Populations, Samples, Parameters, and Statistics
TLDRThe video script introduces fundamental concepts in statistics, emphasizing the distinction between a population and a sample. It explains that a population encompasses all individuals of interest, while a sample is a smaller subset drawn from it. Parameters are used to describe aspects of the population, whereas statistics describe the sample. The video elucidates this through the example of determining the average GPA of students at a college or the average weight of Burger King customers worldwide, highlighting the practical challenges of surveying entire populations and the role of samples in statistical analysis.
Takeaways
- 📊 A population is the entire group of individuals of interest.
- 🔢 A parameter is a numerical characteristic that describes a population.
- 🔍 It is often impractical to survey entire populations due to their large size.
- 🔨 A sample is a smaller subgroup drawn from the larger population.
- 📈 A statistic is a numerical characteristic that describes a sample.
- 🏆 The average GPA of students at a college is an example of a parameter.
- 🧩 Taking 30 students' GPAs from a college and calculating the average results in a statistic.
- 🍔 The example of people eating at Burger King illustrates the concept of population and parameter.
- 🥩 The mean weight of a sample of Burger King eaters is an example of a statistic.
- 🧠 The main goal of statistics is to infer population parameters from sample statistics.
- 📝 The process involves selecting a sample, computing relevant statistics, and applying mathematical methods to make inferences about the population.
Q & A
What is the definition of a population in statistics?
-A population in statistics is the entire set of individuals or items of interest that one wishes to draw conclusions about.
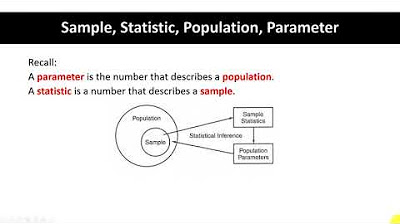
What is a parameter in the context of a population?
-A parameter is a numerical characteristic or measure that describes a property of the entire population, such as the mean or average.
Why is it often difficult to survey entire populations?
-Surveying entire populations can be challenging due to their large size, making it impractical or impossible to collect data from every single individual or item within the population.
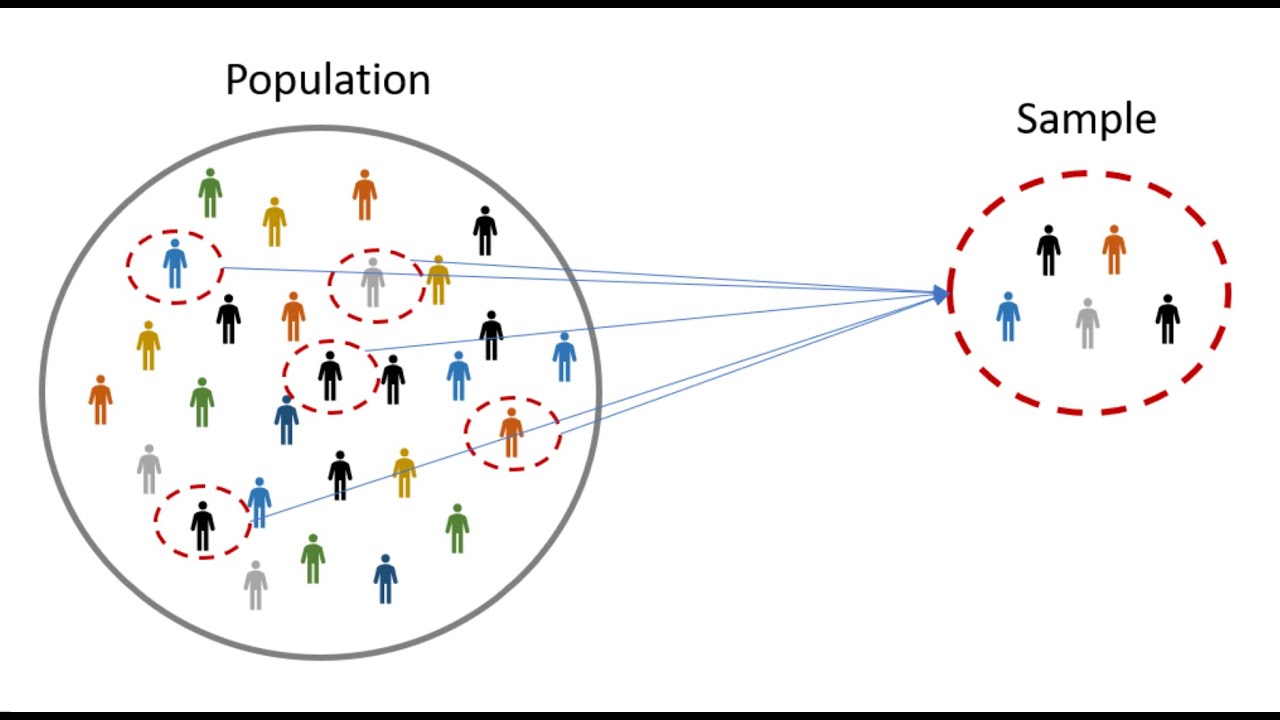
What is a sample in statistics?
-A sample is a smaller, manageable subset of the population that is taken to represent the larger group for the purpose of statistical analysis.
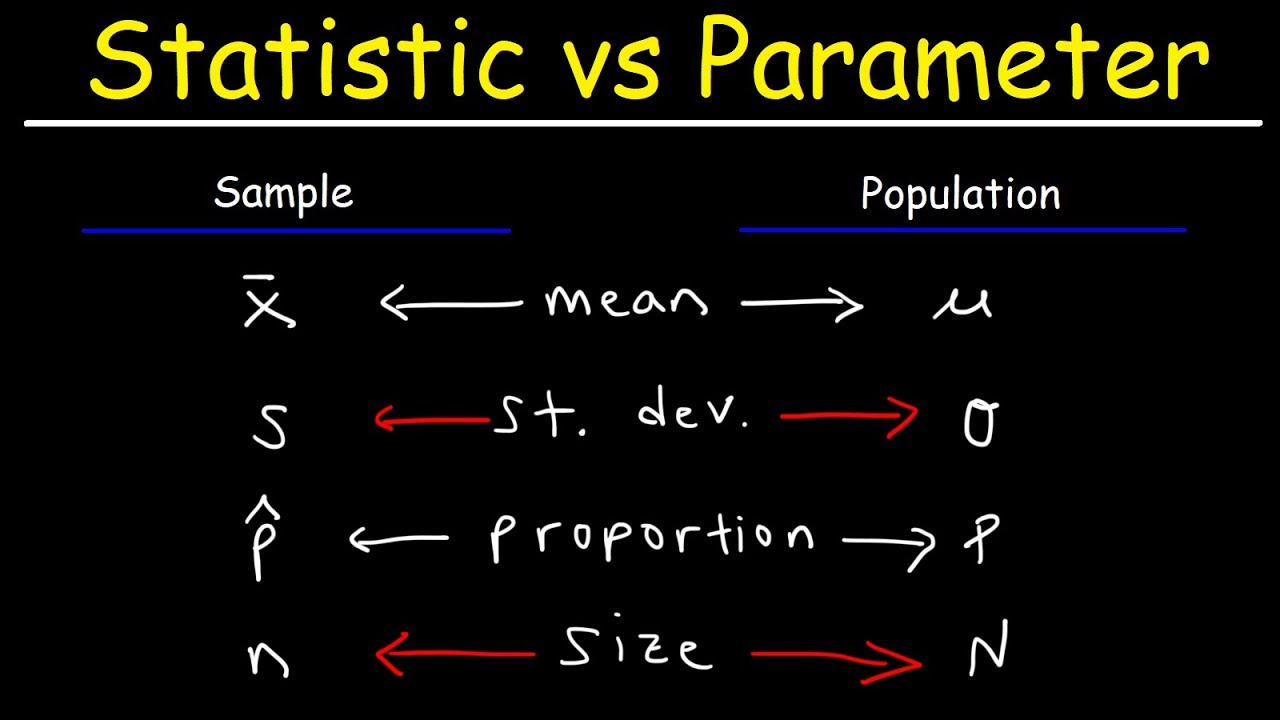
What is the difference between a parameter and a statistic?
-A parameter is a numerical characteristic of the entire population, while a statistic is a numerical characteristic of a sample. The statistic is used to estimate the corresponding parameter.
How is a sample statistic calculated?
-A sample statistic is calculated by performing the same operation (such as finding the average) on the data collected from the sample. For example, the average GPA of a group of students in a sample would be the sum of their GPAs divided by the number of students.
What is the purpose of using a sample statistic to estimate a population parameter?
-The purpose of using a sample statistic to estimate a population parameter is to make inferences about the entire population when it is not feasible to collect data from every member of the population.
How does the concept of 'population' relate to the concept of 'sample' in statistics?
-The population is the entire group of interest, while the sample is a smaller subset taken from this population. The goal is to use the sample to make inferences about the population.
What is an example of a population parameter that might be of interest to a researcher?
-An example of a population parameter that might be of interest to a researcher could be the mean weight of all individuals in the world who eat at a specific fast-food chain, like Burger King.
What is the process of using a sample to make inferences about a population called?
-The process of using a sample to make inferences about a population is called statistical inference.
In the context of the video, what is the main idea or purpose of statistics?
-The main idea of statistics, as presented in the video, is to use samples and their corresponding statistics to make inferences and draw conclusions about the larger population when it is not possible to survey the entire population.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to Populations and Parameters
This paragraph introduces the concept of a population in statistics, defining it as the entire group of individuals or items of interest. It emphasizes that a population can be anything from the GPAs of all students at a college to the average weight of people who eat at Burger King. The paragraph then explains the term 'parameter' as a numerical characteristic that describes an aspect of the population, such as the average GPA or mean weight. It highlights the challenge of surveying entire populations due to their potentially large size and introduces the idea of using samples to represent the population for practical purposes.
📈 Understanding Samples and Statistics
The second paragraph delves into the process of sampling and the role of statistics in representing a population. It defines a sample as a subgroup drawn from the larger population and describes a statistic as the numerical characteristic that describes an aspect of the sample, such as the average GPA or weight of the sampled individuals. The paragraph uses the example of measuring the mean weight of a sample of people who eat at Burger King to illustrate how statistics are derived from samples. It also touches on the broader purpose of statistics, which involves using sample statistics to infer or make predictions about the corresponding parameters of the entire population.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Population
💡Parameter
💡Sample
💡Statistic
💡GPA
💡Mean
💡Statistics
💡Inference
💡Burger King
💡Weight
💡Education
Highlights
The definition of a population is introduced as everything you care about.
A parameter is defined as a number that tells you something about a population.
The population example given involves the GPAs of all students at a local college.
In the real world, it's hard to survey entire populations, so samples are taken.
A sample is a subgroup of the population.
A statistic is a number that describes some aspect of the sample.
The example of a population of all students' GPAs at a school and a parameter being the average GPA is provided.
The concept of taking a sample of 30 students and computing their average GPA as a statistic is explained.
A practical example involving the population of all people in the world who eat at Burger King is given.
The mean weight of the population of Burger King eaters is described as a parameter that's unknown.
The process of taking a sample from the population and calculating the mean weight as a statistic is detailed.
The mean weight of the sample of Burger King eaters is hypothetically given as 175 pounds.
The main idea of statistics is illustrated: having a population of interest, taking a sample, and computing corresponding numbers.
The course's purpose is to teach how to handle populations by using samples and performing calculations.
The transcript emphasizes the importance of understanding the difference between populations and samples in statistical analysis.
Parameters and statistics are critical concepts in understanding and applying statistical methods.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Symbols commonly used in statistics

Statistics - The vocabulary of statistics
Statistic vs Parameter & Population vs Sample
Statistics: Populations & Samples and Parameters vs Statistics
Sample, Statistic, Population, Parameter Part 1
Population And Sample In Statistics Example | Population vs Sample In Statistics | Simplilearn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: