What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?
TLDRThe video lesson titled 'Mixtures' delves into the fundamental concept of mixtures in chemistry, focusing on their composition and behavior. It explains that mixtures consist of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded or reacting to form a new substance. The lesson distinguishes between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, with the former being uniform throughout and the latter having a non-uniform composition. Key examples include rice pudding as a heterogeneous mixture, seawater as a homogeneous mixture, and magnesium as a pure substance. The importance of understanding mixtures is highlighted through their prevalence in chemical reactions, particularly in solutions where substances can interact and react. The lesson also touches on the phase of matter (solid, liquid, or gas) and the composition (pure substance or mixture), using examples like air and carbon monoxide to illustrate these concepts. It concludes by emphasizing the significance of solutions in chemistry, setting the stage for further exploration in subsequent lessons.
Takeaways
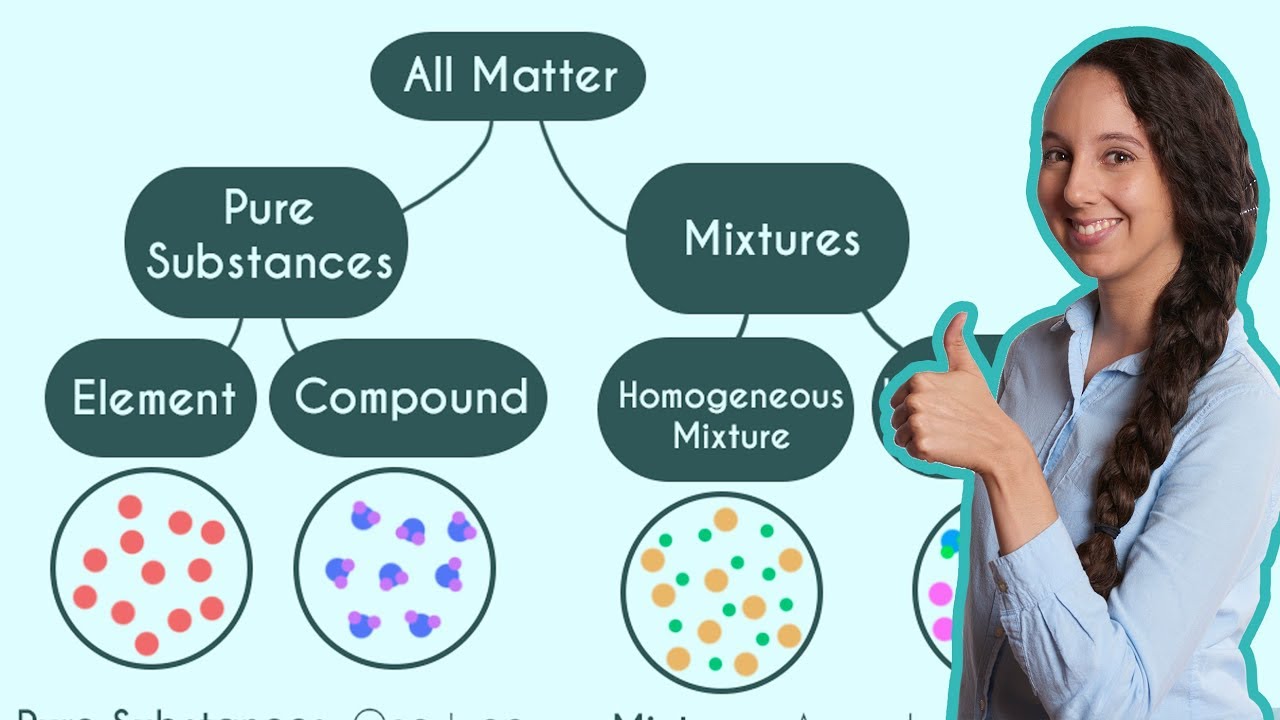
- 🧪 A mixture is defined as two or more substances that are in close proximity and occupy the same space without chemically reacting to form something new.
- 💧 Solutions are a type of homogeneous mixture where one substance is dissolved into another, like salt in water, and are important in chemistry as they allow for thorough mixing and reactions.
- 🔬 Homogeneous mixtures are uniform throughout, while heterogeneous mixtures are non-uniform and may have different compositions in different parts of the mixture.
- 🌊 Seawater is an example of a homogeneous mixture because the dissolved substances are uniformly distributed, even if there are slight differences in different samples.
- 🍚 Rice pudding is likely a heterogeneous mixture because it is not mixed to the point of being uniform, often containing clumps of rice and other ingredients.
- ⚙️ Magnesium, as a pure element on the periodic table, is a pure substance and not a mixture.
- 🧊 Crushed ice is made of water molecules (H2O) and, despite its different appearance from liquid water, is still a pure substance, not a mixture.
- 💧 Distilled water is a pure substance because it has had all other dissolved substances removed through the process of distillation.
- ⛽ Gasoline is a complex, homogeneous mixture containing hydrocarbon molecules and other additives, designed to improve engine performance.
- 🏖 Beach sand is typically a heterogeneous mixture because it has not been thoroughly mixed and can vary in composition from one part of the beach to another.
- 🍷 Wine is a homogeneous mixture with a uniform composition, containing alcohol, additives, and flavors derived from the grape fermentation process.
- 🌬 Air is a homogeneous mixture of gases, including oxygen and nitrogen, that are uniformly distributed due to constant mixing by weather phenomena.
Q & A
What is the basic definition of a mixture in chemistry?
-A mixture is defined as two or more species that are put into close proximity to each other, occupying the same space but not chemically bonding or reacting to form something new.
Why are solutions considered important in chemistry?
-Solutions are important in chemistry because they allow different chemicals to mix very thoroughly with each other, which is necessary for chemical reactions to occur. Many chemical reactions, including those in the human body, happen in a water solution.
What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture is uniform throughout, meaning it has the same composition in any given part, while a heterogeneous mixture is non-uniform, leading to slight differences in composition if sampled from different parts.
How does the process of distillation produce distilled water, and why is it considered a pure substance?
-Distillation involves boiling water so that the vapor condenses and drips into another container, leaving behind most dissolved substances. Since it only contains water molecules (H2O), it is considered a pure substance and also a compound.
What is the difference between a pure substance and a compound?
-A pure substance consists of a single type of particle, which can be an element or a compound. A compound specifically is a type of pure substance that consists of two or more different elements chemically bonded together, like H2O for water.
Why is rice pudding considered a heterogeneous mixture?
-Rice pudding is considered a heterogeneous mixture because it is not mixed uniformly. It often contains clumps of rice and other ingredients that are not evenly distributed throughout the dish.
How is seawater classified in terms of mixture types, and why?
-Seawater is classified as a homogeneous mixture because the salt and minerals are dissolved and uniformly distributed throughout the water, even if sampled from different locations or depths.
What type of mixture is gasoline, and why?
-Gasoline is a homogeneous mixture because it contains various components, such as hydrocarbons and additives, that are uniformly mixed at the molecular level.
Is crushed ice considered a mixture, and if not, why?
-Crushed ice is not considered a mixture because it is simply water in a solid state. It consists of H2O molecules and does not have other substances mixed with it.
What are the key characteristics of a gaseous phase in the context of the provided script?
-In the context of the script, a gaseous phase is characterized by particles that are not bonded together and fill the entire volume of the container, bouncing around and moving freely.
How does the composition of beach sand typically classify it in terms of mixture types?
-Beach sand is typically classified as a heterogeneous mixture because it usually has not been thoroughly mixed and can have varying compositions if sampled from different parts of the beach.
What is the reason why air is considered a homogeneous mixture?
-Air is considered a homogeneous mixture because the composition of gases is generally uniform throughout, and due to natural processes like wind, the mixture is constantly being stirred and remains uniform.
Outlines
🧪 Understanding Mixtures in Chemistry
This paragraph introduces the concept of mixtures within a chemistry context. It explains that mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded or reacting to form a new substance. Mixtures are categorized as either homogeneous, where the components are uniformly mixed, or heterogeneous, where the composition varies throughout. The paragraph also emphasizes the importance of solutions, a type of homogeneous mixture, in facilitating chemical reactions due to the thorough mixing of reactants.
🌊 Classifying Mixtures: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
The second paragraph delves into classifying mixtures and understanding their properties. It uses examples such as rice pudding, seawater, magnesium, and crushed ice to illustrate the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, as well as pure substances. The discussion clarifies that rice pudding is likely heterogeneous due to its non-uniform composition, while seawater is homogeneous due to the even distribution of dissolved substances. Magnesium, as a single element, is a pure substance, and crushed ice, despite its physical state, is also a pure substance because it's composed of identical water molecules.
🏖️ Further Exploration of Mixtures and Their Compositions
This paragraph continues the exploration of mixtures by examining additional examples, including distilled water, gasoline, beach sand, wine, and air. It discusses the process of distillation that results in pure water, the complex composition of gasoline making it a homogeneous mixture, the non-uniform nature of beach sand classifying it as a heterogeneous mixture, the uniform composition of wine also making it a homogeneous mixture, and the uniform distribution of gases in the air, which is also considered a homogeneous mixture. The paragraph concludes with a brief mention of identifying the phase (solid, liquid, or gas) and the composition (pure substance or mixture) of different materials.
🔬 The Importance of Mixtures in Chemical Reactions
The final paragraph reiterates the significance of mixtures, particularly solutions, in chemistry. It highlights that many chemical reactions occur in solutions, which are homogeneous mixtures that allow for thorough interaction between reactants. The paragraph encourages understanding the definitions and solving related problems to build essential chemistry skills, and it teases the continuation of the topic in the next lesson.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mixture
💡Solution
💡Homogeneous Mixture
💡Heterogeneous Mixture
💡Pure Substance
💡Element
💡Compound
💡Distillation
💡Gas
💡Solid
💡Chemical Reaction
Highlights
A mixture is defined as two or more substances that are in the same container but are not chemically reacting to form something new.
Mixtures are important in chemistry as they often serve as the starting point for chemical reactions.
A solution is a type of mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent, such as salt or sugar in water.
In a solution, the solute particles are microscopically dispersed between the solvent molecules without chemical bonding.
Chemical reactions often occur in solutions because the solutes can freely move and interact with each other.
Mixtures can be classified into two main types: homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
A homogeneous mixture is uniform throughout, like a solution, whereas a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition.
The human body is mostly water, which serves as a medium for many chemical reactions, highlighting the importance of solutions in biology.
Rice pudding is an example of a heterogeneous mixture due to the non-uniform distribution of its components.
Seawater is considered a homogeneous mixture because its dissolved components are uniformly distributed.
Magnesium, as a pure element on the periodic table, is an example of a pure substance, not a mixture.
Crushed ice, composed solely of water molecules, is still a pure substance despite its physical state change from liquid to solid.
Distilled water is a pure substance because it has had all other dissolved substances removed through the process of distillation.
Gasoline is a complex, homogeneous mixture composed of organic hydrocarbon molecules and various additives.
Beach sand is typically a heterogeneous mixture due to the variability in its composition across different samples.
Wine is a homogeneous mixture with a uniform composition of alcohol, additives, and flavors.
Air is a homogeneous mixture of gases, including oxygen and nitrogen, that are uniformly distributed.
Understanding the concepts of pure substances, homogeneous, and heterogeneous mixtures is crucial for grasping many principles in chemistry.
The lesson emphasizes the importance of solutions in chemistry, as many chemical reactions take place in a solution.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: