What is Mixture in Chemistry?
TLDRThis informative lecture introduces the concept of a mixture, which occurs when two or more substances physically combine in any ratio. It distinguishes between homogeneous mixtures, where the composition is uniform throughout (like saltwater), and heterogeneous mixtures, which have non-uniform compositions (like oil and water). Examples such as sugar solution, carbonated drinks, air, and coffee illustrate the types of mixtures, offering insights into how substances interact in everyday scenarios.
Takeaways
- 🌟 A mixture is formed when two or more substances are combined physically in any ratio.
- 🍯 Example of a mixture: dissolving sugar in water creates a sugar solution.
- 🌬️ Air is a mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
- 🔁 The definition of a mixture allows for variable proportions, such as 1 gram or 10 grams of sugar in water.
- 🎨 There are two types of mixtures: homogeneous and heterogeneous.
- 🌈 Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout their mass, like salt dissolved in water.
- 🔍 In a homogeneous mixture, it's impossible to differentiate between the individual components, such as salt and water particles.
- 🍹 Other examples of homogeneous mixtures include air, vinegar, and carbonated drinks.
- 📏 Heterogeneous mixtures have non-uniform compositions, like oil floating on water.
- 🍕 Heterogeneous mixtures are easily identifiable by their distinct layers or components, such as coffee with visible coffee grounds or a pizza with different toppings.
- 📝 The key to distinguishing between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures lies in the uniformity of their composition throughout the mixture.
Q & A
What is a mixture?
-A mixture is a combination of two or more substances physically combined together in any ratio.
Can you provide an example of a mixture?
-An example of a mixture is a sugar solution, where sugar is dissolved in water.
What does 'in any ratio' mean in the context of mixtures?
-It means that the substances in a mixture can be combined in varying proportions without changing the fact that it remains a mixture.
What is a homogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture is a type of mixture that has a uniform composition throughout its mass.
How can you identify a homogeneous mixture?
-In a homogeneous mixture, the individual components cannot be easily distinguished from one another, such as salt dissolved in water.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
-A heterogeneous mixture is a type of mixture that has a non-uniform composition, meaning the components are not evenly distributed.
Can you give an example of a heterogeneous mixture?
-An example of a heterogeneous mixture is oil floating on water, where the oil and water layers are visibly distinct.
What are some common examples of homogeneous mixtures?
-Common examples of homogeneous mixtures include air, vinegar, and carbonated drinks.
What are some common examples of heterogeneous mixtures?
-Common examples of heterogeneous mixtures include a mixture of oil and water, coffee, and pizza.
How can you differentiate between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, while a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition with visibly distinct parts.
Is air considered a mixture?
-Yes, air is considered a mixture because it is composed of different gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide physically combined together.
Outlines
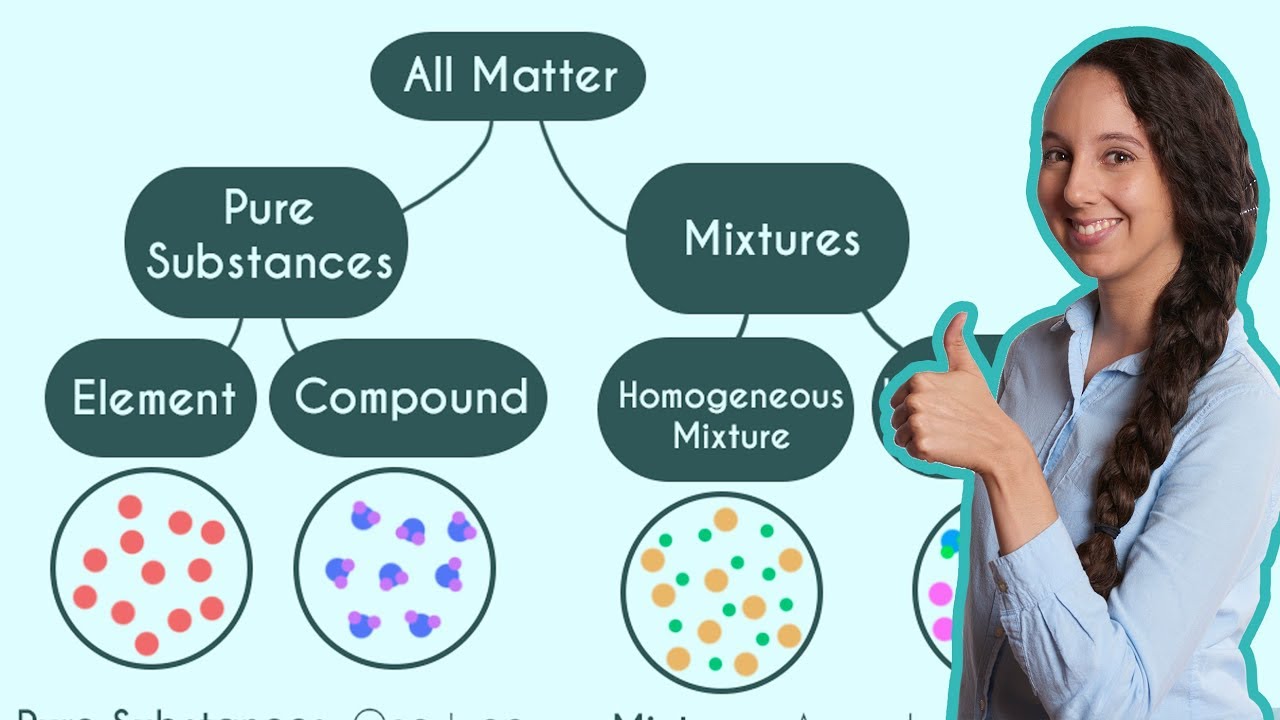
🌟 Introduction to Mixtures and Their Types
This paragraph introduces the concept of a mixture, which is a physical combination of two or more substances in any ratio. It provides examples such as sugar dissolved in water (sugar solution), carbon dioxide in water (carbonated water), coffee, and air, emphasizing that these are mixtures because their components are physically combined. The paragraph then differentiates between two types of mixtures: homogeneous and heterogeneous. A homogeneous mixture is one with a uniform composition throughout, like a salt solution where salt and water are indistinguishable at the particle level. Heterogeneous mixtures, on the other hand, have a non-uniform composition, such as oil floating on water or small pebbles in water. The paragraph concludes by summarizing the key points about mixtures and their types.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Mixture
💡Homogeneous Mixture
💡Heterogeneous Mixture
💡Physical Combination
💡Uniform Composition
💡Non-uniform Composition
💡Carbon Dioxide
💡Nitrogen Gas
💡Oxygen Gas
💡Carbonated Drinks
💡Vincent Van Gogh
Highlights
A mixture is formed when two or more substances are combined physically in any ratio.
An example of a mixture is sugar dissolved in water, forming a sugar solution.
The definition of a mixture allows for variable ratios, such as adding one gram or 10 grams of sugar to water.
Carbon dioxide dissolved in water creates carbonated water, which is also a mixture.
Coffee is a mixture of coffee and water physically combined.
Air is a mixture of different gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Mixtures are categorized into two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout its mass.
An example of a homogeneous mixture is a salt solution, where salt particles are indistinguishable from water particles.
Other examples of homogeneous mixtures include air, vinegar, and carbonated drinks.
A heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition.
Oil added to water forms a heterogeneous mixture due to the visible separation of oil and water layers.
Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include small pebbles in water, coffee, and pizza.
In a heterogeneous mixture, the different compositions are easily distinguishable.
The distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures lies in the uniformity of their composition.
Understanding mixtures and their types is fundamental in chemistry and everyday applications.
The concept of mixtures applies to both simple solutions like sugar water and complex natural compositions like air.
The properties of a mixture can vary greatly depending on whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixture | Chemistry

What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?

Pure Substances and Mixtures | Chemistry

Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures Examples, Classification of Matter, Chemistry
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: