Arrhenius definition of acids and bases | Biology | Khan Academy
TLDRThe video script introduces the modern concept of acids and bases through Svante Arrhenius' definition, awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1903. It explains that an acid increases hydrogen proton concentration in an aqueous solution, while a base increases hydroxide concentration. The script uses hydrochloric acid as an example of a strong acid, illustrating its dissociation into hydrogen ions and chloride anions, and sodium hydroxide as a strong base, which dissociates into hydroxide anions and sodium cations. The explanation highlights the formation of hydronium ions from hydrogen ions and water, and encourages viewers to compare Arrhenius' definition with other definitions of acids and bases.
Takeaways
- 👨🔬 The modern concept of acids and bases is largely attributed to Svante Arrhenius, who also received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1903.
- 🧪 According to Arrhenius, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (protons) when dissolved in an aqueous solution.
- 🔬 Conversely, a base, by Arrhenius' definition, is a substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions when in an aqueous solution.
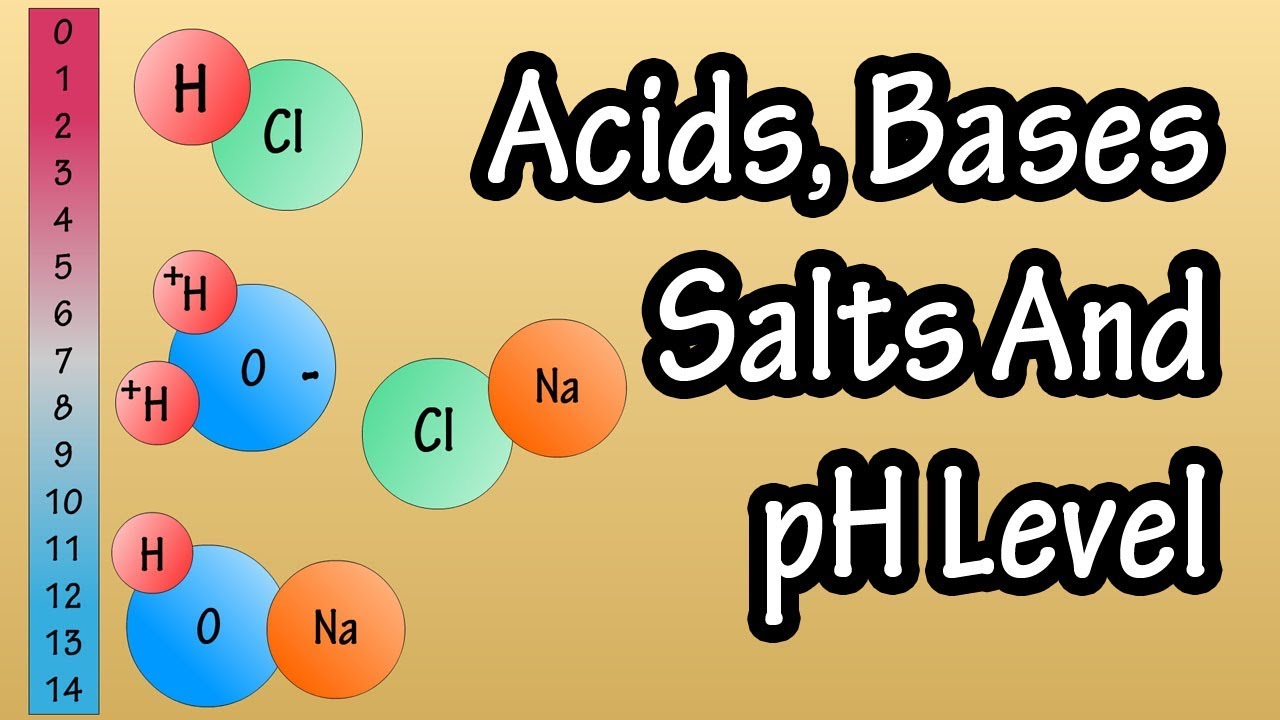
- 🌟 An example of a strong Arrhenius acid is hydrochloric acid (HCl), which readily dissociates in water to form hydrogen ions and chloride ions.
- 💧 Hydrogen ions from an acid like HCl can combine with water molecules to form hydronium ions (H3O+), further increasing the acidity of the solution.
- 🔋 Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is an example of a strong Arrhenius base, which dissociates in water to increase the concentration of hydroxide ions.
- ⚛️ In the case of sodium hydroxide, the hydroxide ion (OH-) has a negative charge and the sodium ion (Na+) has a positive charge, forming an ionic bond in the compound.
- 🔄 The dissociation of sodium hydroxide in water results in the separation of sodium and hydroxide ions, contributing to the solution's basicity.
- 🔬 Understanding the Arrhenius definition is fundamental but also important to compare and contrast with other definitions of acids and bases, such as the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions.
- 📚 The script encourages further exploration of different definitions of acids and bases to gain a comprehensive understanding of their classification in chemistry.
Q & A
Who is considered to have the first modern conception of acids and bases?
-Svante Arrhenius is considered to have the first modern conception of acids and bases.
When was Svante Arrhenius awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry?
-Svante Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1903.
According to Arrhenius' definition, what is an acid?
-According to Arrhenius' definition, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen protons in an aqueous solution.
How does a base behave in an aqueous solution according to Arrhenius' definition?
-According to Arrhenius' definition, a base is a substance that increases the hydroxide concentration in an aqueous solution.
What happens when hydrochloric acid is placed in an aqueous solution?
-When hydrochloric acid is placed in an aqueous solution, it readily dissociates, with the chlorine atom taking the electron from hydrogen, leaving a hydrogen proton and forming a chloride anion.
What is the role of water molecules in the dissociation of hydrochloric acid?
-Water molecules bond with the hydrogen protons released from hydrochloric acid to form hydronium ions (H3O+).
What is the chemical formula for hydronium ion?
-The chemical formula for the hydronium ion is H3O+.
Why is hydrochloric acid considered a strong acid according to the Arrhenius definition?
-Hydrochloric acid is considered a strong acid according to the Arrhenius definition because it increases the concentration of hydrogen protons or hydronium ions in an aqueous solution.
What is an example of a strong Arrhenius base?
-An example of a strong Arrhenius base is sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
What happens when sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water?
-When sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and hydroxide ions (OH-), increasing the hydroxide concentration in the solution.
How does the Arrhenius definition of acids and bases differ from the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions?
-The Arrhenius definition focuses on the presence of hydrogen ions for acids and hydroxide ions for bases in an aqueous solution. The Bronsted-Lowry definition considers acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors, while the Lewis definition views acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to Arrhenius Acids and Bases
This paragraph introduces the modern concept of acids and bases as defined by Svante Arrhenius, the 1903 Nobel Prize winner in Chemistry. According to Arrhenius, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (protons) when dissolved in water, while a base increases the concentration of hydroxide ions. The paragraph provides an example of a strong Arrhenius acid, hydrochloric acid (HCl), which dissociates in water to form hydrogen ions and chloride ions, with the hydrogen ions often bonding with water to form hydronium ions (H3O+). The paragraph also mentions that a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), would be discussed in the subsequent content.
🧪 The Chemistry of Sodium Hydroxide as a Base
The second paragraph delves into the properties of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base according to the Arrhenius definition. It describes the molecular structure of NaOH, highlighting the ionic bond between the positively charged sodium ion (Na+) and the negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-). The hydroxide ion is depicted with three lone pairs of electrons, indicating its readiness to accept protons. When NaOH is dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium and hydroxide ions, thereby increasing the hydroxide ion concentration in the solution. This increase in hydroxide ions is what classifies NaOH as a strong base under the Arrhenius theory. The paragraph also encourages viewers to compare this definition with other definitions of acids and bases, such as the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Svante Arrhenius
💡Acid
💡Base
💡Hydrogen Proton
💡Hydroxide Concentration
💡Hydrochloric Acid
💡Hydronium
💡Sodium Hydroxide
💡Ionic Bond
💡Dissociation
💡Arrhenius Definition
Highlights
Svante Arrhenius is recognized as the originator of the modern conception of acids and bases.
Arrhenius was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1903, being the third recipient.
According to Arrhenius's definition, an acid increases the concentration of hydrogen protons in an aqueous solution.
A base, by Arrhenius's definition, increases the hydroxide concentration when in an aqueous solution.
Hydrochloric acid is an example of a strong Arrhenius acid, readily dissociating in water to increase hydrogen ion concentration.
Hydrogen ions from hydrochloric acid form hydronium ions when bonded with water molecules.
Hydonium ions are represented as H3O+, indicating a positive charge resulting from the hydrogen ion bonding with water.
Chloride ions, resulting from the dissociation of hydrochloric acid, carry a negative charge and are anions.
Sodium hydroxide is an example of a strong Arrhenius base, dissociating in water to increase hydroxide ion concentration.
In aqueous solution, sodium hydroxide dissociates into sodium ions and hydroxide ions.
The hydroxide ion carries a negative charge and is a key component in defining a strong Arrhenius base.
Sodium ions carry a positive charge and are attracted to hydroxide anions, forming an ionic bond in sodium hydroxide.
The dissociation of sodium hydroxide in water leads to an increase in hydroxide ion concentration, defining it as a strong base.
Arrhenius's definition of acids and bases is fundamental to understanding their behavior in aqueous solutions.
The concept of hydronium ions is crucial for understanding the behavior of strong acids in water.
The dissociation of strong acids and bases in water fundamentally alters the solution's ionic composition.
Understanding the dissociation of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide is key to grasping Arrhenius's definition of acids and bases.
The video encourages viewers to compare Arrhenius's definition with other definitions such as Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: