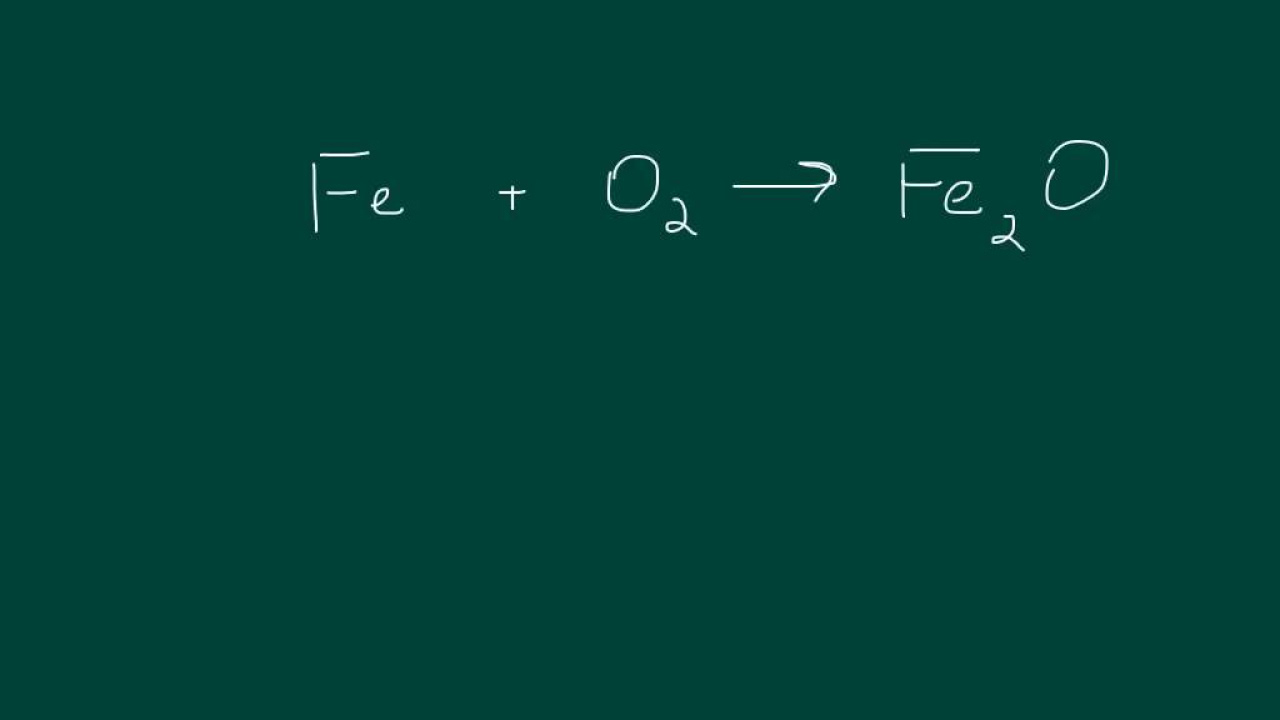Chemical Equation Basics
TLDRThe video from MooMooMath and Science dives into the world of chemical equations, illustrating how they represent the chemical reactions that occur in our everyday life, from the awe-inspiring fireworks to the essential fires that keep us warm. It explains the structure of a chemical equation, where reactants are on the left and products on the right of the equation's arrow. The video uses the example of methane (CH4) combining with oxygen (O2) to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), highlighting how each element is represented by its symbol from the periodic table and how subscript numbers indicate the quantity of ions. The importance of coefficients in front of the formulas is emphasized, as they denote the moles of each substance in the reaction. The video also stresses the law of conservation of mass, stating that atoms are neither created nor destroyed, and that a balanced equation ensures equal numbers of each element on both sides. Finally, it touches on the notation for physical states, such as solid (S), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq), and encourages viewers to learn more about balancing equations through a linked video. The summary concludes by reiterating the key components of chemical equations and inviting viewers to join MooMooMath and Science for daily educational content.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Chemical reactions are ubiquitous and can be both exciting and helpful, like fireworks and fires.
- 📜 A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction, showing reactants and products.
- ➡️ Reactants are listed to the left of the arrow, and products to the right in a chemical equation.
- 🔍 The plus sign (+) indicates which elements or compounds are combining in the reaction.
- 🚫 The arrow (➞) signifies the transformation from reactants to products, indicating what is produced or yielded.
- 🔑 Each capital letter in a chemical formula represents a different element, with symbols found on the periodic table.
- 🔡 Subscripts are used to show the number of atoms of an element within a compound, like H2O for water with two hydrogen atoms.
- 🔢 Coefficients, the numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas, indicate the number of moles of each substance in the reaction.
- ⚖️ Chemical equations must be balanced, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- 💧 The example reaction 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O shows that two moles of hydrogen react with one mole of oxygen to produce two moles of water.
- 🌐 Atoms are conserved in a chemical reaction, meaning they are neither created nor destroyed.
- 📊 Physical states of reactants and products can be indicated with symbols such as S (solid), l (liquid), g (gas), and aq (aqueous).
- 📚 Additional resources, like a video on balancing equations, are available for further understanding.
Q & A
What are chemical reactions and how do they occur in our surroundings?
-Chemical reactions are processes where substances interact to form new substances. They occur all around us, such as in fireworks and fires, and can be both exciting and helpful.
How is a chemical reaction represented?
-A chemical reaction is represented using a chemical equation, which shows the reactants on the left and products on the right of an arrow.
What does the arrow in a chemical equation signify?
-The arrow in a chemical equation indicates the direction of the reaction and what will be produced or yielded.
What are reactants and products in the context of a chemical equation?
-Reactants are the substances that undergo a chemical reaction, and they are found on the left side of the equation. Products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction and are on the right side of the equation.
How does the subscript number in a chemical formula function?
-The subscript number in a chemical formula indicates the number of atoms of that element present in the molecule or compound. For example, in H2O, the '2' indicates there are two hydrogen atoms.
What is the significance of the capital letters in a chemical equation?
-Each capital letter in a chemical equation represents a new element, and these symbols can be found on the periodic table.
What are coefficients in a chemical equation and what do they represent?
-Coefficients are the numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas. They represent the number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
Why is it important for a chemical equation to be balanced?
-A chemical equation must be balanced to ensure that atoms are neither created nor destroyed during the reaction. This means that the number of atoms of each element must be equal on both sides of the equation.
How can the physical states of reactants and products be indicated in a chemical equation?
-The physical states can be indicated using symbols such as S for solid, l for liquid, g for gas, and aq for dissolved in water.
What does the equation '2 H2 + O2 ---> 2 H2O' tell us about the reaction?
-The equation tells us that two moles of hydrogen gas react with one mole of oxygen gas to produce two moles of water.
What is the role of the periodic table in understanding chemical equations?
-The periodic table provides the symbols for every element, which are used in chemical equations to represent the elements involved in the reaction.
How can one learn to balance chemical equations?
-One can learn to balance chemical equations by studying the principles of balancing, which typically involves ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. The video creator also provides additional resources, such as a note in the show notes for a video on balancing equations.
Outlines
🧪 Understanding Chemical Equations
This paragraph introduces the concept of chemical equations and their importance in representing chemical reactions. It explains that reactants are listed on the left side of the equation and products on the right, with the arrow indicating the transformation. The example given involves methane (CH4) reacting with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The paragraph also covers the significance of element symbols, subscripts indicating the number of ions, and coefficients representing the number of moles of each substance. It emphasizes the law of conservation of mass, stating that atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a reaction, and that a balanced equation has equal numbers of each element on both sides. Additionally, it mentions the notation for physical states such as solid (S), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq), and how these are used in chemical equations.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemical Reaction
💡Chemical Equation
💡Reactants
💡Products
💡Subscripts
💡Coefficients
💡Periodic Table
💡Balancing Equations
💡Physical States
💡Law of Conservation of Mass
💡Moles
Highlights
Chemical reactions are ubiquitous and can be both exciting and helpful, such as in fireworks and fires.
Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions.
Reactants are listed on the left side of the arrow, and products on the right.
The plus sign before the arrow indicates the combination of elements or compounds.
The arrow in a chemical equation signifies the yield or what the reaction will produce.
In the given example, methane (CH4) combines with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Each capital letter in a chemical equation represents a different element, which can be found on the periodic table.
Subscripts after a letter denote the number of ions of that element present in the equation.
Coefficients are the numbers placed before the formulas, indicating the moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
For instance, in the reaction 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O, two moles of hydrogen react with one mole of oxygen to produce two moles of water.
Atoms are conserved in a chemical reaction; they are neither created nor destroyed.
A balanced chemical equation ensures that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
Physical states of reactants and products can be indicated using symbols such as S (solid), l (liquid), g (gas), and aq (dissolved in water).
The example given involves a solid and a liquid producing a gas dissolved in water.
The video provides a note in the show notes for a video on balancing chemical equations.
Chemical equations are fundamental in understanding how different substances interact and transform during a reaction.
MooMooMath and Science uploads new math and science videos every day to educate viewers on various topics.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: