Energy | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids
TLDRThis engaging video script introduces the concept of energy, highlighting its various forms such as kinetic, potential, mechanical, chemical, electrical, and gravitational energy. It explains how energy is neither created nor destroyed but transforms from one form to another, using everyday examples like eating, sunlight, and street lights to illustrate the point. The script also touches on the efficiency of energy use, mentioning that only 10% of a light bulb's energy is used for light, with 90% creating heat, emphasizing the importance of understanding energy in our daily lives.
Takeaways
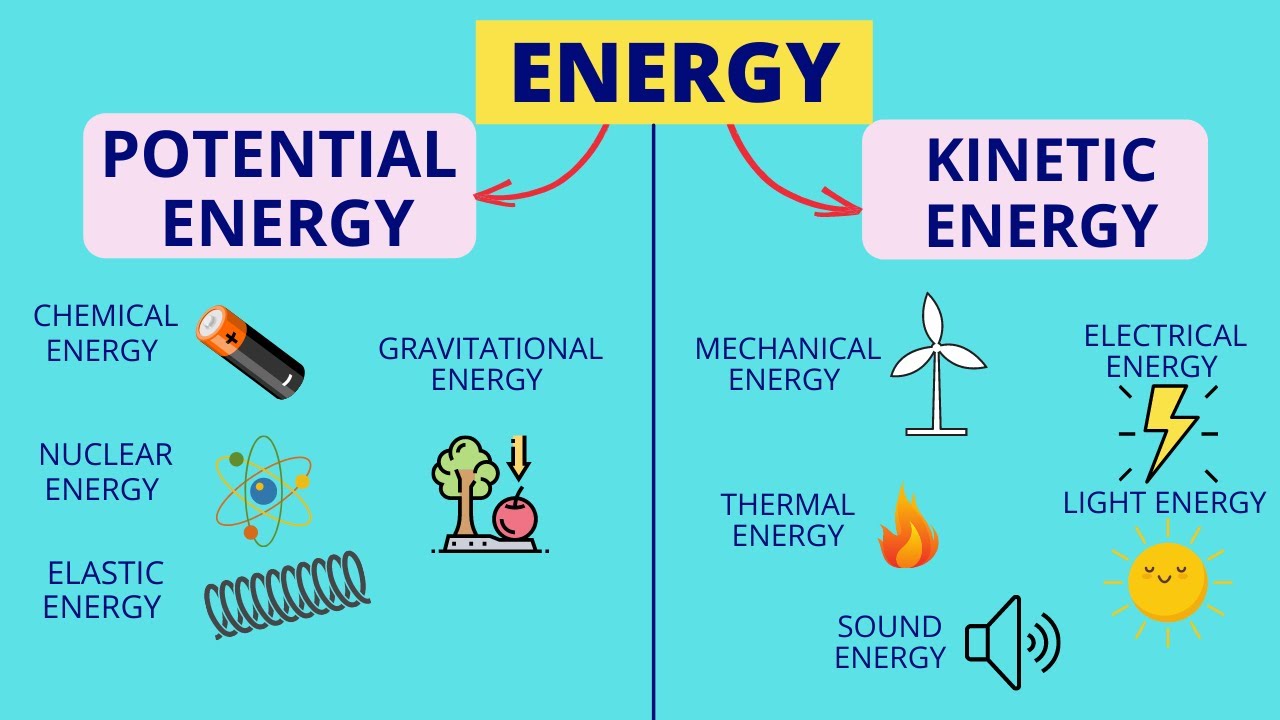
- 🌞 Energy is the capacity to do work and is found in various forms.
- 🍔 When we eat, our body converts food into energy for activities.
- 🏫 Sunlight provides heat and light, which are forms of solar energy.
- 💡 Street lights utilize electrical energy to illuminate our paths.
- 🏃 Kinetic energy is associated with motion, like the moving air around us.
- 🔋 Potential energy is stored energy within an object, ready to be released.
- 🔄 Energy守恒定律 states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
- 🏌️♂️ Mechanical energy is the combination of potential and kinetic energy in an object, like a demolition ball.
- 🌿 Chemical energy is released during chemical reactions, such as digestion.
- ⚡ Electrical energy powers devices like light bulbs, converting it into light and heat.
- 🌱 Gravitational energy is the force that causes objects to fall due to Earth's gravity.
- 💡 Only 10% of a light bulb's energy is used for light; 90% is converted to heat.
Q & A
What is the fundamental concept of energy discussed in the script?
-The fundamental concept discussed is that energy is the ability to do work and it exists in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, mechanical, chemical, electrical, and gravitational energy.
How does the body obtain energy from food?
-The body breaks down food to release energy that can be used for work and play.
What are the two main forms of energy mentioned in the script?
-The two main forms of energy mentioned are kinetic energy, which is the energy in motion, and potential energy, which is the energy stored inside an object.
How is kinetic energy exemplified in the script?
-Kinetic energy is exemplified by the movement of air around us, as it is in motion.
What happens to the ball's energy when it is pushed?
-When the ball is pushed, its potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy as it starts rolling.
What is the principle that energy can neither be destroyed nor created?
-This principle, known as the conservation of energy, states that energy can only change forms, not be created or destroyed.
What is mechanical energy?
-Mechanical energy is the sum of potential and kinetic energy in an object. For example, a demolition ball has potential energy at rest and kinetic energy when it moves.
How is chemical energy released during digestion?
-Chemical energy is released during digestion as food is broken down into simpler components.
What is the nature of electrical energy?
-Electrical energy is associated with electricity, which can produce light and heat, as seen in a light bulb.
How does gravitational energy work?
-Gravitational energy is the motion caused by gravity, such as an object falling to the ground due to Earth's gravitational pull.
What percentage of energy in a light bulb is used to create light, and what happens to the rest?
-Only 10 percent of a light bulb's energy is used to create light, while 90 percent is converted into heat.
How does the script relate friendship to energy?
-The script compares friendship to energy by saying that just like energy, friendship cannot be destroyed.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Energy
This paragraph introduces the concept of energy, defining it as the ability to do work. It explores various forms of energy such as kinetic, potential, mechanical, chemical, electrical, and gravitational energy. The paragraph uses everyday examples to illustrate these concepts, such as the energy we get from food, sunlight, street lights, and the energy transformation in a demolition ball. It also touches on the idea that energy cannot be destroyed or created, only transformed from one form to another, and ends with a metaphor comparing friendship to energy.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Mechanical Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Electrical Energy
💡Gravitational Energy
💡Photosynthesis
💡Conservation of Energy
💡Efficiency
💡Friendship
Highlights
Energy is defined as the ability to do work.
Energy can be found in various forms, such as in food, sunlight, and electrical energy.
The human body converts food into energy for work and play.
Sun's energy is received in the form of heat and light at school.
Street lights utilize electrical energy to provide illumination.
Kinetic energy is associated with motion.
Potential energy is stored energy within an object.
Air movement is an example of kinetic energy.
Potential energy can be transformed into kinetic energy, as demonstrated with a rolling ball.
Energy conservation principle states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Mechanical energy is the combination of potential and kinetic energy in an object.
Chemical energy is released during chemical reactions, such as digestion.
Electrical energy powers devices like light bulbs, which also produce heat.
Gravitational energy is the motion caused by gravity, like an object falling to the ground.
Plants convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
A light bulb's energy is mostly converted into heat, with only 10% used for light.
The concept of energy is likened to friendship, suggesting it is enduring and cannot be destroyed.
The analogy of a demolition ball illustrates the transformation of potential to kinetic and then to mechanical energy upon impact.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

GRADE-4 | SECOND TERM 2024 |CONCEPT 3.1..Energy chains & law of conservation of Energy YALLA SCIENCE

Types of Energy - General Science for Kids!

Energy Stores and Transfers
Energy | Forms of Energy | Law of Conservation of Energy | Science Lesson for Kids

GCSE Physics - Conservation of Energy #4

GCSE Physics - Energy Stores, Transferring Energy & Work Done #1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: