One-Way ANOVA with LSD (Least Significant Difference) Post Hoc Test in Excel
TLDRDr. Grande's video tutorial demonstrates how to perform a Least Significant Difference (LSD) post-hoc test in Microsoft Excel, following an ANOVA analysis. The video guides viewers through the process of identifying significant differences between groups using fictitious data, with a focus on unequal sample sizes. It explains conducting an ANOVA, calculating the LSD value, and comparing mean differences to determine statistical significance, ultimately comparing results obtained from both Excel and SPSS.
Takeaways
- 📊 The video is a tutorial on performing a Least Significant Difference (LSD) post-hoc test using Microsoft Excel, following an ANOVA analysis.
- 🔍 LSD is used to identify specific group differences after an ANOVA indicates a significant overall effect.
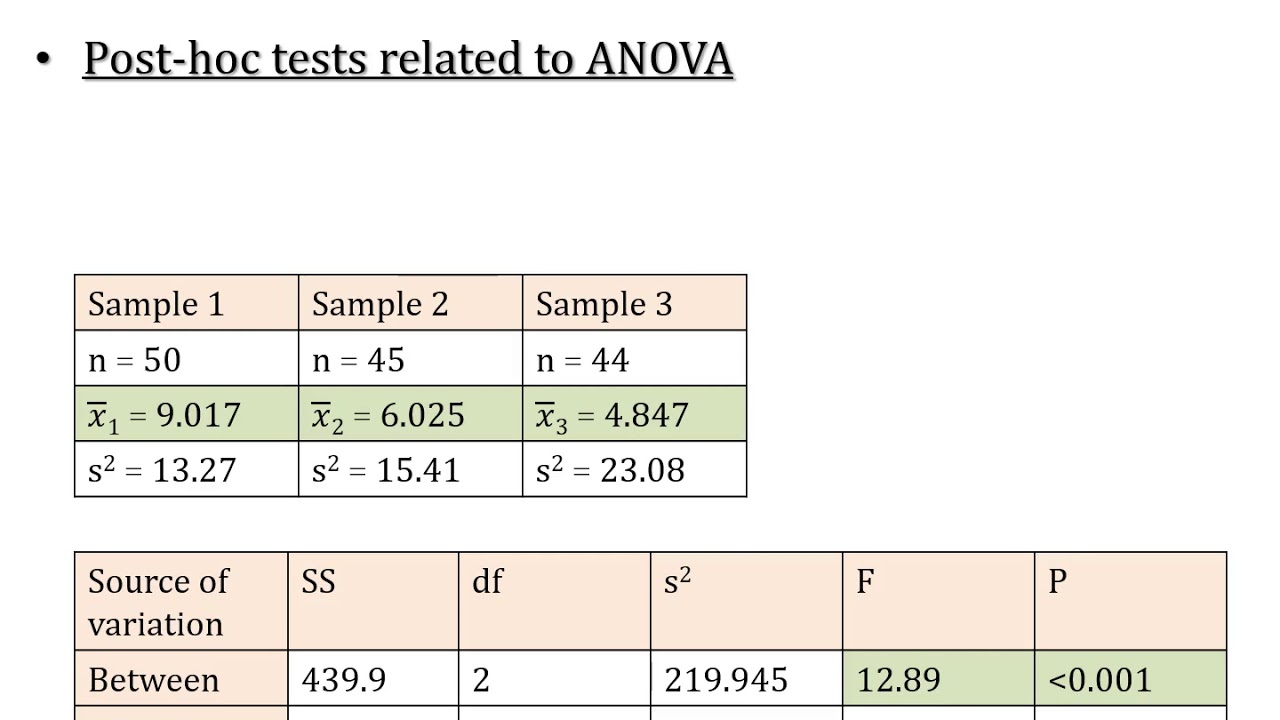
- 📈 The example data involves three groups: CBT, group therapy, and treatment as usual, with different sample sizes.
- 🧑🏫 The presenter explains how to enable the Data Analysis Toolpack in Excel if it's not already available.
- 📝 The ANOVA test is conducted using the Data Analysis Toolpack, with input ranges including labels for the groups.
- 📊 The output of the ANOVA provides sample sizes, average scores, and statistical information like degrees of freedom and P-value.
- 📉 A significant finding in the ANOVA is indicated by a P-value below the alpha level (0.05 in this case).
- 🔢 The LSD formula is explained, involving the critical value of T, degrees of freedom, and mean square within from the ANOVA table.
- ✅ The presenter demonstrates how to calculate the LSD value and compare it with the absolute value of the mean differences between groups.
- 📊 The video also shows how to perform the same analysis in SPSS, using the post-hoc test feature with LSD under equal variances assumed.
- 🔑 The final comparison in both Excel and SPSS leads to the conclusion of significant differences between certain group pairs.
Q & A
What does LSD stand for in the context of the video?
-LSD stands for Least Significant Difference, a statistical test used to determine where differences lie among groups after performing an ANOVA.
What is the purpose of conducting an ANOVA before an LSD post-talk test?
-The purpose of conducting an ANOVA is to determine if there is a statistically significant difference overall among the groups. The LSD post-talk test is then used to identify which specific pairs of groups have significant differences.
Can the LSD post-talk test be used with both equal and unequal sample sizes?
-Yes, the LSD post-talk test can be used with both equal and unequal sample sizes, as demonstrated in the video with the example of different sample sizes for the CBT, group therapy, and treatment as usual.
How can one enable the Data Analysis function in Excel if it is not available?
-To enable the Data Analysis function in Excel, go to File, then Options, and in the Excel Options dialogue, navigate to Add-ins. Under Manage, select 'Excel Add-ins', and ensure that 'Analysis ToolPak' is checked.
What is the input range for the ANOVA in the video?
-The input range for the ANOVA in the video is from A1 to C31, which includes the labels and all the data for the groups.
What does the alpha value represent in the context of ANOVA and LSD tests?
-The alpha value represents the level of significance or the probability of making a Type I error (false positive). In the video, it is set to 0.05, which is a common threshold for statistical significance.
What is the formula used to calculate the Least Significant Difference (LSD) in the video?
-The formula used in the video to calculate the LSD is LSD = T(α, df) * sqrt(Mean Square Within / (1/n1 + 1/n2)), where T(α, df) is the critical value of T at the specified alpha and degrees of freedom, and n1 and n2 are the sample sizes of the two groups being compared.
How does one determine if there is a statistically significant difference between two group means using LSD?
-To determine if there is a statistically significant difference, compare the calculated LSD value with the absolute value of the mean difference between the two groups. If the absolute mean difference is greater than the LSD, there is a statistically significant difference.
What is the critical value of T used in the video for the LSD calculation?
-The critical value of T used in the video for the LSD calculation is 1.99, which corresponds to a two-tailed T distribution with an alpha of 0.05 and 80 degrees of freedom.
How does the video demonstrate the comparison of group means using the LSD test?
-The video demonstrates the comparison by calculating the absolute value of the mean difference between the CBT and group therapy levels and comparing it to the calculated LSD value. If the absolute mean difference exceeds the LSD, the difference is statistically significant.
What is the result of the LSD test when comparing the CBT and group therapy levels in the video?
-The result of the LSD test when comparing the CBT and group therapy levels shows a statistically significant difference, as the absolute value of the mean difference (5.169) is greater than the calculated LSD value (3.02).
How does the video compare the results obtained from Excel with those from SPSS?
-The video shows that after conducting the same analysis in SPSS, the results obtained are consistent with those from Excel, confirming the statistical significance of the difference between the CBT and group therapy levels.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to LSD Post Hoc Test in Excel
Dr. Grande introduces a video tutorial on conducting a Least Significant Difference (LSD) post hoc test using Microsoft Excel. The test is utilized after an ANOVA to pinpoint the specific differences between groups. The video features fictitious data with three groups: CBT, group therapy, and treatment as usual, aiming to measure functioning through an assessment. The purpose of the ANOVA is to determine if there is a statistically significant overall difference, while the LSD test reveals which specific pairs of groups differ significantly. The video covers the process of conducting an ANOVA and setting up the LSD test in Excel, including enabling the Data Analysis Toolpak if necessary.
🔍 Performing LSD Test Calculations and SPSS Comparison
This paragraph details the step-by-step process of calculating the LSD value in Excel. It begins with determining the critical value of T from the two-tailed inverse of the student's T-distribution, using the specified alpha level and degrees of freedom from the ANOVA results. The calculation continues with the mean square within from the ANOVA table and the sample sizes of the groups being compared. The resulting LSD value is then compared to the absolute difference between the group means to assess statistical significance. The video also demonstrates how to perform the same analysis in SPSS, using its General Linear Model and post hoc tests to confirm the findings from Excel, ensuring the consistency of results across different statistical software.
📞 Conclusion and Offer of Assistance
In the concluding paragraph, Dr. Grande offers help to viewers who may have questions or concerns about conducting an LSD post hoc test in Excel. The video aims to be informative and assists viewers in understanding the statistical process thoroughly. Dr. Grande encourages viewers to reach out for further assistance, emphasizing a supportive and educational approach to statistical analysis.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡LSD
💡ANOVA
💡Post Hoc Test
💡Sample Size
💡Degrees of Freedom
💡Mean Square Within
💡Critical Value
💡Statistical Significance
💡Mean Difference
💡SPSS
💡Excel
Highlights
Introduction to performing an LSD post-talk test using Microsoft Excel for analyzing data after ANOVA.
Explanation of LSD (Least Significant Difference) and its use in identifying specific group differences after ANOVA.
Presentation of fictitious data involving three groups: CBT, group therapy, and treatment as usual.
Assumption that all scores are from an assessment measuring functioning.
Description of how ANOVA determines overall statistical significance but not specific group differences.
LSD post-talk test applicability to both equal and unequal sample sizes.
Guidance on enabling the Data Analysis function in Excel if not present.
Step-by-step process of conducting ANOVA in Excel using the Data Analysis tool.
Importance of interpreting the P-value in determining statistical significance in ANOVA.
Calculation of the Least Significant Difference using the formula provided.
Determination of the critical value of T using the two-tailed inverse of the student's T-distribution.
Comparison of the calculated LSD value to the absolute value of mean differences between groups.
Statistical significance found between the CBT and group therapy levels using the LSD test.
Demonstration of conducting the same analysis in SPSS for comparison.
Use of SPSS's post hoc tests to confirm the LSD findings from Excel.
Highlighting the consistency of results between SPSS and Excel for the LSD test.
Conclusion and offer of assistance for any questions or concerns regarding the LSD post-talk test in Excel.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Statistics 101: ANOVA Post Hoc in Excel (Fisher's LSD)
Tukey-Kramer Post Hoc Test after One-Way ANOVA in Excel
Fisher's LSD Explained
LSD; Least Significant Difference; Post Hoc Test of ANOVA; Comparison of Means (Part B)
LSD; Least Significant Difference; Post Hoc Test of ANOVA; Comparison of Means (Part A)

Statistics 101: ANOVA Post Hoc Test (Fisher's LSD)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: