How To Navigate Using the Stars
TLDRThis script explores the ancient and modern practice of celestial navigation, revealing how different cultures perceived stars. It explains the importance of Polaris, the North Star, for northern hemisphere navigation and the Southern Cross for the south. The video also covers techniques for determining directions using stars, such as using Orion's belt and the Pointer Stars, providing practical methods for finding North, South, East, and West by observing the night sky.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Without clouds, approximately 6,000 stars can be seen in the night sky from any location on Earth, but this number is reduced in areas with heavy light pollution.
- 🗺 Throughout history, various cultures have had their own interpretations of what stars represent, from divine beings in Greek mythology to celestial lenses for gods in Yakut beliefs.
- 💫 In Chinese mythology, some stars are associated with specific individuals, such as Jīn Yú and Nu Lang, whose love story is celebrated in the Qixi Festival.
- 🔭 Modern understanding recognizes stars as giant gas clouds undergoing nuclear fusion, which is a stark contrast to the ancient stories.
- 🧭 Navigation using stars is one ancient practice that continues to be relevant, with both ancient travelers and modern sailors and pilots using stars to navigate.
- 🌐 The stars used for navigation differ between the northern and southern hemispheres due to the visibility of certain constellations.
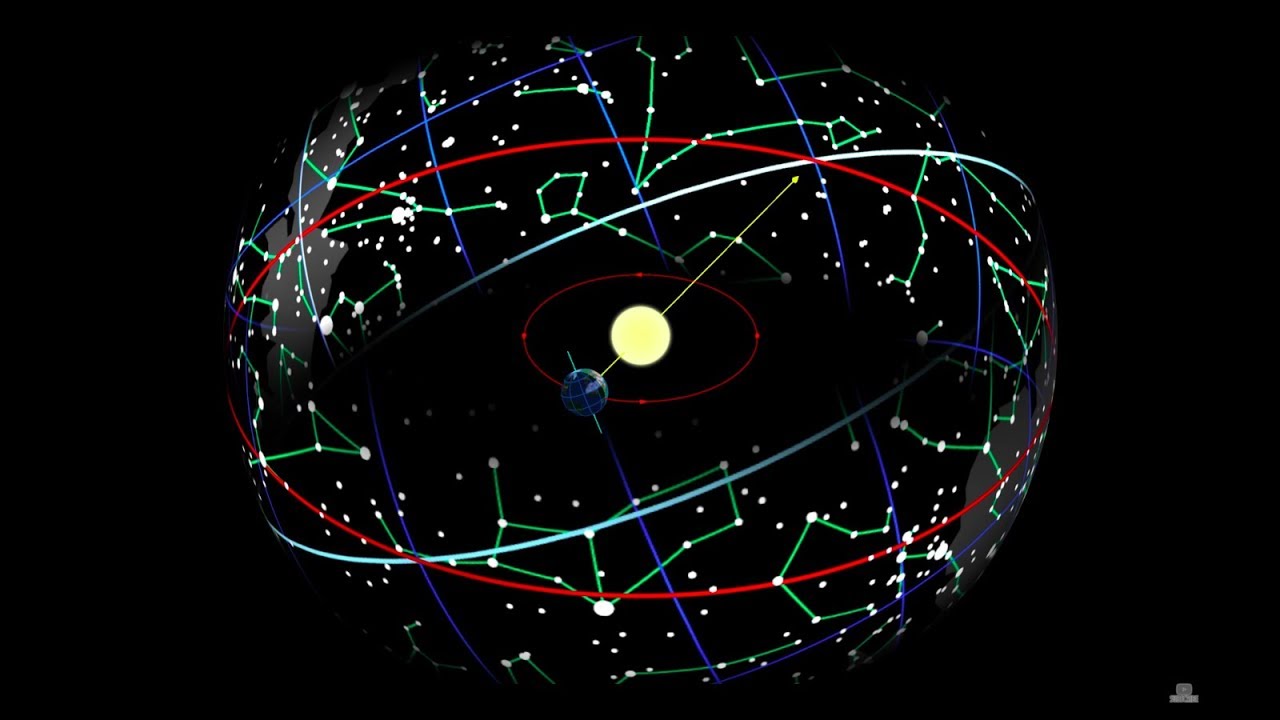
- 🌟 Polaris, the North Star, is a crucial navigational aid in the northern hemisphere, as it remains nearly stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it.
- 🦄 Finding the North Star is facilitated by locating the Big Dipper and following the line created by the stars Dubhe and Merak.
- 🌊 For navigating south, the constellation Orion and his belt are used to determine the direction, with the line extended from his 'sword' pointing towards the south.
- 🔮 In the southern hemisphere, the Southern Cross, or Crux, is used for navigation, with the help of the Pointer Stars to confirm its location.
- 📍 Additional navigational tricks include using the position of stars at the horizon to determine cardinal directions, such as using Orion's belt to find East and West near the equator.
Q & A
How many stars are visible in the night sky without clouds?
-About 6,000 stars are visible in the night sky without clouds.
Why is the number of visible stars lower in areas with heavy light pollution?
-The number of visible stars is lower in areas with heavy light pollution because the artificial lights interfere with the visibility of fainter stars.
What did the Greeks believe constellations to be?
-The Greeks believed constellations to be sentient, divine beings awarded a place among the stars for some great deed done long ago.
How did the Paiute tribe view the stars?
-The Paiute tribe believed that stars were the children of the Father Sun and the Mother Moon, eaten every day by the Sun and nursed back to life by the Moon.
In Chinese mythology, who are Jīn Yú and Nu Lang, and what is their story?
-In Chinese mythology, Jīn Yú is 'the girl who weaves the clouds' and Nu Lang is 'the herdsman who cares for the cattle of the Heavens'. They were in love, and the Gods placed them on either side of the Milky Way to ensure they were never distracted from their duties, allowing them to meet only once a year on the 7th day of the 7th month.
What is the significance of Polaris, the North Star, in navigation?
-Polaris, the North Star, is significant in navigation because it sits virtually on top of true North and barely moves in the sky, serving as a constant reference point for travelers.
How can one find the North Star using the Big Dipper?
-To find the North Star using the Big Dipper, locate the two end stars called Dubhe and Merak, and follow the path they make to find Polaris at the end of the handle.
What constellation is used to navigate southward, and how is it used?
-Orion is the constellation used to navigate southward. By locating Orion's belt and following the direction of his sword down to the horizon, the point should lead south.
What is the Southern Cross, and how is it used for navigation in the southern hemisphere?
-The Southern Cross, officially known as Crux, is used for navigation in the southern hemisphere. By drawing a line from the top and bottom stars of the Crux and another line perpendicular from the Pointer Stars, the intersection point can be used to find South.
How can one determine East and West using Orion's belt near the celestial equator?
-By locating the leading star of Orion's belt, Mintaka, the point on the horizon where it rises is always true East, and where it sets is always true West.
What is a simple method to determine cardinal directions using two sticks and a star?
-A simple method involves planting two sticks in the ground and aligning them with a chosen star. As the star moves out of alignment, the direction of its movement indicates the cardinal direction you are facing (e.g., if the star rises, you are facing East).
Outlines
🌌 Ancient and Modern Star Navigation
This paragraph delves into the historical and cultural interpretations of stars around the world, from Greek constellations representing divine beings to Chinese myths about star-crossed lovers. It also touches on the practical use of stars for navigation, explaining the challenges of using moving celestial bodies for long journeys and the importance of finding a consistent reference point. The explanation highlights the significance of Polaris, the North Star, in the northern hemisphere and how it can be located using the Big Dipper. Additionally, it introduces the concept of using Orion's belt to find the southern direction but notes the limitations of this method.
📍 Southern Hemisphere Star Navigation Techniques
The second paragraph focuses on navigating in the southern hemisphere where Polaris is not visible. It introduces the Southern Cross, or Crux, and the Pointer Stars as key navigational aids. The summary explains how to use the Crux and Pointer Stars to estimate the South direction by drawing imaginary lines in the sky. It also describes alternative methods for determining East and West near the equator using Orion's belt and the rising and setting points of the star Mintaka. The paragraph concludes with a simple trick using two sticks and a star to determine cardinal directions based on the star's movement relative to the sticks.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Stars
💡Constellations
💡Polaris
💡Orion
💡Southern Cross
💡Navigation
💡Light Pollution
💡Mythology
💡Nuclear Fusion
💡Equinoxes
💡Celestial Equator
Highlights
Approximately 6,000 stars are visible in the night sky without clouds, varying with light pollution.
Historically, different cultures had unique beliefs about the nature and significance of stars.
Greeks envisioned constellations as divine beings, while the Paiute tribe saw stars as celestial children.
In Chinese mythology, stars represented people, such as Jīn Yú and Nu Lang, with a romantic tale associated.
Yakut and Turk people had their own interpretations of stars as crystal lenses and rips in a celestial tent.
Contrary to ancient beliefs, stars are now understood as giant gas clouds undergoing nuclear fusion.
Navigation remains a consistent use of stars from ancient times to the present.
Stars' movement due to Earth's rotation makes them unreliable for direct navigation.
The need for a fixed reference point in the sky for consistent navigation is emphasized.
Polaris, the North Star, is nearly stationary and a crucial navigational aid in the northern hemisphere.
Finding Polaris involves locating Ursa Minor or using Ursa Major's end stars as a guide.
Navigating south requires using the constellation Orion and his belt stars to find the direction.
In the southern hemisphere, the Southern Cross, or Crux, is used for navigation.
The Pointer Stars help in identifying the Southern Cross for navigational purposes.
A method to estimate south in the southern hemisphere involves drawing lines from the Crux and Pointer Stars.
Finding north in the southern hemisphere is challenging due to the Earth blocking Polaris.
Orion's belt can help determine true East and West near the celestial equator.
A simple method using two stakes and a star can indicate cardinal directions based on the star's movement.
The video encourages viewers to learn more about stars and their uses beyond navigation.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: