiation is used for sterilization in the medical industry and water purification, hardening dental fillings, detecting counterfeit currency, and forming images for certain organisms.
How is the speed of light related to all types of electromagnetic radiation?
-Despite differences in wavelength, frequency, and energy, all types of electromagnetic radiation travel at the same speed, which is approximately 300,000,000 meters per second.
Outlines
🌞 The Essence of Light and Its Impact on Life
This paragraph introduces the concept of light, a phenomenon that is both ubiquitous and fundamental to life. It is described as the element that separates day from night and brings hope during dark times. The paragraph delves into the various forms of light, from natural sources like the sun and moon to artificial ones like lamps and torches. The sun's light is identified as electromagnetic radiation (EMR), which is part of a broader spectrum that includes visible light. The visible spectrum, detectable by human eyes, is highlighted as a small fraction of the entire EM spectrum. The paragraph also touches on the biological significance of sunlight for plant growth, the water cycle, and overall health. It sets the stage for a deeper exploration of light's properties and its relationship with life.
🌈 Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum
This paragraph provides an in-depth look at the electromagnetic spectrum, explaining the concept of wavelength, frequency, and energy as the distinguishing factors among different types of electromagnetic radiation. It uses the analogy of waves in the ocean to clarify these concepts, illustrating how wavelength and frequency are inversely related and how energy varies with them. The paragraph then takes us through the different members of the EM spectrum, from radio waves with the longest wavelengths and lowest energy to gamma rays with the shortest wavelengths and highest energy. Each type of radiation is associated with various applications, such as radio waves for broadcasting, microwaves for communication and heating, infrared for heat therapy and cooking, visible light for illumination, ultraviolet for sterilization and currency verification, X-rays for medical imaging, and gamma rays for cancer treatment and astronomical observations. The paragraph emphasizes the diversity and importance of these radiations in our daily lives.
🚀 The Unifying Speed of Electromagnetic Radiation
In this concluding paragraph, the script brings together the commonality of all electromagnetic radiations: their uniform speed of approximately 300,000,000 meters per second, the fastest known speed in the universe. It recaps the main points discussed in the session, including the nature of light as electromagnetic radiation, the seven types of radiation in the EM spectrum, and the factors that differentiate them. The paragraph also invites viewers to reflect on the different behaviors of light with matter, hinted at by the letter 'R', presumably referring to reflection and refraction. The session ends with an invitation for viewers to engage with the content through likes, subscriptions, and comments, and to stay tuned for more detailed explorations in future videos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
💡Electromagnetic Spectrum
💡Visible Light
💡Wavelength
💡Frequency
💡Energy
💡Rods and Cones
💡Infrared (IR)
💡Ultraviolet (UV)
💡X-rays
💡Gamma Rays
Highlights
Light is a phenomenon that separates day from night and brings hope in dark times.
Light comes in many colors but is collectively perceived as white.
Light's speed is unmatched, symbolizing its power and swiftness.
Light is responsible for the joy of sight and the ability to see.
The sun is considered the giver of life on earth and a symbol of light across cultures.
Sunlight plays a crucial role in food production, water cycle balance, and overall health.
Understanding light involves looking beyond the visible spectrum.
Natural light sources include the sun, moon, lightning, and bioluminescent creatures.
Artificial light sources range from candle flames to modern light fixtures.
The sun emits electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light.
The visible light is a small fraction of the vast electromagnetic spectrum.
The human eye's rods and cones allow us to perceive color within the visible spectrum.
Invisible types of electromagnetic radiation have unique applications and characteristics.
Wavelength, frequency, and energy are interdependent factors that differentiate types of electromagnetic radiation.
Radio waves, with the longest wavelengths, are used for broadcasting and telecommunication.
Microwaves are utilized in appliances and telecommunication technologies.
Infrared radiation is associated with heat and has various applications, including cooking and therapy.
Visible light enables us to see the colorful world and is essential for various lighting needs.
Ultraviolet radiation has applications in sterilization, dentistry, and currency verification.
X-rays are vital for medical imaging and security scanning.
Gamma rays, despite their dangers, are used in cancer treatment and astronomical observations.
All types of electromagnetic radiation travel at the same speed, the fastest in the universe.
Light interacts differently with matter, exhibiting behaviors that begin with the letter 'R'.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: