Introductory Statistics: What Is A Parameter? (Includes Examples of Parameters and Populations)
TLDRThe video script introduces the concept of a parameter as a numerical summary of a population, emphasizing that parameters are typically unknown and describe a group of individuals or items. It uses examples such as the number of red cars in the United States and characteristics of adults or schools to illustrate different types of parameters like percentages, averages, and counts. The importance of statistics in estimating these unknown parameters is highlighted, showcasing its practical applications in understanding and making inferences about large populations.
Takeaways
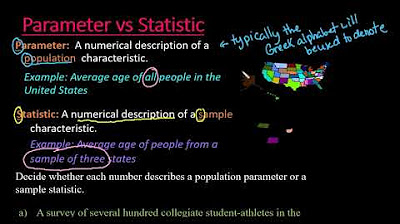
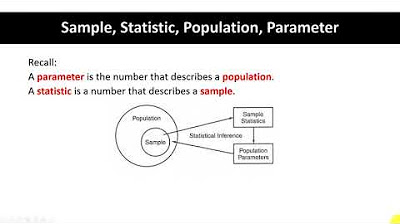
- 📈 A parameter is a numerical summary that describes a population.
- 🌟 Parameters are often unknown and represent a challenge in statistics.
- 🚗 The example of the number of red cars in the United States illustrates the concept of a parameter.
- 📊 The population in statistical terms refers to the entire group of interest, which can be very large and diverse.
- 📉 Parameters can be of different types, such as percentages, averages, or counts.
- 🎓 The percentage of married adults, average age, and number of adults over 70 are all examples of parameters for the population of adults in the United States.
- 🏫 For schools in Africa, parameters might include average number of students, proportion of high schools, and total number of teachers.
- 🤔 The difficulty in knowing the exact values of parameters highlights the importance of estimation in statistics.
- 🔍 Statistics is used to make educated guesses and provide estimates for unknown parameters.
- 🌍 Large populations make it impractical to know exact parameter values, thus estimation becomes crucial.
Q & A
What is a parameter according to the script?
-A parameter is a numerical summary of a population.
What does the term 'population' refer to in this context?
-In this context, 'population' refers to the group of individuals that we are interested in, which can be very large and sometimes even unknown.
Can you provide an example of a parameter from the script?
-An example of a parameter given in the script is the number of red cars in the United States.
Why is it difficult to know the exact value of a parameter?
-It is difficult to know the exact value of a parameter because the population it represents is often very large, making it hard to gather data on every single individual in that population.
What are the different types of numerical summaries that can be parameters?
-Different types of numerical summaries that can be parameters include percentages, averages, and counts.
How can statistics help with parameters that are unknown?
-Statistics can help by providing educated guesses or estimates for the values of these unknown parameters, based on the data that is available.
What is the population of interest in the example about adults in the United States?
-The population of interest in the example about adults in the United States is all the adults living in the country.
What are some specific parameters that might be of interest when studying adults in the United States?
-Some specific parameters might include the percentage of adults who are married, the average age of adults, and the number of adults older than 70 years old.
In the context of schools in Africa, what parameters were discussed?
-The parameters discussed in the context of schools in Africa were the average number of students per school, the proportion of schools that are high schools, and the total number of teachers.
Why is it important to have an understanding of parameters in statistics?
-Understanding parameters is important in statistics because they provide a way to describe and summarize populations, which can help us make informed decisions and predictions based on the data we have.
How might the knowledge of the average number of students in schools in Africa influence educational policies?
-Knowing the average number of students in schools in Africa could indicate whether there is a need for more schools or resources, which can guide educational policies and interventions to improve the quality of education.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to Parameters and Populations
This paragraph introduces the concept of a parameter in statistics, emphasizing its role as a numerical summary of a population. The population is defined as the group of individuals (or objects, in the case of cars) that a statistician is interested in. It is noted that these populations are often large and the exact parameters, such as the total number of red cars in the United States, are unknown and difficult to determine. The importance of understanding that parameters are typically unknown yet crucial for describing a population is highlighted.
📈 Types of Parameters and their Application
The paragraph delves into the different types of parameters that can describe a population, using the example of adults in the United States and schools in Africa. It explains that parameters can be percentages, averages, or counts, and these numbers provide various insights into the population of interest. The paragraph also touches on the challenge of knowing these parameters due to the large size of the populations, setting the stage for the role of statistics in making educated estimates about these unknown quantities.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Parameter
💡Population
💡Numerical Summary
💡Unknown
💡Red Cars
💡Statistics
💡Estimate
💡Percentage
💡Average
💡Count
💡Proportion
Highlights
Definition of a parameter - a numerical summary of a population
Parameters are often unknown and can be difficult to determine
Example of a parameter: the number of red cars in the United States
Population is the group of individuals of interest, which can be very large
Parameter as a quantity that describes a population, such as the number of red cars
Different types of parameters: percentages, averages, and counts
Parameter example: the percentage of married adults in the United States
Parameter example: the average age of adults in the United States
Parameter example: the number of adults older than 70 in the United States
Application of parameters in the context of schools in Africa
Parameter example: the average number of students per school in Africa
Parameter example: the proportion of schools that are high schools in Africa
Parameter example: the total number of teachers in African schools
Challenge of determining parameters due to the large size of populations
The role of statistics in estimating the values of parameters
Practical application: using statistical estimates to inform decisions, such as building more schools
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: