What is Kinetic and Potential Energy? [Stored Energy & Energy of Movement]
TLDRIn this educational video, Mr. Lara introduces viewers to the concepts of kinetic and potential energy, defining energy as the capacity to do work or cause change. The script explains various forms of energy, including gravitational, elastic, chemical, nuclear, mechanical, electrical, sound, radiant, and thermal. It emphasizes that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred, and illustrates the transformation between potential and kinetic energy with examples like a bicycle going downhill or a roller coaster in motion.
Takeaways
- 📚 Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change.
- ⚙️ Changes in energy can occur in various forms such as temperature, chemical structure, or the movement of an object.
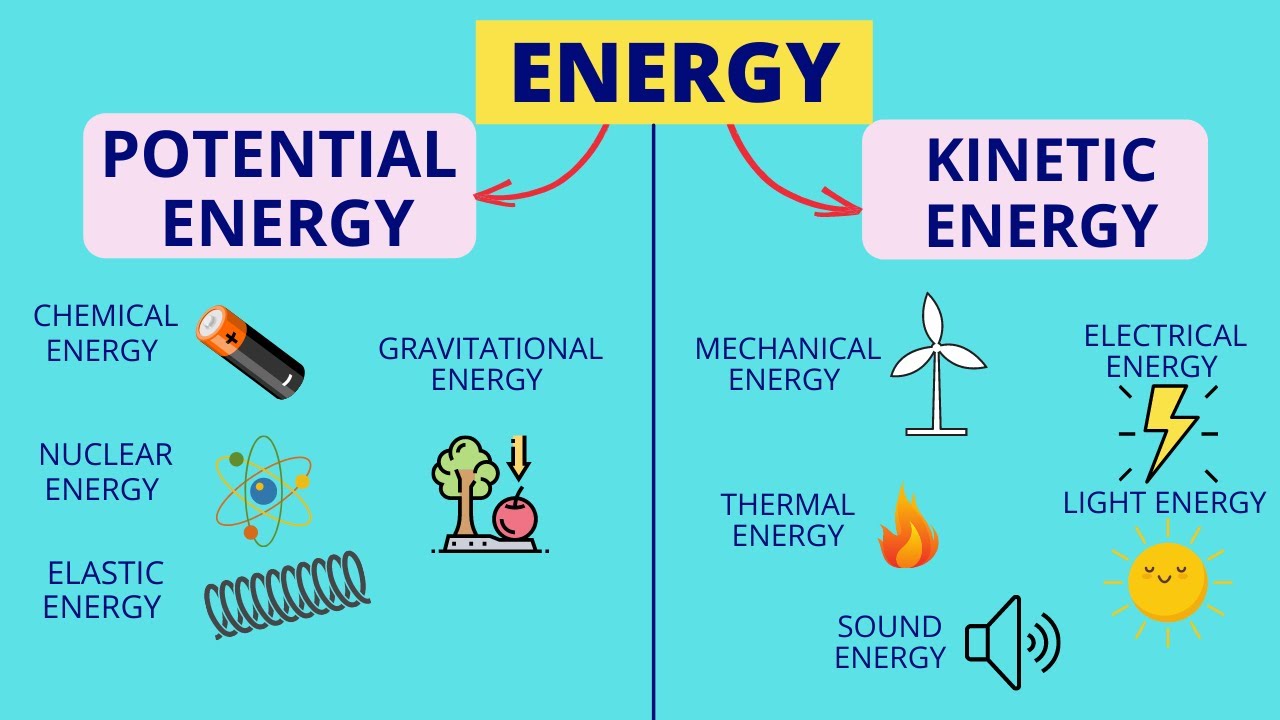
- 🔋 All energy within a system is classified as either potential or kinetic and is measured in joules.
- 🏋️ Potential energy is stored energy and can be found in four types: gravitational, elastic, chemical, and nuclear.
- 🏃♂️ Kinetic energy is the energy of motion or movement, including mechanical, electrical, sound, radiant, and thermal energies.
- 🚴♀️ Mechanical energy involves movement such as cycling, skateboarding, or driving.
- 🔌 Electrical energy is the movement of charged particles within a closed circuit, powering electronic devices.
- 🔊 Sound energy is the energy that moves in sound waves, like those from a speaker.
- 🌞 Radiant energy is electromagnetic energy that travels through sunlight, radio waves, and x-rays.
- 🌡️ Thermal energy is the heating of objects causing atoms and molecules to vibrate, move rapidly, and collide.
- 🔄 Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred between objects or systems.
- 🎢 Examples of potential energy transforming into kinetic energy include a bicycle going downhill and a roller coaster starting from the top.
Q & A
What is the definition of energy?
-Energy is defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause a change. It can exist in various forms and can be transferred between objects or systems but cannot be created or destroyed.
What are the two main classifications of energy?
-The two main classifications of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy, while kinetic energy is energy in motion.
How is energy measured?
-Energy is measured in units called joules. A joule represents the amount of energy needed for a change to take place within a system.
What are the four types of potential energy mentioned in the script?
-The four types of potential energy mentioned are gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical energy, and nuclear energy.
Can you provide an example of gravitational potential energy?
-An example of gravitational potential energy is a child on a slide, a ball at the top of a hill, or a hammer that is raised.
What is an example of elastic potential energy?
-Examples of elastic potential energy include a stretched spring, a rubber band, or a stretched bow.
What types of kinetic energy are mentioned in the script?
-The types of kinetic energy mentioned are mechanical energy, electrical energy, sound energy, and radiant energy.
How can potential energy be transformed into kinetic energy?
-Potential energy can transform into kinetic energy when an object or system is allowed to change due to external forces, such as gravity. For instance, a bicycle at the top of a hill has potential energy, which is converted to kinetic energy as it goes down the hill.
What happens to the potential and kinetic energy of a roller coaster as it goes down a hill?
-As the roller coaster goes down the hill, its potential energy decreases while its kinetic energy increases. The stored energy at the top of the hill is transformed into the energy of movement as the roller coaster descends.
What is the significance of the law of conservation of energy?
-The law of conservation of energy states that all forms of energy can never be created or destroyed but can only be transferred between objects or systems. This principle is fundamental in understanding energy transformations and the dynamics of physical processes.
How does the concept of kinetic energy relate to everyday activities like cycling or driving a car?
-Kinetic energy relates to everyday activities as it involves the energy of motion. When cycling or driving a car, the mechanical energy from the movement of these activities is an example of kinetic energy in action.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Kinetic and Potential Energy
This paragraph introduces the concepts of kinetic and potential energy, explaining that energy is the ability to do work or cause change. It outlines that energy can change in various forms, such as temperature, chemical structure, or the motion of an object. The paragraph emphasizes that energy within a system is classified as either potential or kinetic and is measured in joules. Potential energy is defined as stored energy, while kinetic energy is associated with motion. The paragraph also lists different types of potential energy, including gravitational, elastic, chemical, and nuclear energy, providing examples for each. Kinetic energy is described as energy in motion, with examples like mechanical energy from cycling or driving, electrical energy from charged particles, sound energy from speakers, radiant energy from sunlight and radio waves, and thermal energy from heated objects.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Potential Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Elastic Potential Energy
💡Chemical Energy
💡Nuclear Energy
💡Mechanical Energy
💡Electrical Energy
💡Sound Energy
💡Radiant Energy
💡Thermal Energy
Highlights
Kinetic and potential energy are fundamental concepts in physics, found all around us.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change.
Energy can change in various forms such as temperature, chemical structure, or the speed and position of an object.
All energy within a system is classified as either potential or kinetic and is measured in joules.
Potential energy is defined as stored energy, while kinetic energy is energy in motion.
There are four types of potential energy: gravitational, elastic, chemical, and nuclear.
Gravitational potential energy can be seen in a child on a slide, a ball at the top of a hill, or a raised hammer.
Elastic potential energy is found in objects like a stretched spring, rubber band, or a stretched bow.
Chemical energy is stored energy found in fossil fuels, sunlight captured by plants, batteries, and calories in food.
Nuclear energy is potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom.
Kinetic energy involves movement and can be found in mechanical energy, electrical energy, sound energy, radiant energy, and thermal energy.
Mechanical energy is involved in activities like cycling, skateboarding, and driving a car.
Electrical energy powers electronic devices through the movement of electrically charged particles within a closed circuit.
Sound energy moves and travels in sound waves, like those from a speaker.
Radiant energy is the electromagnetic energy that travels through sunlight, radio waves, and x-rays.
Thermal energy is the heating of objects that cause atoms and molecules to vibrate, move rapidly, and collide with each other.
All forms of energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can only be transferred between objects or systems.
Potential energy can transform into kinetic energy, and vice versa, such as a bicycle rider going downhill.
The roller coaster example illustrates the transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy as it goes down the hill.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

GCSE Physics - Energy Stores, Transferring Energy & Work Done #1

Energy Stores and Transfers

Types of Energy - General Science for Kids!
Energy | Forms of Energy | Law of Conservation of Energy | Science Lesson for Kids
6.1 Energy and the First Law of Thermodynamics | High School Chemistry

Types of Energy & the Law of Conservation of Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: