World War II (short version)
TLDRWorld War II, the largest armed conflict in human history, involved tens of millions of fighters globally. It began with post-WWI sanctions leading to economic collapse and nationalistic resurgence in Germany, which saw the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi party. The Axis Powers, including Germany, Italy, and Japan, pursued aggressive expansionist policies, leading to the invasion of Poland and the onset of WWII. The war was marked by Blitzkrieg tactics, the Holocaust, and the formation of resistance movements. Major turning points included the Battle of Stalingrad and the D-Day landings. The war concluded with Hitler's suicide, the fall of Berlin, and Japan's surrender following the atomic bombings. The aftermath saw the establishment of the United Nations and the rise of the United States and USSR as superpowers, setting the stage for the Cold War.
Takeaways
- 🏳️🌈 The Treaty of Versailles held Germany responsible for WWI, leading to heavy sanctions and economic collapse.
- 📈 The German economy suffered hyperinflation, with the mark's value increasing by 1,000 billion between 1914 and 1923.
- 💥 The Wall Street Crash of 1929 had a global impact, including a significant rise in unemployment in Germany.
- ⚫️ Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party rose to power in 1933, exploiting the economic and nationalistic sentiments.
- 🌐 Germany, Italy, and Japan formed the Axis Powers, pursuing aggressive expansionist policies.
- 🇩🇪 Germany's Blitzkrieg strategy led to rapid conquests in Europe, including the occupation of France.
- 🤝 The USSR's non-aggression pact with Germany was followed by a surprise attack, bringing the USSR into the Allied camp.
- 🇺🇸 The United States entered WWII following the attack on Pearl Harbor, shifting focus to the Pacific and aiding the USSR.
- 💣 The Holocaust led to the systematic murder of millions, including Jews, in concentration and extermination camps.
- 🌍 The Normandy landings marked a significant turning point, with the Allies pushing towards the liberation of Europe.
- 🏙️ The end of WWII saw massive destruction, over 60 million deaths, and a reshaping of global power dynamics.
Q & A
What were the consequences for Germany and its allies after World War I?
-Germany and its allies were defeated, held solely responsible for the war, and faced heavy sanctions. The Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman empires were dismantled, Germany had to repay a large debt, and it lost colonies and some territories to the victors and to the recreated state of Poland. These sanctions were seen as a humiliation by the German people.
How did the economic situation in Germany affect the rise of the Nazi party?
-The German economy was severely weakened by excessive debt and hyperinflation, leading to a devaluation of its currency. This economic crisis, coupled with the 1929 Wall Street crash and high unemployment rates, created a fertile ground for the rise of nationalism. In 1933, the Nazi party, led by Adolf Hitler, rose to power, capitalizing on the discontent and promising economic recovery.
What was the Blitzkrieg strategy used by Hitler's military?
-Blitzkrieg was a new military strategy that involved rapid, high-intensity attacks in a concentrated area, which surprised opposition defenses. It was characterized by the use of air power close support, and deep penetrations by armored and motorized or mechanized infantry. This strategy allowed the German army to quickly overrun much of Europe at the beginning of World War II.
Why did Japan's expansionist policy lead to an embargo by the United States?
-Japan's expansionist policy, which included the occupation of French Indochina and aggressive actions in the Pacific, was seen as a threat to the United States' interests in the region. In response, the US imposed an embargo on oil and steel, which were critical resources for Japan's military and industrial capabilities.
What was the significance of the attack on Pearl Harbor?
-The surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese on December 7, 1941, significantly damaged the US Pacific Fleet and led the United States to formally enter World War II as part of the Allied forces. This event marked a major turning point in the war, bringing the US into direct conflict with the Axis Powers.
How did the formation of the Axis Powers impact World War II?
-The Axis Powers, consisting of Germany, Italy, and Japan, combined their military and economic resources to pursue their aggressive foreign policies. This alliance allowed them to coordinate their efforts and posed a significant threat to Allied forces, leading to widespread conflict across Europe, Africa, and the Pacific.
What was the Atlantic Wall and why was it built?
-The Atlantic Wall was a series of military installations built by Hitler along the coast of Western Europe to protect against a potential invasion from the Allies. It was designed to deter and delay any amphibious assault, allowing German forces time to respond.
What was the role of the Soviet Union in the later stages of World War II?
-The Soviet Union played a crucial role in the later stages of World War II. After suffering initial setbacks, the Soviets counterattacked and began a rapid westward advance, forcing the German army to concentrate on the Eastern Front. The Soviet Union's efforts were instrumental in the eventual defeat of Germany.
How did the Normandy landings contribute to the end of World War II in Europe?
-The Normandy landings, also known as D-Day, on June 6, 1944, marked the beginning of the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi control. It was the largest seaborne invasion in history and opened a second front in the war, forcing Germany to fight on multiple fronts, which significantly contributed to its defeat.
What was the human cost of World War II?
-World War II resulted in a heavy human toll, with at least 60 million people killed, the majority of whom were civilians. The war caused widespread destruction and suffering, with entire cities leveled and millions displaced.
How did World War II reshape the global balance of power?
-World War II led to the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as global superpowers. The old European powers were left exhausted and in ruins, while the United Nations was created to maintain peace and international security. However, the ideological differences between the US and USSR eventually led to the Cold War and indirect confrontations around the world.
Outlines
🏛 Origins and Prelude to World War II
This paragraph outlines the aftermath of World War I, including the harsh sanctions on Germany and its allies, leading to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party. It discusses the economic struggles Germany faced, the rebirth of German military power, and the aggressive foreign policies that set the stage for World War II. The annexation of Austria and invasion of Czechoslovakia are highlighted, along with the signing of a non-aggression pact with the USSR and the eventual invasion of Poland that marked the beginning of the war.
🌍 World War II: The Global Conflict
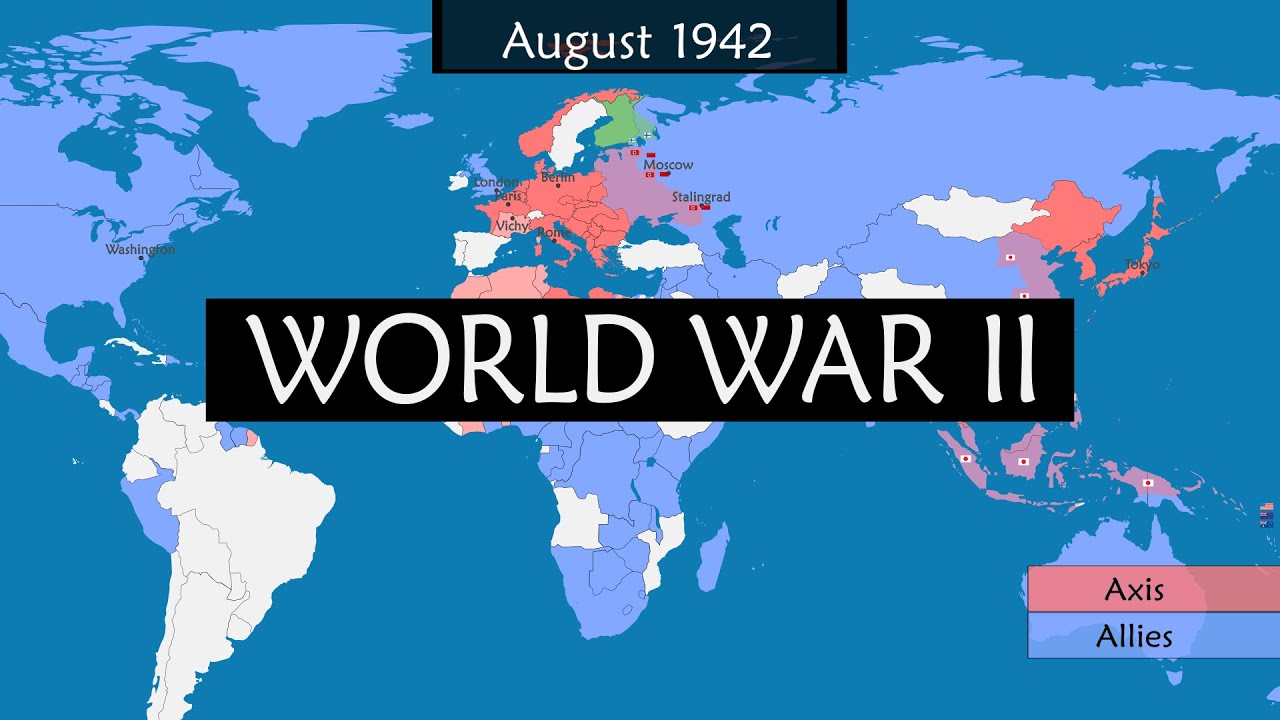
The second paragraph delves into the formation of the Axis Powers, the Soviet Union's expansion, and the entry of various dominions and colonies into the war. It covers the failure of Germany to conquer Britain, the shift in Hitler's strategy to invade the USSR, and the subsequent delays caused by Italy's military setbacks. The paragraph also details the resistance movements across Europe, the significant military operations such as the siege of Leningrad, the Battle of Moscow, and the Holocaust. It further describes the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by Japan, the United States' entry into the war, and the subsequent Pacific and European campaigns, leading to the liberation of Paris and the Allied push towards Germany.
🏙️ The End of World War II and Aftermath
The final paragraph summarizes the end of the war with Hitler's suicide and Germany's surrender. It describes the combined efforts of the United States and the USSR to defeat Japan, including the Soviet invasion of Manchuria and the U.S. deployment of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The paragraph highlights the immense human cost of the war, the division and occupation of Germany and Austria, and the emergence of the United States and USSR as global superpowers. It concludes with the establishment of the United Nations and the onset of the Cold War, characterized by indirect confrontations around the world.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡World War II
💡Blitzkrieg
💡Axis Powers
💡Holocaust
💡Pearl Harbor
💡Cold War
💡Nazi Party
💡Atlantic Wall
💡United Nations
💡Resistance Movements
💡Totalitarian Regime
Highlights
World War II was the largest armed conflict in human history, involving tens of millions of fighters worldwide.
At the end of WWI, Germany and its allies were held solely responsible, leading to heavy sanctions and the dismantling of empires.
The harsh economic sanctions on Germany after WWI, including an onerous debt, led to hyperinflation and a weakened economy.
The rise of nationalism in Germany in 1933 paved the way for the Nazi party and Adolf Hitler's rise to power.
Despite the restrictions after WWI, the Nazi regime in Germany restored military service and pursued an aggressive foreign policy.
Italy, frustrated with its WWI gains, fell under fascist rule under Benito Mussolini and pursued colonial expansion.
The Spanish Civil War from 1936-1939 saw the USSR and International Brigades support the Republican government against the nationalist forces backed by Italy and Germany.
Japan took advantage of the Chinese Civil War to expand its territory and committed atrocities including using chemical/biological weapons and massacring civilians.
Germany's Blitzkrieg strategy involved rapid, high-intensity attacks that surprised opposition defenses.
The fall of France in 1940 left Germany with indirect control of French colonies without deploying troops.
The Soviet Union's seizure of the Baltic states and part of Romania marked its alignment with the Axis Powers.
The surprise Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 led the United States to enter the war on the Allied side.
The Holocaust resulted in the extermination of millions of Jews, resistance fighters, political opponents, and other targeted groups in concentration camps.
The D-Day landings on June 6, 1944 marked a major turning point with the liberation of Paris and the beginning of the end for the Axis powers.
The United Nations was established in the war's aftermath to maintain peace and international security, though the US and USSR would later engage in indirect conflicts.
The human toll of World War II was immense, with at least 60 million dead, the majority being civilians.
The war resulted in the destruction of many cities and left the old European powers exhausted and in ruins.
The United States and Soviet Union emerged as the world's remaining superpowers in the post-war era.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: