Atoms and Matter for Kids
TLDRThis educational script delves into the fundamental concepts of matter, atoms, and the properties of substances. It explains that matter consists of atoms, the basic building blocks of elements, and how these atoms combine to form molecules and mixtures. The script also distinguishes between physical and chemical changes, using relatable examples like water's states and rust formation. It highlights the unique properties of matter, such as conductivity, malleability, and the differences between pure substances and mixtures, including solutions and alloys.
Takeaways
- 📚 Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space.
- 🔬 Atoms are the tiny building blocks of matter, smaller than a flea, a grain of sand, or a blood cell.
- 💫 An atom consists of a nucleus (made of protons and neutrons) and electrons that orbit around the nucleus.
- ⚛️ The number of protons in an atom determines the type of element it is.
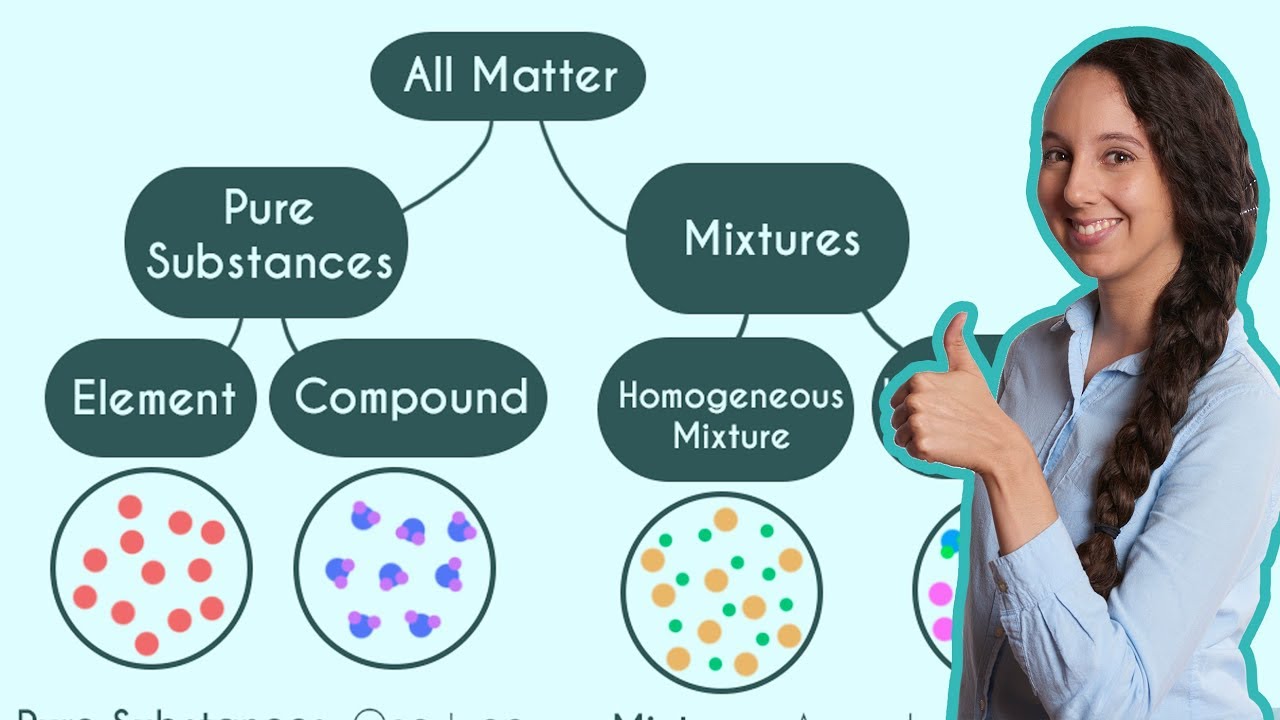
- 🌊 Elements are pure substances made up of only one kind of atom, like helium, oxygen, and gold.
- 🔄 Matter can change states (solid, liquid, gas) under certain conditions, such as melting or boiling.
- 🌡 The temperature at which a substance changes state is called its melting point or boiling point.
- 🧪 Physical properties of matter can be detected with the senses, like feeling cold when touching a metal doorknob.
- 🔩 Metals have various properties including conductivity, luster, and malleability.
- 🧴 A mixture is a combination of different atoms and molecules that can be physically separated, like a fruit salad.
- 💧 A solution is a special kind of mixture where one substance (like salt) dissolves into another (like water), and can be separated with a physical change.
Q & A
What is the definition of matter?
-Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
What are the tiny building blocks of matter called?
-The tiny building blocks of matter are called atoms.
How can atoms be observed?
-Atoms can be observed using special tools such as electron microscopes, although they may still appear fuzzy.
What are the subatomic particles that make up the center of an atom called?
-The center of an atom, known as the nucleus, is made up of protons and neutrons.
What is the term for the tiny particles that move around the outside of an atom's nucleus?
-The tiny particles zipping around the outside of the nucleus are called electrons.
What is the term used to describe substances made up of only one kind of atom?
-Substances made up of only one kind of atom are called elements.
What is a molecule formed by the bonding of different kinds of atoms?
-A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction.
What are the three common states of matter?
-The three common states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
What is the term for the point at which a liquid turns to a solid?
-The point at which a liquid turns to a solid is called the freezing point.
What is a physical change in matter?
-A physical change in matter is a change in form or state that does not alter the chemical properties of the substance.
What is a mixture in the context of matter?
-A mixture is a material system made up of two or more different substances which are not chemically combined.
What is a solution in the context of mixtures?
-A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances, where one is dispersed evenly throughout the other.
Outlines
📚 Understanding Matter and its Properties
This paragraph introduces the concept of matter, explaining it as anything with mass that occupies space. It delves into the composition of matter, discussing atoms as the fundamental building blocks. The script highlights the structure of an atom, including the nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, and electrons orbiting the nucleus. It further explains the difference between elements and compounds, using helium, oxygen, and water molecules as examples. The paragraph also touches on the states of matter and the properties of matter, such as melting and boiling points, and physical properties that can be detected by senses.
🌡️ Thermal Conductivity and the Nature of Metals
This section discusses the concept of thermal conductivity, using the example of a metal doorknob feeling colder than a wooden door despite being at the same temperature. It explains that metals are better conductors than wood, leading to a quicker transfer of heat. The paragraph also explores other properties of metals, such as luster, malleability, and electrical conductivity. It then transitions into a discussion on physical and chemical changes, differentiating between the two using examples like boiling water, crushing a can, and rusting nails. The concept of mixtures is introduced, contrasting them with pure substances and explaining how they can be separated through physical changes.
💧 Mixtures, Solutions, and Alloys
This paragraph delves into the topic of mixtures, differentiating between mixtures and pure substances. It uses the example of a fruit salad to illustrate how mixtures can be separated through physical changes. The script then introduces solutions as a special type of mixture, demonstrating how salt can be separated from water through evaporation. The concept of air as a mixture is also discussed, highlighting its composition of nitrogen and oxygen. The paragraph concludes with a discussion on alloys, specifically bronze, and how their melting points can be used to separate the constituent metals.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Atoms
💡Elements
💡Molecules
💡States of Matter
💡Physical Properties
💡Conductivity
💡Malleability
💡Mixtures
💡Solutions
💡Chemical Changes
Highlights
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space.
Atoms are the tiny building blocks of matter, smaller than a flea or a grain of sand.
An atom is too small to be seen without a microscope.
Atoms are composed of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons.
The number of protons in an atom determines the type of element.
Helium is an element with two protons.
Molecules are formed when different kinds of atoms bond together.
Water (H2O) is a molecule made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Matter can exist in different states: solid, liquid, and gas.
The temperature at which a substance changes state is called its melting point or boiling point.
Physical properties of matter can be detected with the senses, such as feeling cold.
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Malleability is a property of metals that allows them to be shaped into different forms.
Physical changes do not alter the chemical properties of matter.
Chemical changes result in new substances with different properties, such as rust on iron.
Mixtures are combinations of different atoms and molecules that can be separated by physical changes.
A solution is a special kind of mixture where one substance is dissolved in another, like salt in water.
Air is a mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen and oxygen.
Alloys are mixtures of metals, such as bronze which is an alloy of copper and tin.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: