Positive and Negative Charge
TLDRIn this informative segment, Mr. Andersen explores the concept of positive and negative electric charges through the analogy of balloons. He explains that like charges repel each other while opposite charges attract, and introduces the idea of charge polarization in neutral objects, demonstrating how a charged object can induce a separation of charges in a neutral object, leading to attraction. The explanation is complemented by a PHET simulation that visually supports the concepts discussed.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Objects with no charge are neutral, having equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
- 💫 Rubbing objects together can transfer charges, leading to one object becoming positively charged and the other negatively charged.
- 🚫 Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other.
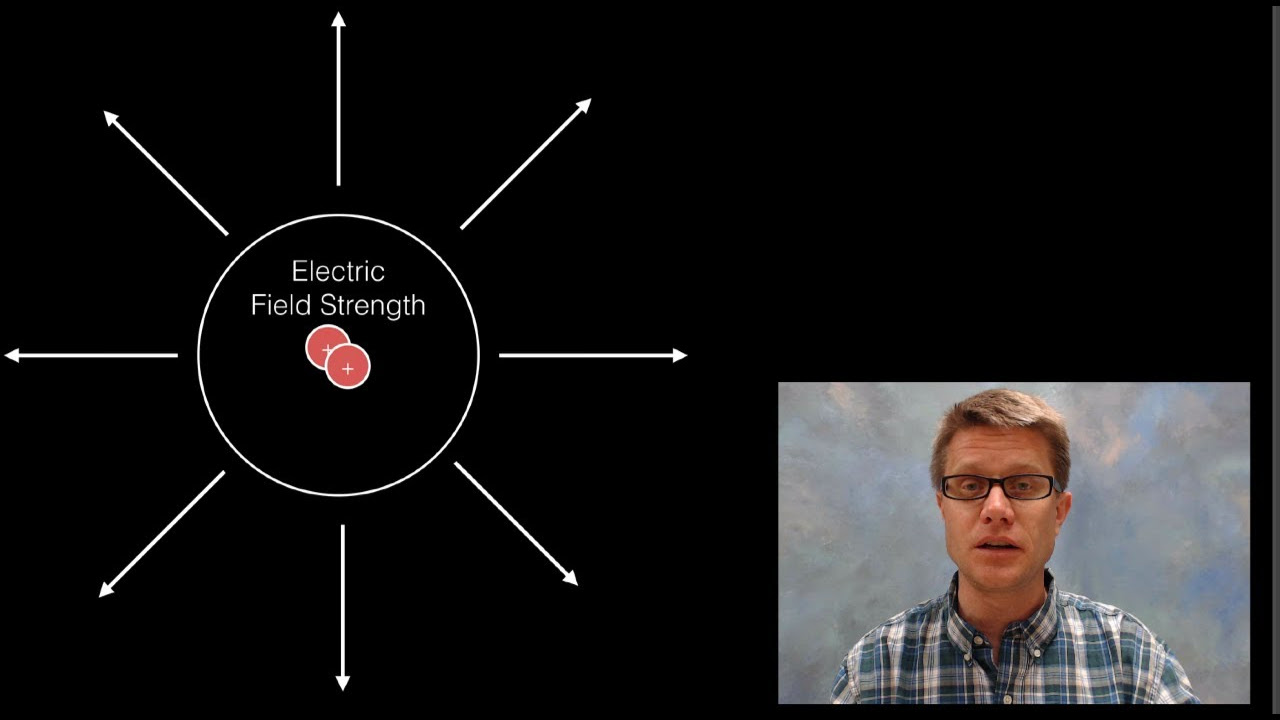
- 🔄 Polarization occurs when a charged object induces a separation of charges in a neutral object, causing an attractive force.
- 🏠 A charged balloon can stick to a neutral wall due to the polarization effect.
- 🎈 Two balloons with the same charge will repel each other when brought close together.
- 🎈 Two balloons with opposite charges will attract each other when in proximity.
- 🔄 The distribution of charges within an object determines whether it is positively, negatively, or neutrally charged.
- 🔗 PHET simulations can help visualize and understand the behavior of electric charges and their interactions.
- 🌟 The transfer of charges from one object to another can result in one object being attracted to a charged object, such as a sweater.
- 📚 Understanding the two-charge model of electric charge is fundamental to grasping the principles of electrostatics.
Q & A
What are the two types of electric charges that scientists speculate exist?
-The two types of electric charges that scientists speculate exist are positive and negative charges.
What happens when you bring two objects with the same charge close to each other?
-When two objects with the same charge are brought close to each other, they will repel each other.
What occurs when two objects with opposite charges are placed next to each other?
-When two objects with opposite charges are placed next to each other, there will be an attractive force between them, causing them to be drawn towards each other.
How does a neutral object become charged when it comes into contact with a charged object?
-A neutral object becomes charged when it comes into contact with a charged object through the process of polarization, where the charges within the neutral object are redistributed, creating a separation of charges.
What is the outcome when a charged balloon is brought near a wall that does not have a charge?
-When a charged balloon is brought near a wall that does not have a charge, the wall can become polarized, leading to an attractive force between the charged balloon and the wall.
How does rubbing a balloon on a sweater affect its charge?
-Rubbing a balloon on a sweater transfers negative charges from the sweater to the balloon, resulting in the balloon becoming negatively charged.
What is the significance of the two-charge model in understanding electric charge?
-The two-charge model is significant in understanding electric charge as it explains the interactions between charged objects, the concept of neutrality, and the process of polarization.
What happens when two balloons, both negatively charged, are brought close to each other?
-When two balloons, both negatively charged, are brought close to each other, they will repel each other due to the like charges.
How can a charged object affect the charges within a neutral object?
-A charged object can affect the charges within a neutral object by polarizing it, causing the charges within the neutral object to redistribute and creating an attractive force between the two objects.
What is the role of charge distribution in determining whether an object is positively or negatively charged?
-The distribution of charges plays a crucial role in determining whether an object is positively or negatively charged. If there is a greater number of negative charges, the object is negatively charged, and if there is a greater number of positive charges, the object is positively charged.
What can be concluded about the interaction between charged objects based on the script?
-Based on the script, it can be concluded that like charges repel each other and opposite charges attract each other, and that charged objects can induce polarization in neutral objects, leading to attraction.
Outlines
🔋 Understanding Positive and Negative Charges
The paragraph introduces the concept of positive and negative charges through the example of a neutral balloon being rubbed on the head to acquire a charge. It explains that like charges repel each other while opposite charges attract. The concept of a neutral object having equal amounts of positive and negative charges is discussed, as well as the polarization of charges when a charged object is brought near a neutral one, leading to attraction. The use of a simulation by PHET to illustrate these concepts is mentioned, along with a demonstration of charging a balloon and observing its interactions with different objects.
🌟 Recap and Application of Electric Charge Principles
This paragraph summarizes the key points from the previous discussion, emphasizing the understanding of the two-charge model of electric charge. It reiterates that neutral objects have equal amounts of positive and negative charges, and that the distribution of these charges determines whether an object is positively or negatively charged. The paragraph also highlights the learning objective of explaining how the polarization of electric charge in a neutral object can result in attraction when in proximity to a charged object.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Positive and Negative Charges
💡Polarization
💡Attraction and Repulsion
💡Electric Charge
💡Neutral Object
💡Charged Object
💡PhET Simulation
💡Rubbing
💡Transfer of Charges
💡Two-Charge Model
💡Electric Field
Highlights
Mr. Andersen introduces the concept of positive and negative charges in AP physics essentials double O 7.
Rubbing a neutral balloon on the head imparts a charge to the balloon.
A charged balloon will be repelled by a similarly charged object and attracted to one with an opposite charge.
A neutral object has equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
A charged object has an unequal distribution of electric charges.
Opposite charges attract each other, while like charges repel.
A charged balloon can polarize a neutral object, causing an attractive force.
Polarization involves moving charges within a neutral object to create a temporary charge distribution.
The process of polarization is demonstrated with a charged balloon and a neutral wall.
Rubbing a balloon on a sweater transfers negative charges from the sweater to the balloon, creating a negatively charged object.
When a negatively charged balloon approaches a neutral wall, it polarizes the wall, causing an attraction without charge transfer.
Two balloons with the same negative charge will repel each other, demonstrating the repulsion of like charges.
The two-charge model of electric charge explains the behavior of charged objects.
The distribution of charges determines whether an object is positively or negatively charged.
Understanding polarization and charge separation in neutral objects can lead to the prediction of attractive forces.
A charged balloon and a previously neutral wall exhibit an attractive force due to polarization.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: