TYPES OF ENERGY | Physics Animation
TLDRIn this educational episode by Earthben, viewers embark on an intriguing journey through the world of physics, focusing on the diverse types of energy. The video starts with an exploration of kinetic and potential energy, laying the foundation for understanding energy's nature. It then dives into thermal, radiant, light, chemical, nuclear, electrical, gravitational, and mechanical energy, explaining each type's production, properties, and real-world applications. Through engaging examples like the warmth of a hot pot, the power of lightning, and the thrill of a roller coaster, Earthben makes complex concepts accessible and fascinating. This episode promises to enlighten learners about energy's various forms and their significance in our daily lives and the universe.
Takeaways
- 🌡️ Thermal Energy is the energy produced when temperature rises, causing atoms and molecules to move faster and collide with each other.
- 💡 Radiant Energy is a form of electromagnetic energy, including visible light, X-rays, and heat from the sun, transmitted through electromagnetic waves.
- 💥 Light Energy is a type of electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye, formed by the movement of photons, which are produced when an object's atoms heat up.
- ⚗️ Chemical Energy is stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules and is released during chemical reactions, found in food, wood, and photosynthesis.
- ⚡️ Electrical Energy is generated by the movement of electrons and is a form of kinetic energy, examples include lightning and electric eels.
- 🌐 Gravitational Energy is the potential energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field, increasing as it moves further from the Earth's center.
- 🏎️ Mechanical Energy is the energy an object acquires due to its motion or position, which can be kinetic (like a moving car) or potential (like a ball lifted above the ground).
- ♻️ Nuclear Energy comes from the nucleus of atoms and is released through nuclear fusion or fission, used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
- 🔥 The hotter a substance is, the more thermal energy it has, and the faster its particles move.
- 🌳 Plants use light energy during photosynthesis to capture energy from the sun and produce their food.
- 🔄 Nuclear power plants must shut down every 18 to 24 months to dispose of used uranium fuel, which becomes radioactive waste.
Q & A
What are the two broad categories of energy mentioned in the script?
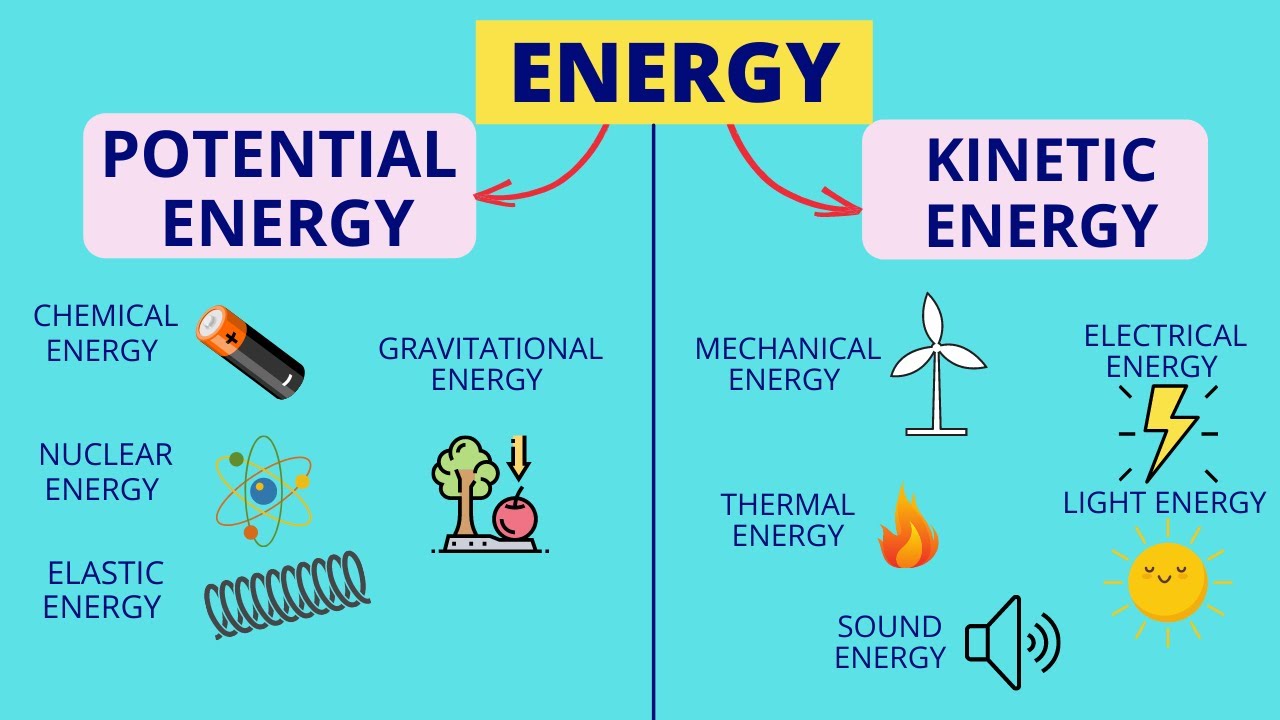
-The two broad categories of energy mentioned are kinetic energy and potential energy.
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of moving objects.
How is thermal energy produced?
-Thermal energy is produced when there is a rise in temperature, causing atoms and molecules to move faster and collide with each other.
What is an example of how thermal energy is transferred?
-An example is when you touch a hot pot, the thermal energy from the pot is transferred to your hand, causing a burn sensation.
What is radiant energy and how is it related to light energy?
-Radiant energy is a form of electromagnetic energy, which can take the form of visible waves, known as light energy.
How is light energy formed?
-Light energy is formed through the movement of photons, which are produced when an object's atoms heat up.
What is chemical energy and where is it stored?
-Chemical energy is stored in the bonds that connect atoms and molecules. It is released when a chemical reaction takes place.
How is nuclear energy released?
-Nuclear energy is released through nuclear fusion or nuclear fission processes.
What are the two ways nuclear energy can be generated?
-Nuclear energy can be generated through nuclear fusion, where nuclei are fused together, or nuclear fission, where nuclei are split apart.
What is electrical energy and how is it related to electron movement?
-Electrical energy is caused by the movement of electrical charges called electrons. The faster the electrons move, the more electrical energy they carry.
How is gravitational energy related to an object's position?
-Gravitational energy is the potential energy stored by an object due to its position relative to a reference point, such as the Earth's center. It increases as an object moves further away from this reference point.
What is mechanical energy and how can it be categorized?
-Mechanical energy is the energy an object acquires due to its motion or position. It can be categorized as either kinetic energy, when the object is in motion, or potential energy, when the object is at rest.
Outlines
🌡️ Types of Energy - Introduction and Thermal Energy
This paragraph introduces the topic of energy in physics, focusing on the basic forms of energy: kinetic and potential. It further elaborates on other types of energy including thermal, radiant, light, chemical, nuclear, electrical, gravitational, and mechanical energy. The main focus is on thermal energy, explaining it as the energy produced by the rise in temperature causing atoms and molecules to move faster. An example of transferring thermal energy from a hot pot to one's hand is provided to illustrate the concept.
🌞 Radiant and Light Energy, Chemical and Nuclear Energy
This paragraph delves into radiant energy, which is a form of electromagnetic energy, and light energy, a visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. It explains how light energy is formed through the movement of photons and its various applications, including natural light from the sun and artificial light from sources like candles and light bulbs. The paragraph also covers chemical energy stored in atomic bonds and its release during chemical reactions, highlighting its widespread use in everyday life. Additionally, it introduces nuclear energy, discussing its sources, the process of nuclear fission, and the operation of nuclear power plants.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Thermal Energy
💡Radiant Energy
💡Light Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Nuclear Energy
💡Electrical Energy
💡Gravitational Energy
💡Mechanical Energy
Highlights
Energy can be categorized into two broad topics: kinetic energy and potential energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy of moving objects.
Potential energy is energy that is stored.
Thermal energy is produced when there is a rise in temperature, causing atoms and molecules to move faster.
Thermal energy transfer occurs when a hotter substance increases the thermal energy of another substance through contact.
Radiant energy is a form of electromagnetic energy, which includes light energy.
The sun produces radiant energy that reaches Earth as light.
Light energy is a type of kinetic energy in the electromagnetic spectrum, formed through the movement of photons.
Chemical energy is stored in the bonds that connect atoms and molecules.
Chemical reactions release stored chemical energy, which is widely used in various forms such as food, wood burning, and photosynthesis.
Nuclear energy comes from the nucleus of atoms and is released through nuclear fusion or fission.
Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission of uranium to generate electricity.
Electrical energy is caused by the movement of electrical charges, known as electrons.
Lightning is an example of electrical energy.
Gravitational energy is the potential energy stored by an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
Mechanical energy is the energy an object acquires due to its motion or position.
A moving car possesses mechanical energy in the form of kinetic energy.
A ball lifted over your head has mechanical energy in the form of potential energy.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Energy | Forms of Energy | Law of Conservation of Energy | Science Lesson for Kids

What is Kinetic and Potential Energy? [Stored Energy & Energy of Movement]

Types of Energy - General Science for Kids!

Conversion of Energy

Energy | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids

Types of Energy & the Law of Conservation of Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: