List of Mathematical Symbols in English | Math Symbols Vocabulary Words
TLDRThis script offers an insightful overview of fundamental mathematical symbols and their applications. It covers basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, alongside equality and inequality signs. The transcript delves into approximation, congruence, relational operators, and set theory, including union, intersection, and the empty set. It also touches on geometric concepts such as angles, perpendicularity, and parallelism, concluding with the golden ratio and percent representation, making it a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to understand the language of mathematics.
Takeaways
- 🔢 Mathematics Symbols: The script introduces various mathematical symbols used in equations and expressions.
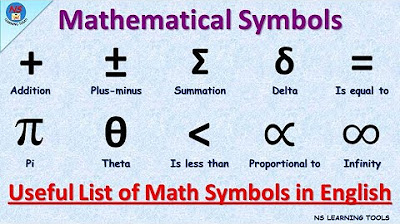
- ➕ Plus Sign: Represents addition, as shown in the example '5+2=7'.
- ➖ Minus Sign: Indicates subtraction, exemplified by '7-3=4'.
- ✖️ Times Sign: Symbolizes multiplication, demonstrated with '5x2=10'.
- ➗ Division Sign: Denotes division, illustrated in '10÷2=5'.
- ✓ Equal Sign: Used to show equality, as in '10-2=8'.
- ≠ Not Equal To: Signifies inequality between two expressions.
- ≈ Approximately Equal: Used for expressing a weak approximation.
- ≅ Congruent To: Indicates congruence in geometry.
- 🔺 Greater Than: Symbol '>' is used to show '8 > 4', one value is greater than another.
- 🔻 Less Than: Symbol '<' as in '5 < 8', represents one value being less than another.
- ± Plus or Minus: Indicates a range or possible variation around a value.
- ∞ Infinity: Represents an unbounded quantity, larger than any number.
- ≥ Greater Than or Equal To: Symbol '≥' shows 'X ≥ 3', indicating a value is either greater than or equal to another.
- ≤ Less Than or Equal To: Symbol '≤' signifies being less than or equal to a certain value.
- ≡ Equivalent: Used to denote that two expressions are the same.
- ⇒ Implies: Represents a logical implication where one statement follows from another.
- ∅ Empty Set: Symbolizes a set with no elements.
- △ Triangle: Often used in geometry and set theory.
- ∀ For All: Indicates a universal quantification in logic and mathematics.
- π Pi: Represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- ∠ Angle: Symbol used to denote the figure formed by two rays.
- ⊥ Right Angle: Indicates an angle of exactly 90 degrees.
- ° Degree: A unit of angle measurement where '1 turn = 360°'.
- { Braces: Used to group elements or expressions in mathematics and programming.
- [ Brackets: Similar to braces but with different uses in various contexts.
- ( Parentheses: Used to enclose expressions or arguments in mathematical operations.
- ∑ Summation: Represents the sum of a sequence of numbers.
- ∫ Integral: Symbolizes the process of integration in calculus.
- ∩ Intersection: Represents the common elements of two sets.
- ∪ Union: Indicates the combined elements of two or more sets.
- ∴ Therefore: Used to conclude a logical argument.
- ∵ Because: Introduces the reason for a statement in a logical argument.
- √ Square Root: Symbol for finding a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
- ⊥ Perpendicular: Indicates two lines that intersect at a right angle.
- ∥ Parallel: Describes two lines that never meet, always remaining the same distance apart.
- ϕ Golden Ratio: A mathematical constant approximately equal to 1.618, known for its aesthetic properties.
- & Ampersand: Used in various contexts to mean 'and' or to connect items.
Q & A
What is the mathematical symbol used to represent addition?
-The plus sign (+) is used to represent addition in mathematics, as in the example 5 + 2 = 7.
How is subtraction represented in mathematical symbols?
-Subtraction is represented by the minus sign (-), for example, 7 - 3 equals 4.
What is the symbol for multiplication?
-Multiplication is denoted by the times sign (×) or sometimes by the multiplication sign (*), as shown in 5 × 2 = 10.
What does the division sign look like and how is it used?
-The division sign is represented by the division slash (÷), used as in the example 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
What is the equal sign used to indicate?
-The equal sign (=) is used to indicate that two expressions are equal, or have the same value.
What is the symbol used to denote inequality?
-The 'is not equal to' symbol (≠) is used to denote that two expressions are not equal.
What symbol is used to express an approximate equality?
-The 'approximately equal to' symbol (≈) is used to express a weak approximation between two values.
What does the 'congruent to' symbol mean in geometry?
-The 'congruent to' symbol (≅) indicates that two geometric figures are identical in shape and size.
What are the symbols for 'greater than' and 'less than'?
-The 'greater than' symbol (>) and 'less than' symbol (<) are used to compare values, as in 8 > 4 and 5 < 8.
What does the 'plus or minus' symbol represent?
-The 'plus or minus' symbol (±) represents the variation or uncertainty in a value.
What is the infinity symbol and what does it represent?
-The infinity symbol (∞) represents the concept of unbounded quantity, something without end.
What are the symbols for 'greater than or equal to' and 'less than or equal to'?
-The 'greater than or equal to' symbol (≥) and 'less than or equal to' symbol (≤) are used to indicate that one value is either greater than or equal to, or less than or equal to another value, respectively.
What does the 'equivalent to' symbol mean?
-The 'equivalent to' symbol is not mentioned in the transcript, but it typically means that two expressions or values are equivalent or have the same meaning.
What is the 'implies' symbol used for in logic?
-The 'implies' symbol (⇒) is used in logic to show that one statement implies or leads to another.
What does the 'empty set' symbol represent?
-The 'empty set' symbol (∅) represents a set with no elements in it.
What are the symbols for 'for all', 'pi', and 'angle'?
-The 'for all' symbol (∀) is used to denote that a statement applies to all elements in a set. 'Pi' (π) is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. The angle symbol (∠) is used to denote an angle.
What does the 'right angle' symbol represent?
-The 'right angle' symbol (⊥) represents an angle of exactly 90 degrees.
How many degrees are in a full circle?
-A full circle is equal to 360 degrees, as mentioned in the script.
What are the symbols for braces, brackets, and parentheses?
-Braces ({ and }) are used to group elements together. Brackets ([ and ]) are often used in mathematics to denote sets or intervals. Parentheses (( and )) are used to enclose expressions or to indicate the order of operations.
What does the integral symbol represent?
-The integral symbol (∫) represents the concept of integration in calculus, which is a method of finding the area under a curve.
What are the symbols for 'intersection of two sets' and 'union of two sets'?
-The intersection symbol (∩) is used to denote the common elements of two sets, while the union symbol (∪) is used to denote all elements from two sets combined.
What do the symbols 'therefore' and 'because' represent in logic?
-The 'therefore' symbol (∴) and 'because' symbol (∵) are used in logic to indicate the conclusion and the reason, respectively.
What is the symbol for square root and how is it used?
-The square root symbol (√) is used to denote the mathematical operation that finds the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
What do the symbols for 'perpendicular' and 'parallel' represent?
-The 'perpendicular' symbol is not explicitly mentioned, but it typically is represented by a small 't'. The 'parallel' symbol (∥) indicates that two lines are equidistant from each other at all points and never intersect.
What is the golden ratio and how is it represented?
-The golden ratio (φ) is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.618, that appears in various aspects of art, architecture, and nature.
What is the symbol for 'ampersand' and how is it used?
-The ampersand symbol (&) is used in various contexts to represent 'and', often in place of the word for stylistic or typographical reasons.
What does the percent symbol represent?
-The percent symbol (%) represents a proportion of 1/100, used to express a ratio or a fraction of a whole.
Outlines
📚 Mathematics Symbols Overview
This paragraph introduces a variety of mathematical symbols and their meanings. It starts with basic arithmetic operators such as the plus (+), minus (-), times (x), and division (÷) signs, illustrating their use with simple equations like 5+2=7 and 10÷2=5. The equal sign (=) is explained as a representation of equality, with an example given for 10-2=8. The paragraph also covers inequality symbols like 'not equal to' and 'approximately equal to', used for expressing differences and weak approximations, respectively. The congruence symbol (≅), comparison operators (>, <), and the plus or minus (±) symbol are also mentioned. The section on inequalities includes 'greater than or equal to' (≥) and 'less than or equal to' (≤). The paragraph concludes with a brief mention of advanced mathematical concepts such as infinity, the empty set, and various geometric and logical symbols like 'for all', 'angle', 'right angle', 'degree', and the golden ratio. It also touches on mathematical notation for sets, including intersection, union, and integral signs, as well as logical connectors like 'therefore', 'because', and 'implies'. Additionally, symbols for square roots, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and mathematical grouping like braces, brackets, and parentheses are included.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡plus
💡minus
💡times sign
💡division sign
💡equal sign
💡greater than
💡less than
💡infinity
💡sum of
💡square root
Highlights
Mathematics Symbols are essential for expressing mathematical concepts and operations.
The plus symbol represents addition, as exemplified by the equation 5+2=7.
The minus symbol is used for subtraction, illustrated by the example 7-3=4.
The times sign or multiplication sign indicates multiplication, shown in 5x2=10.
The division sign is used to denote division, as in the equation 10÷2=5.
The equal sign signifies that two expressions are equal, demonstrated by 10-2=8.
The 'is not equal to' symbol denotes inequality between two expressions.
The 'is approximately equal to' symbol is used for expressing a weak approximation.
The 'is congruent to' symbol indicates that two shapes or figures are identical in shape and size.
The 'greater than' symbol compares two values, as in 8 > 4.
The 'less than' symbol is used to show that one value is smaller than another, such as 5 < 8.
The 'plus or minus' symbol represents an approximate value or range, like infinity.
The 'is greater than or equal to' symbol, X ≥ 3, shows that a value is either greater than or equal to another.
The 'is less than or equal to' symbol denotes that a value is less than or equal to another.
The 'equivalent' symbol is used to show that two expressions or values are the same.
The 'implies' symbol is used in logic to show that one statement implies another.
The 'empty set' symbol represents the set with no elements.
The 'triangle' symbol is used in geometry to denote a triangle shape.
The 'for all' symbol is used in logic and set theory to indicate a universal quantification.
The symbol 'pi' represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
The 'angle' symbol is used to denote an angle in geometric figures.
The 'right angle' symbol indicates a 90-degree angle.
The 'degree' symbol represents the unit of measurement for angles, where 1 turn equals 360°.
Braces, brackets, and parentheses are used to group expressions or elements in mathematics.
The 'sum of' symbol is used to denote the total of a series of numbers or elements.
The 'integral' symbol is used in calculus to represent the process of integration.
The 'intersection of two sets' symbol represents the common elements between two sets.
The 'union of two sets' symbol denotes the combination of all elements from two or more sets.
The 'therefore' and 'because or since' symbols are used to indicate a conclusion or reason in logical arguments.
The 'square root' symbol is used to find a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
The 'perpendicular' symbol indicates two lines that intersect at a right angle.
The 'parallel' symbol is used to denote two lines that never intersect.
The 'golden ratio' symbol represents a mathematical ratio found in art, architecture, and nature.
The 'ampersand' symbol is used to denote 'and' in mathematical expressions.
The 'percent' symbol is used to express a number as a fraction of 100.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
List of Mathematical Symbols in English | Math Symbols Vocabulary | 65 Mathematics Symbols
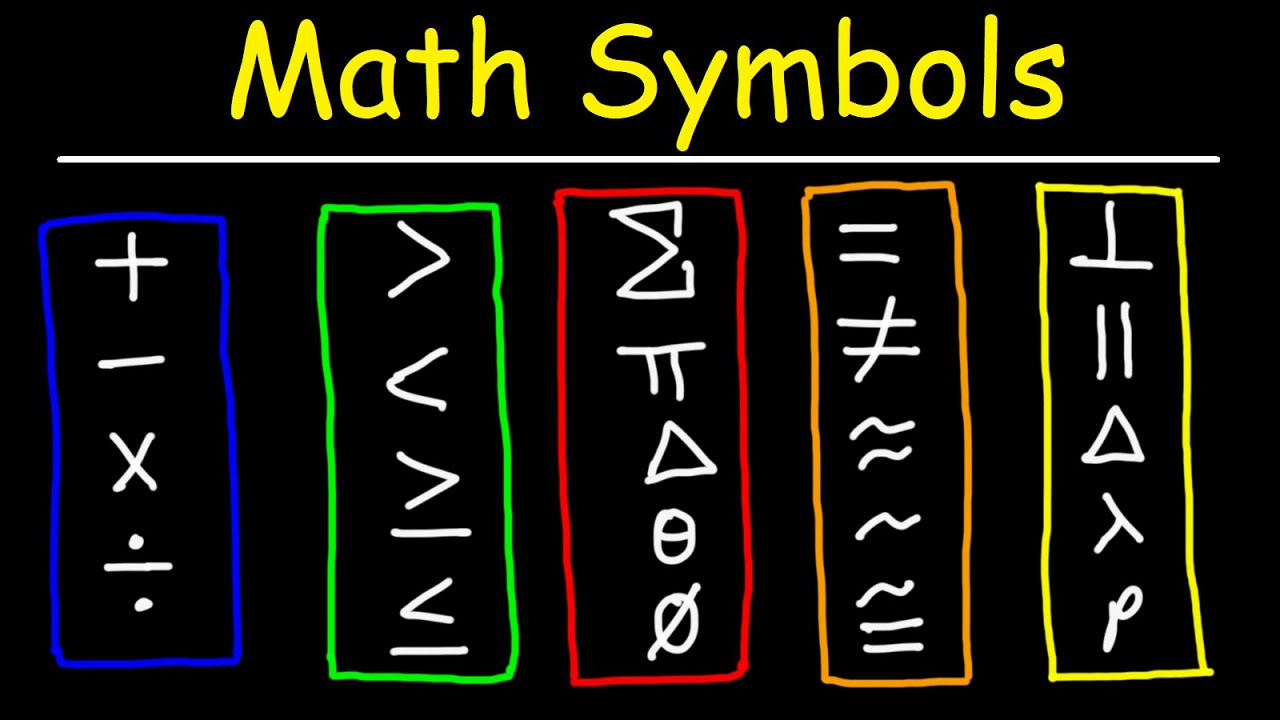
Top 50 Mathematical Symbols In English and Greek

Excel Math - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division & Exponents
Free English Class! Topic: Math! ➗➕➖ (Lesson Only)

Basic Math Review

Set Theory: Types of Sets, Unions and Intersections
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: