Classifying Matter With Practice Problems | Study Chemistry With Us
TLDRIn this educational video, Melissa guides viewers through the fundamental concepts of matter, focusing on its classification into pure substances and mixtures. She explains the differences between elements, compounds, and the types of mixtures—homogeneous and heterogeneous. With practical examples like coffee, orange juice, and air, Melissa clarifies these concepts, making chemistry accessible and engaging. She encourages self-practice and offers a free study plan for further learning.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is focused on studying matter and its classification, aiming to help viewers understand the basics for an upcoming exam.
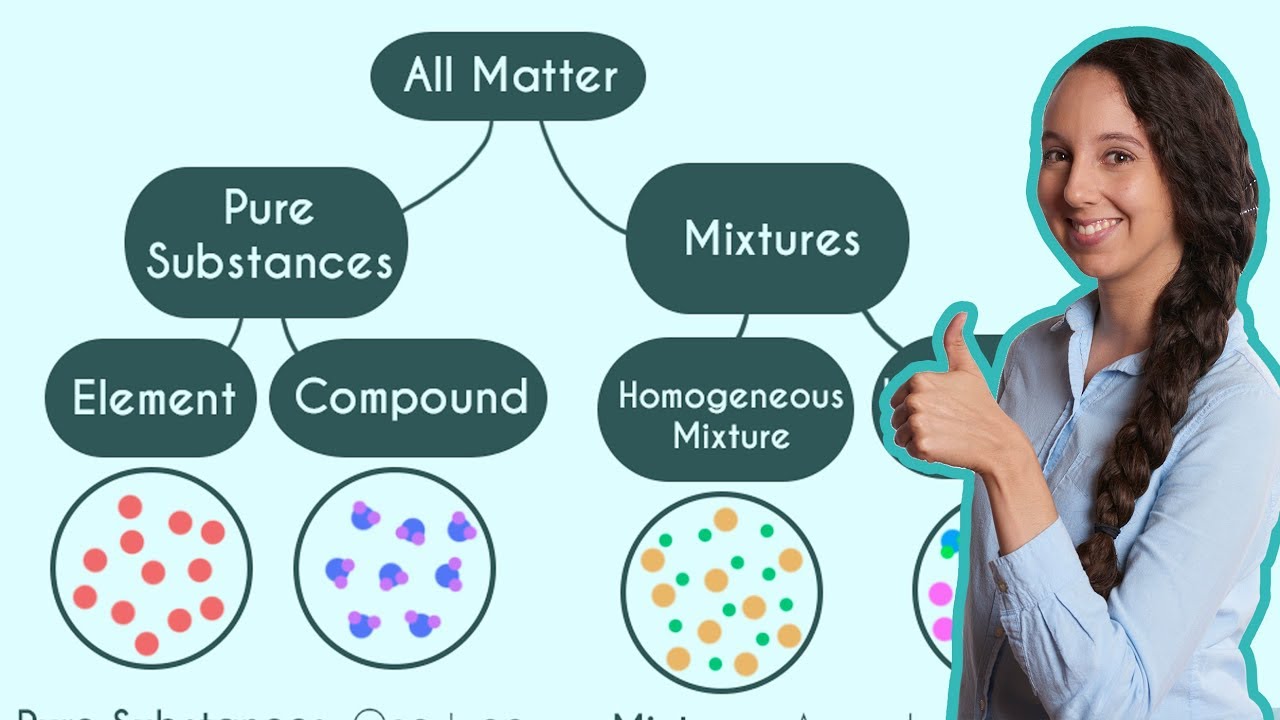
- 🧪 Matter is classified into two main types: pure substances and mixtures, with pure substances being further divided into elements and compounds.
- 🔬 An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, such as iron or silver, and cannot be broken down further.
- 🤝 A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together, like NaCl (sodium chloride) which is an ionic compound made of a metal and a nonmetal.
- 🔀 Ionic compounds consist of one metal and one nonmetal, with the metal being positively charged and the nonmetal negatively charged.
- 🌐 Covalent compounds, not detailed in the script, are formed by nonmetals sharing electrons, an example given is carbon dioxide (CO2).
- 💧 Mixtures are composed of two or more different types of atoms and molecules and can be classified as homogeneous or heterogeneous based on their uniformity.
- ☕ A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, like black coffee, where water and coffee grounds are uniformly mixed.
- 🍹 Heterogeneous mixtures have distinct layers or components that are not uniformly mixed, like wet sand or a drink with layers.
- 🤔 The script encourages viewers to practice identifying pure substances and mixtures with examples, emphasizing the importance of understanding the concepts for multiple-choice questions.
- 📝 The video ends with a reminder to visit the instructor's website for more help and a teaser for the next video.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is the study of matter, focusing on classifying matter into pure substances and mixtures, with further breakdown into elements, compounds, and different types of mixtures.
What is a pure substance according to the script?
-A pure substance, as described in the script, is composed of only one type of atom or molecule, and cannot be broken down further into simpler substances.
What are the two main categories of pure substances mentioned in the script?
-The two main categories of pure substances mentioned are elements and compounds. Elements are substances that consist of only one type of atom, while compounds consist of two or more different elements chemically combined.
What is an element in the context of chemistry?
-An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, such as iron or silver, and cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
What is a compound and how is it different from an element?
-A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically combined. Unlike elements, compounds cannot be separated into their constituent elements by physical means.
What are the two types of compounds mentioned in the script?
-The two types of compounds mentioned in the script are ionic compounds, which consist of a metal and a nonmetal, and covalent compounds, which consist of two or more nonmetals.
What is an ionic compound and how is it formed?
-An ionic compound is formed when a metal and a nonmetal chemically bond through the transfer of electrons, resulting in a compound with positively and negatively charged ions, such as NaCl (sodium chloride or salt).
What is a homogeneous mixture and how does it differ from a heterogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture is uniform throughout and has the same composition in any given part, such as black coffee. A heterogeneous mixture, on the other hand, has different layers or distinct parts, like wet sand with sand and water visibly separated.
How does the script differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures?
-The script differentiates between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures based on their uniformity. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition, while heterogeneous mixtures have distinct layers or components that are not uniformly mixed.
What is an example of a heterogeneous mixture given in the script?
-An example of a heterogeneous mixture given in the script is wet sand, where sand and water are mixed but remain visibly distinct.
What is the significance of classifying matter into pure substances and mixtures in the script?
-Classifying matter into pure substances and mixtures helps in understanding the fundamental nature of materials, their composition, and how they interact with each other, which is essential for various scientific and practical applications.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Matter and Classification
This paragraph introduces the concept of matter, emphasizing the importance of understanding its classification. It begins with the definition of pure substances, which are composed of a single type of atom or molecule, and then contrasts them with mixtures made of two or more different types. The paragraph delves into the specifics of pure substances, distinguishing between elements like iron or silver and compounds, which can be either ionic (composed of a metal and a nonmetal) or covalent (composed of nonmetals). Examples provided include NaCl (salt) for ionic compounds and CO2 (carbon dioxide) for covalent compounds. The paragraph also touches on the classification of mixtures into homogeneous (uniform mixtures like coffee) and heterogeneous (non-uniform mixtures with distinct layers). It encourages viewers to practice identifying pure substances and mixtures with examples and promises to review the answers together.
🧐 Classifying Everyday Substances as Pure or Mixtures
The second paragraph continues the discussion on matter by applying the concepts to everyday examples. It challenges the viewer to classify various substances as either pure substances or mixtures, and if mixtures, whether they are homogeneous or heterogeneous. The substances discussed include orange juice (considered a homogeneous mixture without pulp), tea with sugar (a homogeneous mixture), air (a homogeneous mixture of gases), and blood (a tricky example that appears homogeneous but is actually heterogeneous due to the presence of different cells and plasma). The paragraph also addresses the confusion around coffee and tea, explaining why adding cream to coffee makes it heterogeneous while adding sugar to tea does not. The goal is to help viewers understand the nuances of classifying substances based on their composition and appearance, with a final prompt to visit the instructor's website for further assistance.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Pure Substance
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Ionic Compound
💡Covalent Compound
💡Mixture
💡Homogeneous Mixture
💡Heterogeneous Mixture
💡Classification
💡Study Plan
Highlights
Introduction to the study session with Melissa, focusing on understanding matter and its classification.
Emphasis on downloading the free study plan for better study guidance.
Explanation of the difference between pure substances and mixtures in the context of matter.
Definition of a pure substance as being composed of only one type of atom or molecule.
Clarification on the concept of elements as pure substances that cannot be broken down further.
Introduction to compounds as pure substances made of two or more elements.
Differentiation between ionic and covalent compounds based on their constituent elements.
Description of ionic compounds as composed of a metal and a nonmetal with opposite charges.
Covalent compounds explained as consisting of two or more nonmetals.
Introduction to mixtures, differentiated from pure substances.
Homogeneous mixtures described as uniform and consistent throughout.
Heterogeneous mixtures characterized by distinct layers or components.
Practical examples given to illustrate the concepts of pure substances and mixtures.
Interactive exercise for the audience to classify different substances as pure or mixtures.
Discussion on the tricky nature of classifying substances like air and blood as mixtures.
Explanation of how descriptive factors can change the classification of a mixture.
The importance of understanding the composition of substances for correct classification.
Encouragement to visit Melissa's website for further study materials and support.
Conclusion of the study session with a recap of the key points covered.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9

Pure Substances and Mixtures | Science for Kids

What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?

Classifying Matter: Elements, Compounds, Mixtures (Chemistry)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: