What is DNA and How Does it Work?
TLDRThe script from Stated Clearly offers a clear explanation of DNA, the molecule that acts as a blueprint for life. It describes DNA as a long, spiraling ladder composed of atoms. DNA's primary function is to guide the formation of proteins, which are crucial for life, by directing the arrangement of amino acids. Amino acids link together like Legos to form proteins, which are essential for cell function. DNA communicates with the cytoplasm through RNA, which carries the genetic code to ribosomes, the protein-building machinery. The ribosomes read the RNA code to assemble amino acids into functional proteins. This process, while complex, is grounded in chemistry and forms the basis of life as we know it.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that forms the shape of a long, spiraling ladder.
- 🛠️ DNA acts as a blueprint or recipe for living organisms, guiding the formation of complex life forms.
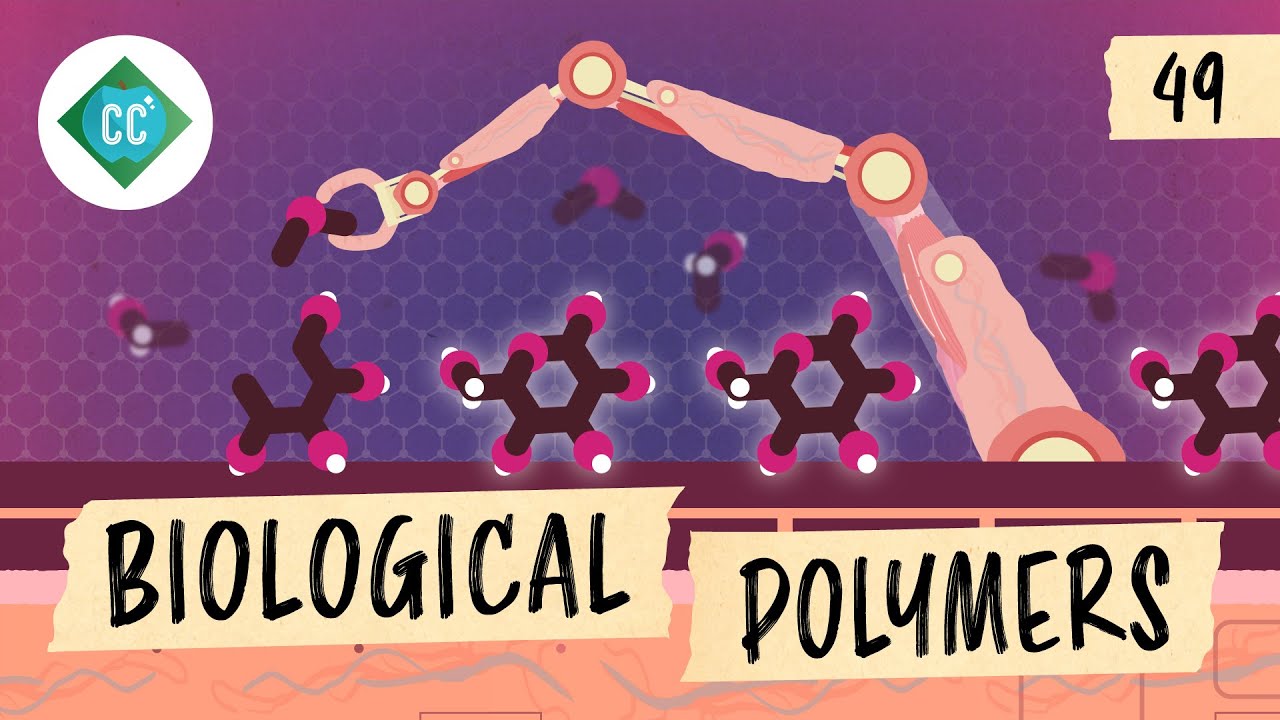
- 🧱 Amino acids are the building blocks of life, with about twenty different kinds, each with a unique shape.
- 🔗 Amino acids can be attached to each other like Legos to form a vast variety of proteins.
- 🤝 Proteins, along with other chemicals, combine to form living cells, which then make up tissues and organs.
- 🧬 DNA's primary function is to instruct amino acids on how to line up and form the perfect protein shapes.
- 📜 DNA is composed of four different kinds of chemicals, represented by different colors and letters in its structure.
- 📚 A single strand of DNA contains millions of letters of genetic code, which is read like a book.
- 📄 Special chemicals inside the nucleus make partial copies of the DNA code, known as RNA.
- 🕳️ RNA, being smaller, can pass through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm where it interacts with ribosomes.
- 🔧 Ribosomes are protein-building machines that read the RNA code and assemble amino acids into proteins.
- 🔡 The RNA code is read in sets of three letters, which determine the type of amino acid to be added to the protein chain.
- 🌱 Once proteins are built, they perform various functions, including helping to form new cells.
Q & A
What is DNA and what is its basic structure?
-DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of atoms that form a long, spiraling ladder-like structure. It acts as a blueprint for living organisms.
How is DNA related to the concept of a blueprint in biology?
-DNA serves as a blueprint because it contains the genetic instructions necessary for the development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
What are amino acids and why are they important?
-Amino acids are small organic compounds that are the building blocks of proteins. They are crucial because proteins are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs.
How do amino acids combine to form proteins?
-Amino acids link together like Legos to create proteins. Each amino acid has a unique shape, and they can be arranged in various sequences to form different types of proteins.
What is the significance of the shape of proteins in their function?
-The shape of a protein is critical to its function. If a protein is not the correct shape, it usually will not work properly, which can affect the overall health and function of an organism.
What is one of the main functions of DNA?
-One of the main functions of DNA is to provide instructions for the arrangement of amino acids to form proteins with the correct shape and function.
Can you describe the simplified model of DNA presented in the script?
-The simplified model of DNA shows the steps of the ladder made up of four different kinds of chemicals represented by different colors and letters. This represents the genetic code.
How does DNA interact with the cytoplasm to convert amino acids into proteins?
-DNA interacts with the cytoplasm through a process where special chemicals inside the nucleus make partial copies of the DNA code, called RNA, which then carry the genetic information to the cytoplasm.
What is the role of RNA in the process of protein synthesis?
-RNA acts as a messenger, carrying the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then use this code to assemble amino acids into proteins.
What are ribosomes and what is their function in protein synthesis?
-Ribosomes are protein-building machines that read the RNA code three letters at a time to determine the sequence in which amino acids should be linked to form a protein.
How does the process of DNA creating RNA and RNA creating protein relate to the formation of life?
-The process of DNA creating RNA and RNA creating proteins is fundamental to life. Proteins are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cells, tissues, and organs, which collectively form living creatures.
Outlines
🧬 DNA: The Blueprint of Life
This paragraph introduces DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, as a fundamental molecule that acts as a blueprint for all living organisms. It explains DNA's structure as a long, spiraling ladder composed of atoms. The script delves into the role of DNA as a guide for constructing proteins, which are vital for life and are made up of amino acids. Amino acids are described as the building blocks of life, with unique shapes that can be linked together like Lego bricks to form a vast array of proteins. The importance of proteins having the correct shape for their function is highlighted, and DNA's role in directing the formation of these proteins is emphasized. The paragraph also provides a simplified model of DNA, explaining the genetic code and how it is transcribed into RNA, which then translates into proteins through the ribosome's action. The process is depicted as a chemically based, yet sophisticated and almost magical, series of events that lead to the creation of life.
📚 Further Exploration of DNA
The second paragraph serves as a call to action for viewers to subscribe to the channel for more content and to engage with the material by posting questions or comments in the comment section. It also directs viewers to StatedClearly.com for additional information about DNA. The paragraph ends with an encouraging note for viewers to stay curious, indicating the channel's intent to foster a community of lifelong learners interested in understanding the intricacies of science.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡DNA
💡Amino Acids
💡Proteins
💡Genetic Code
💡RNA
💡Ribosomes
💡Cytoplasm
💡Nucleus
💡Codons
💡Protein Synthesis
💡Cells
Highlights
DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of atoms forming a long, spiraling ladder structure.
DNA acts as a blueprint or recipe for living things, raising the question of how a molecule can dictate the complexity of life.
Amino acids are the building blocks of life, with about twenty different kinds, each with a unique shape.
Amino acids can be linked together like Legos to form proteins, which are essential for life.
Proteins, along with other chemicals, form living cells, which then make up tissues, organs, and eventually living creatures.
DNA's primary function is to instruct amino acids on how to line up and form into perfect protein shapes.
DNA contains a genetic code made up of four different chemicals, represented by different colors and letters.
A single strand of DNA is millions of letters long and resides in the cell's nucleus.
RNA is a partial copy of the DNA code that helps convert amino acids into proteins.
RNA's small size allows it to pass through the nucleus and into the cytoplasm where ribosomes are located.
Ribosomes are protein-building machines that read the RNA code to assemble amino acids into proteins.
The RNA code is read in sets of three letters, determining the type of amino acid to be added next in the protein chain.
Proteins, once formed, perform various functions, including aiding in the formation of new cells.
DNA is a molecular blueprint for living things, working through the process of DNA creating RNA, which then creates protein.
The entire process, though complex, is based in chemistry and can be studied and understood.
Jon Perry from Stated Clearly provides an engaging explanation of DNA's role and function in the video.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: