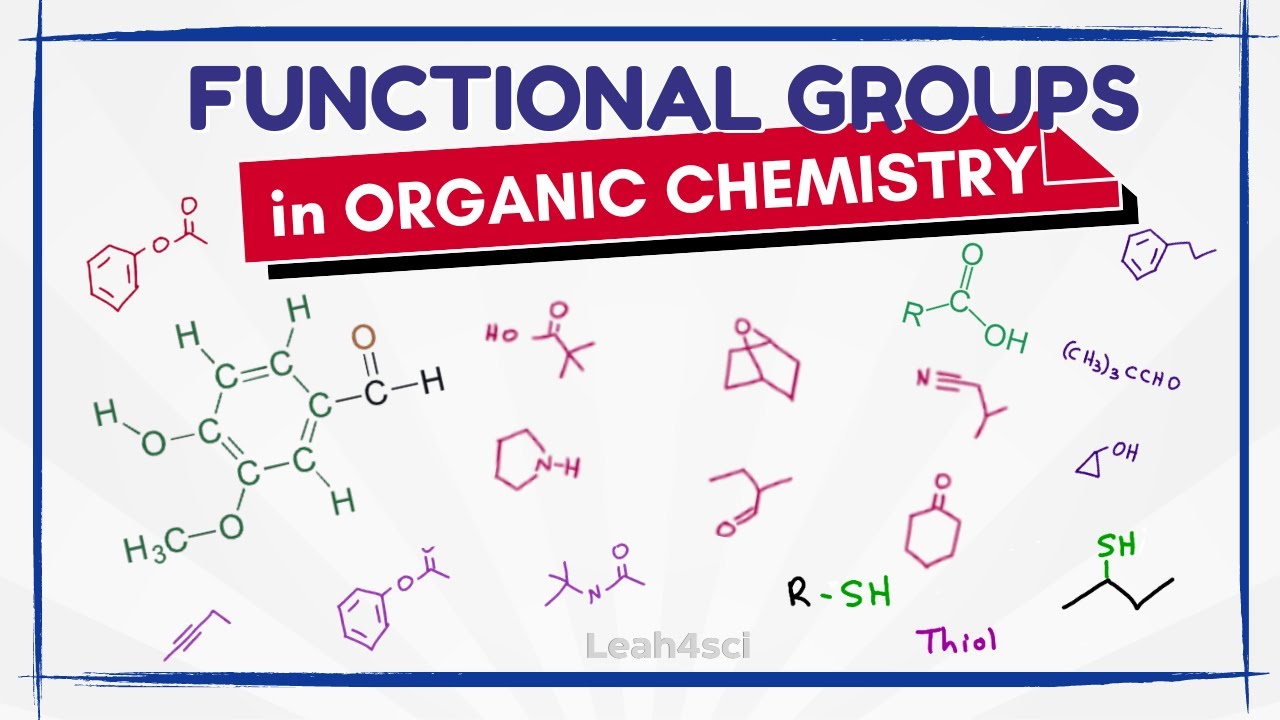
Identifying Functional Groups | Study With Us
TLDRThis video transcript focuses on the identification of functional groups in organic chemistry, a crucial skill for students aiming for academic success in the subject. The session involves 13 practice problems that challenge viewers to recognize and label various functional groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, ethers, and carboxylic acids. The video emphasizes the importance of practice and the need to treat exercises without notes as a simulation of test conditions. It also highlights the significance of understanding these groups in organic chemistry reactions and the overall course performance.
Takeaways
- 📚 Organic chemistry success relies on understanding functional groups, which are the focus of this study session.
- 🎯 Practicing identifying functional groups is compared to playing a game, where the goal is to spot specific features among a variety of structures.
- 📈 There are three difficulty levels for identifying functional groups, starting with basic structures and moving to more complex ones.
- 🔍 Alkenes are characterized by a double bond between carbon atoms, while alkynes have a triple bond.
- 🌐 Aromatic rings, like benzene, have three double bonds and are drawn with a specific ring structure.
- 🍺 Alcohols contain an R group connected to a hydroxyl (-OH) group, whereas carboxylic acids have a carbonyl group (C=O) directly bonded to a hydroxyl group.
- 🥫 Ethers are characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two R groups, with a focus on how the oxygen interrupts the carbon chain.
- 🍯 Epoxides are a type of cyclic ether with a three-membered ring including the oxygen, and are important to recognize as distinct from other ethers.
- 🧪 Amides, primary amines, and nitriles contain a nitrogen atom in different bonding configurations, which is key to distinguishing them.
- 📝 For effective studying, it's advised to practice without notes open, treating practice problems as if they were a test to truly gauge understanding and retention.
- 🚀 Joining an email list provides access to study resources, including practice problems and videos, to help achieve an A in organic chemistry.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the study session in the transcript?
-The main focus of the study session is to practice identifying functional groups in organic chemistry.
How can students access the practice problems mentioned in the transcript?
-Students can access the practice problems by signing up for the email list using the link provided in the description.
What is the significance of functional groups in organic chemistry?
-Functional groups are significant in organic chemistry because they determine the chemical properties of molecules and are essential for classifying reactions and compounds.
What is the difference between an aldehyde and a ketone?
-The difference between an aldehyde and a ketone is that an aldehyde has a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group, while a ketone has two R groups (carbon chains) bonded to the carbonyl group.
How can you identify an epoxide among other functional groups?
-An epoxide can be identified as a type of cyclic ether with three atoms in the ring and a carbonyl group that is not part of a larger ring structure.
What is the role of the carbonyl group in organic chemistry?
-The carbonyl group, which consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom, is a key functional group in organic chemistry that appears in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and other compounds, influencing their reactivity and properties.
What are some tips for remembering the different types of functional groups?
-Some tips for remembering functional groups include associating them with visual patterns, using mnemonic devices, and practicing with various examples to reinforce the connection between their structure and name.
Why is it important to practice without notes during study sessions?
-Practicing without notes during study sessions is important because it helps students to test their memory and understanding of the material, simulating the conditions of an actual exam where notes will not be allowed.
What is the significance of the R group in organic chemistry?
-The R group, or alkyl group, is a carbon chain that can be attached to a functional group in organic compounds. It is significant because it affects the compound's structure and reactivity, and understanding R groups is crucial for identifying and working with various organic compounds.
How can the presence of halogens in a compound affect its classification?
-The presence of halogens in a compound can affect its classification by making it an organo-halide (or haloalkane), where the halogen is bonded to a carbon chain. This changes the compound's reactivity and properties compared to non-halogenated compounds.
Outlines
😀 Identifying Functional Groups
The video introduces the topic of identifying functional groups in organic chemistry. It starts with a study session focusing on practice problems to help students ace their exams. The session includes discussions on different difficulty levels of problems and strategies for effective studying, such as practicing without notes. The importance of understanding functional groups without reliance on notes is emphasized.
🔍 Understanding Basic Functional Groups
This section discusses various basic functional groups, including hydrocarbons, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic rings. It explains the structures and characteristics of each group, providing examples for clarity. The discussion also covers alkyl halides, esters, and acid chlorides, highlighting their structural differences and how they are identified.
🔬 Exploring Functional Groups with Oxygen
Here, the focus shifts to functional groups containing oxygen. The discussion covers alcohols, ethers, epoxides, and carbonyl compounds (aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and anhydrides). It highlights the structural features of each group and provides insights into distinguishing between them based on their bonding patterns.
🌟 Examining Functional Groups with Nitrogen
This section delves into functional groups containing nitrogen, such as amines, amides, and nitriles. It explains the classification of amines based on the number of R groups bonded to nitrogen (primary, secondary, and tertiary). The discussion also covers the structural characteristics of nitriles and nitro groups.
⚗️ Exploring Functional Groups with Sulfur
The focus of this part is on functional groups containing sulfur, including thioethers, thioesters, and sulfides. It explains the structural differences between these groups and their counterparts containing oxygen. The discussion emphasizes the importance of recognizing sulfur-containing functional groups in organic chemistry.
🧩 Applying Knowledge to Problem Solving
In this segment, the video presents practice problems to apply the knowledge gained about functional groups. It discusses strategies for problem-solving and emphasizes the importance of careful observation and understanding of structural features. The session aims to enhance students' ability to identify functional groups accurately in complex molecules.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Functional Groups
💡Organic Chemistry
💡Practice Problems
💡Alkene
💡Alcohol
💡Ether
💡Amide
💡Carbonyl Group
💡Aldehyde
💡Ketone
Highlights
The study session focuses on practicing problems on identifying functional groups in organic chemistry.
Students are encouraged to download practice problems to reinforce learning.
The session employs a matching format to identify functional groups in chemical structures.
Participants struggle to recall functional groups and their characteristics, highlighting the importance of practice and note-taking.
The tutor provides guidance on identifying hydrocarbons, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic rings.
Differentiating between alkyl halides and organohalogen compounds is discussed.
Classification of alcohols, ethers, and epoxides is explained.
The tutor clarifies the distinction between cyclic ethers and epoxides.
Carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids are addressed.
Students learn to differentiate between esters and anhydrides.
Identifying acid chlorides and amides is practiced.
The session also covers functional groups containing nitrogen, including amines and nitriles.
Discussion extends to sulfur-containing functional groups like thiols, sulfides, and thioesters.
Participants engage in labeling exercises to reinforce understanding.
The session emphasizes the importance of recognizing functional groups for organic chemistry success.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: