Complete Human Anatomy quiz | Can You Answer these Questions about the Human Body?
TLDRThis engaging quiz dives into the intricacies of human anatomy, focusing on 11 major organ systems. It covers a range of topics from the skeletal system, highlighting the types of bones and joints, to the muscular system, explaining muscle types and their functions. The quiz continues through the integumentary, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems, testing knowledge on their primary functions, components, and related medical conditions. The script is informative, providing correct answers to each question and aiming to educate viewers on the complex yet fascinating structure and function of the human body.
Takeaways
- 💀 The skeletal system consists of approximately 206 bones and includes long, short, and irregular bones, but not 'thick' bones.
- 🤲 The ball and socket joint, such as the shoulder or hip joint, allows for the greatest range of motion.
- 🦴 Sesamoid bones are small, round bones found within tendons, like the patella.
- 🦳 The axial skeleton does not include the pelvis but comprises the skull and ribs.
- 🚶♂️ Osteoclasts are bone cells that break down and reabsorb bone tissue.
- 🦴 The clavicle is commonly known as the collarbone.
- 🧠 The nervous system is not primarily responsible for the movement of the body but for sensory input and homeostasis.
- 🧠 The brain stem regulates vital functions like breathing and heart rate.
- 💊 The neurotransmitter serotonin is involved in mood, appetite, and sleep regulation.
- 🏃♀️ Type 1 muscle fibers are best suited for endurance activities like long-distance running.
- 💪 The biceps muscle group is responsible for bending the elbow, while the hamstrings flex the knee.
- 🧘♀️ The integumentary system's primary function is to protect the body from injury and infection.
- 👂 The ceruminous glands are responsible for producing earwax.
- 🫀 The cardiovascular system's main function is to transport oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
- ❤️ The left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
- 🩸 Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to the body's tissues.
- 🧬 The lymphatic system maintains fluid balance and immune function.
- 👶 The hormone prolactin stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- 🌡️ The color of urine gets darker when dehydrated, indicating a higher concentration of waste products.
- 🚰 The kidneys filter blood and excrete waste products like urea.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
-The primary function of the skeletal system is to provide structural support for the body and protect internal organs.
Which type of joint allows for the greatest range of motion?
-The ball and socket joint allows for the greatest range of motion, as exemplified by the shoulder and hip joints.
How many bones are there in the adult human skeletal system?
-There are approximately 206 bones in the adult human skeletal system.
What are the small round bones found in tendons called?
-The small round bones found in tendons are called sesamoids.
Which bone cell is responsible for breaking down and reabsorbing bone tissue?
-Osteoclasts are the bone cells responsible for breaking down and reabsorbing bone tissue.
What is commonly referred to as the collarbone?
-The clavicle is commonly referred to as the collarbone.
What is the primary function of the muscular system?
-The primary function of the muscular system is to facilitate movement, maintain posture, and generate heat.
Which type of muscle is voluntary and under conscious control?
-Skeletal muscle is voluntary and under conscious control.
What is the main energy source for muscle contractions?
-ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is the main energy source for muscle contractions.
What is the connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone called?
-The connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone is called tendon.
Which muscle group is responsible for bending the elbow?
-The biceps muscle group is responsible for bending the elbow.
What is the primary function of the integumentary system?
-The primary function of the integumentary system is to protect the body from injury and infection.
Which layer of skin is responsible for producing new skin cells?
-The epidermis is the layer of skin responsible for producing new skin cells.
What is the scientific name for the oil produced in the sebaceous glands?
-The scientific name for the oil produced in the sebaceous glands is sebum.
Which hormone is responsible for stimulating the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow?
-Erythropoietin is the hormone responsible for stimulating the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
What is the primary function of the cardiovascular system?
-The primary function of the cardiovascular system is to transport oxygen and nutrients to the cells and remove waste products.
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
-Arteries carry blood away from the heart to various parts of the body.
What is the largest artery in the body?
-The aorta is the largest artery in the body.
Which organ's main function is to clean the blood of toxins and transform the waste into urine?
-The kidneys are the organs that clean the blood of toxins and transform the waste into urine.
What is the name of the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder?
-The ureter is the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
What is the medical term for the presence of blood in the urine?
-The medical term for the presence of blood in the urine is hematuria.
What is the monthly release of an egg from the ovary called?
-The monthly release of an egg from the ovary is called ovulation.
What is the function of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
-The function of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system is the secretion of seminal fluid.
What hormone is responsible for stimulating milk production in the mammary glands?
-Prolactin is the hormone responsible for stimulating milk production in the mammary glands.
Which hormone is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics?
-Testosterone is the hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Outlines
💀 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Quiz
This paragraph introduces a quiz on human anatomy, focusing on the skeletal and muscular systems. It presents multiple-choice questions about different types of bones, joints, and their functions. The quiz covers topics such as the number of bones in the adult skeleton, the role of sesamoid bones, the axial skeleton components, bone cells like osteoclasts, and specific bones like the clavicle and vertebra. It also delves into muscle types, their energy source, connective tissues, and muscle functions, including the identification of muscle groups responsible for certain movements and the types of muscle contractions.
🧘♂️ Integumentary and Nervous Systems Exploration
The second paragraph continues the anatomy quiz, shifting focus to the integumentary and nervous systems. Questions in this section address the layers of skin, types of sweat glands, hair color determinants, and the skin's structure. It also covers common skin conditions like acne and the primary functions of the integumentary system. The nervous system portion quizzes on its primary functions, parts of the brain, types of neurons, neurotransmitters, and the roles of various brain lobes. This section tests knowledge on sensory input, motor control, and the complex interactions within the nervous system.
🌡️ Endocrine and Cardiovascular Systems Overview
This paragraph delves into the endocrine and cardiovascular systems, with questions about hormone production, types of hormones, and the location of glands. It identifies the pancreas as the insulin-producing gland, describes the function of cortisol, and locates the adrenal glands. The paragraph also touches on the role of various hormones in bodily functions, such as oxytocin in childbirth and erythropoietin in red blood cell production. The cardiovascular system is explored through questions about its primary function, types of blood vessels, heart chambers, and valves. Conditions like atherosclerosis and terms like bradycardia are also discussed.
💧 Lymphatic and Respiratory Systems Examination
The focus of this paragraph is the lymphatic and respiratory systems. It starts by defining the lymphatic system's primary functions and the fluid it circulates, lymph. The quiz asks about lymphocytes, lymph nodes, and the lymphatic system's overall structure and function. Moving on to the respiratory system, questions cover the diaphragm's role, alveoli's function in gas exchange, and conditions like emphysema. The average lung capacity and the process of breathing are also examined, including the role of the epiglottis and the function of the trachea.
🍲 Digestive System and Its Processes
This paragraph is dedicated to the digestive system, starting with the process of digestion beginning with ingestion. It covers bile production by the liver, the role of pepsin in protein breakdown, and the small intestine as the primary site for nutrient absorption. The function of the pancreas, villi in increasing nutrient absorption, and the hormones that stimulate bile release and hunger are also discussed. The paragraph wraps up with questions on the absorption in the large intestine, the gut microbiome, and the hormones related to appetite and digestion.
🚰 Urinary and Reproductive Systems Insights
The final paragraph covers the urinary and reproductive systems. It explains the kidneys' role in filtering blood and producing urine, identifies urea as a waste product, and describes the urinary tract including the ureter and urination process. Terms like hematuria and the role of renin are introduced. The reproductive system section discusses ovulation, sex chromosomes, fertilization, and the function of the prostate gland. It also covers terms like zygote, prolactin's role in milk production, and the development of male secondary sexual characteristics with testosterone. The paragraph concludes with the role of the uterus in fetal development.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Skeletal System
💡Muscular System
💡Integumentary System
💡Nervous System
💡Endocrine System
💡Cardiovascular System
💡Lymphatic System
💡Respiratory System
💡Digestive System
💡Urinary System
💡Reproductive System
Highlights
The skeletal system consists of 11 major organ systems and is made up of approximately 206 bones.
Ball and socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip, allow for the greatest range of motion.
Sesamoid bones are small, round bones found in tendons, like the patella or kneecap.
The axial skeleton includes the skull and ribs, but not the pelvis.
Osteoclasts are bone cells that break down and reabsorb bone tissue.
The clavicle, or collarbone, connects the shoulder blade to the sternum.
Skull bones are connected by sutures, not synovial or cartilaginous joints.
The patella, or kneecap, is a sesamoid bone that protects the knee joint.
Vertebrae protect the spinal cord and provide structural support.
Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles controlled by conscious effort.
ATP is the main energy source for muscle contractions.
Tendons are connective tissues that attach muscles to bones.
Smooth muscles in the digestive tract move food via involuntary contractions.
Muscles do not produce insulin, which is made by the pancreas.
Type 1 muscle fibers are suited for endurance activities like long-distance running.
Eccentric muscle contractions occur when the muscle lengthens while under tension.
The biceps brachii muscle group is responsible for bending the elbow.
The hamstrings flex the knee and are involved in walking and running.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Body Organs

ATI TEAS Anatomy & Physiology Made Easy with Smart Edition Academy

EMT 1-4: Overview of the Human Body and Physiology

Lucent Science in Hindi | Part 21 : Nervous System | Lucent Science by Rituraj Sir
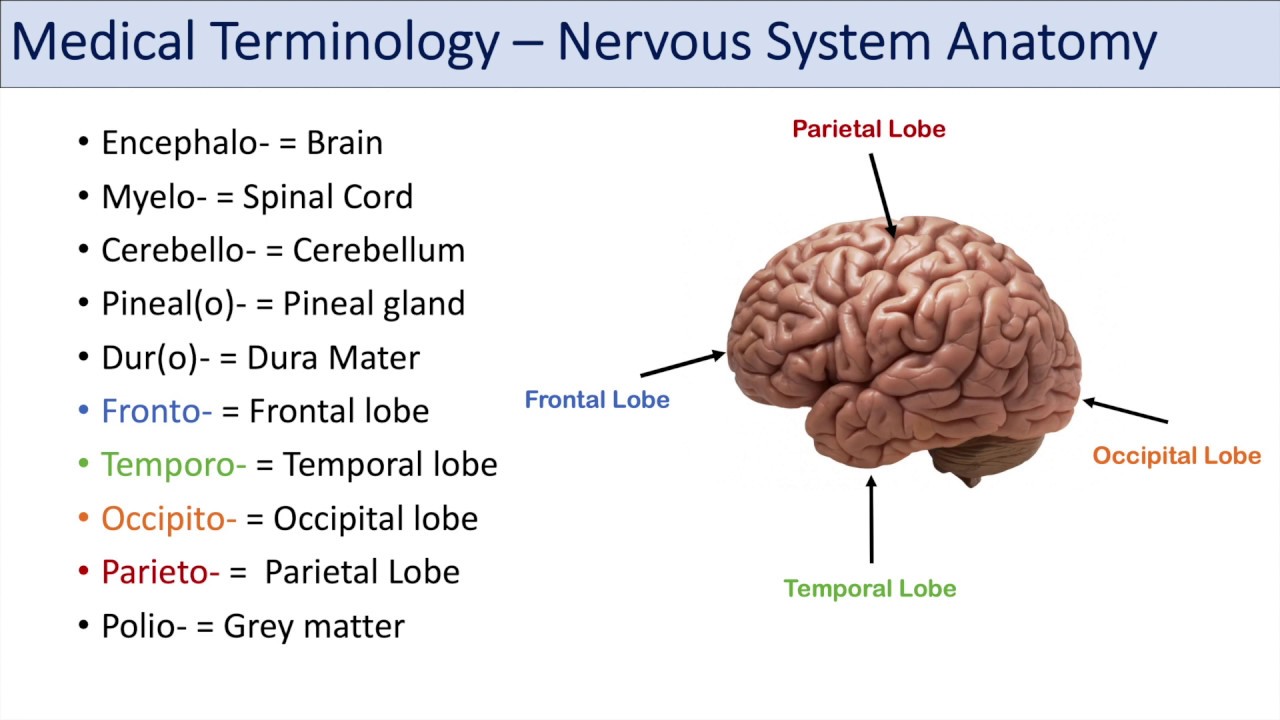
Medical Terminology | Lesson 8 | Nervous System, Cardiorespiratory and Endocrine Anatomy Terms

Respiratory System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: