World War 2 Allied Conferences: AP European History
TLDRIn this educational video, Paul Sargent explores the pivotal wartime conferences of World War II, highlighting how the Allies strategized not only to defeat Germany but also to shape the post-war world. Key meetings like the Atlantic Charter, Casablanca, Tehran, Yalta, and Potsdam set the stage for international cooperation, the United Nations, and the division of Germany. These conferences also sowed the seeds for the Cold War, illustrating the complex dynamics between the West and the Soviet Union, which would define global politics for decades to come.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Allied wartime conferences of World War II were crucial for planning both the conduct of the war and the post-war world.
- 📜 The Atlantic Charter in August 1941 was an agreement between FDR and Churchill emphasizing self-determination and the creation of the United Nations.
- 🏛 At Casablanca in 1943, the Allies decided on unconditional surrender and the invasion of Europe through Italy, which upset Stalin.
- 🔄 The Tehran Conference in November 1943 saw the 'Big Three' agree on an Allied invasion of Western Europe and post-war terms, with Stalin promising to fight Japan after Germany's defeat.
- 🌏 The Yalta Conference in February 1945 resulted in agreements on the United Nations structure, free elections in Eastern Europe, and division of Germany into occupation zones.
- 💥 The Potsdam Conference in August 1945 involved new leaders and focused on Japan's unconditional surrender, war crimes trials, and Germany's demilitarization.
- 📊 The United Nations was envisioned to have a General Assembly and a Security Council with five permanent members having veto power.
- 🛑 Stalin's refusal to hold free elections in Eastern Europe during the Potsdam Conference highlighted the growing tension between the East and the West.
- 🕊️ The conferences laid the groundwork for an international community aimed at preventing future world wars.
- 🔍 The division between the communist East and the democratic West set the stage for the Cold War era.
Q & A
What was the main purpose of the wartime conferences during World War II?
-The main purpose of the wartime conferences was to plan not only how to fight the war and defeat Germany and its allies, but also to determine what the world should look like after the war, setting the groundwork for the post-war world.
What were the two major points agreed upon in the Atlantic Charter?
-The Atlantic Charter agreed on no territorial changes against the wishes of the inhabitants of a region, reinforcing the idea of self-determination, and the establishment of a General Assembly, which would later be called the United Nations, as a permanent engine for security.
Why did the decision to invade Europe through Italy first at the Casablanca Conference upset Stalin?
-The decision upset Stalin because his forces were besieged in Leningrad and fighting in Stalingrad, bearing the brunt of the German army, and he felt sidelined as Britain and the United States made strategic decisions without his input.
What was agreed upon at the Tehran Conference involving the 'Big Three'?
-At the Tehran Conference, the 'Big Three' agreed on an Allied invasion of Western Europe in 1944, discussed the post-war world, and Stalin agreed to turn his attention to fighting Japan after Germany's defeat. However, Eastern Europe became a point of contention.
What were the key points of agreement at the Yalta Conference?
-At the Yalta Conference, it was agreed that Stalin would enter the Pacific War within three months after Germany's surrender, hold free elections in Eastern Europe, and create a plan for the United Nations with a General Assembly and a Security Council, which included the five major powers having veto power.
What was the significance of the United Nations as envisioned in the Yalta Conference?
-The United Nations was envisioned as an international community aimed at preventing a third world war and maintaining global peace and security, with a General Assembly for participation and a Security Council for decision-making, including five permanent members with veto power.
What was the main topic of discussion at the Potsdam Conference?
-The main topics at the Potsdam Conference were the warning to Japan for unconditional surrender, the division of Germany into occupation zones, war crimes trials for the Nazis, Germany's demilitarization, and the agreement on reparations from each zone.
Why did the Potsdam Conference mark a turning point in the relationship between the Allies?
-The Potsdam Conference marked a turning point as it highlighted the growing conflict between the West and the East, especially with Stalin refusing free elections in Eastern Europe and Truman ordering the atomic bombing of Hiroshima.
What were the consequences of the Allied conferences for the post-war world?
-The consequences included the defeat of Germany, the establishment of the United Nations, the division of Germany, and the setting of the stage for the Cold War between the communist East and the Democratic West.
How did the wartime conferences shape the geopolitical landscape after World War II?
-The wartime conferences shaped the geopolitical landscape by defining the terms of the post-war world, leading to the creation of international organizations like the United Nations, and setting the stage for the ideological and political divide known as the Cold War.
Outlines
🌏 World War II Allied Conferences Overview
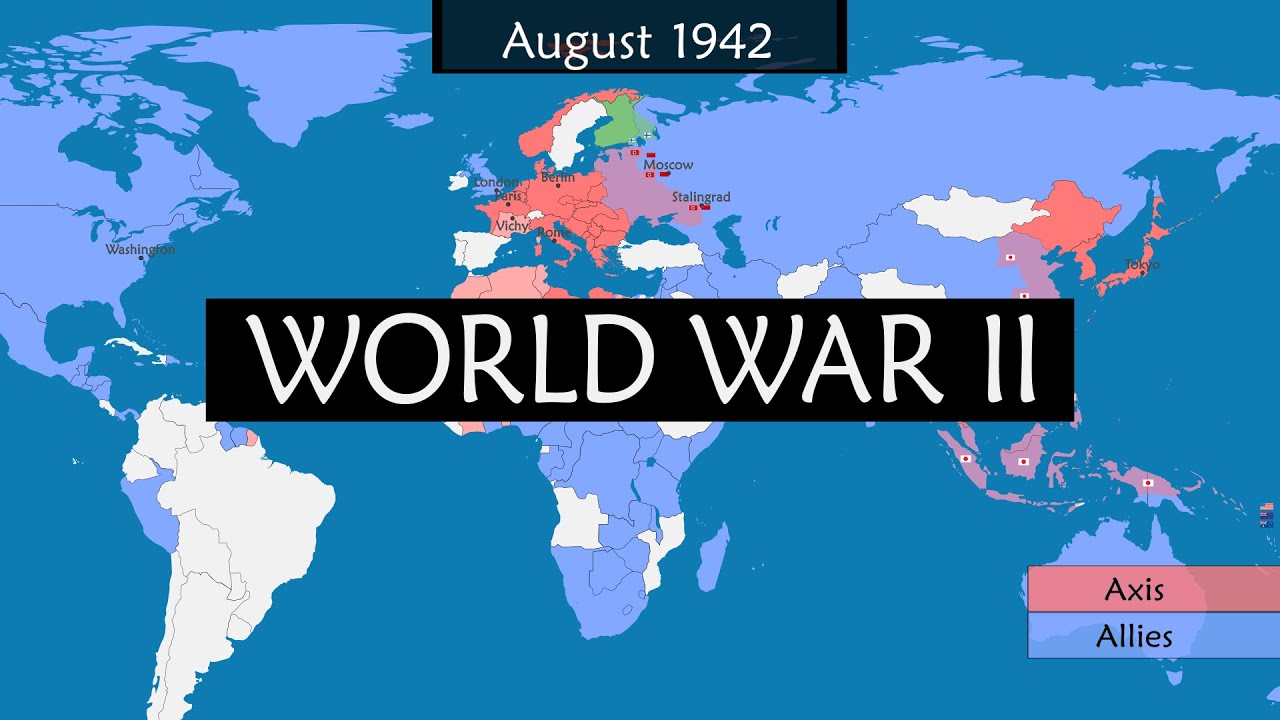
This paragraph introduces the importance of the wartime conferences during World War II, where the Allies not only strategized to defeat Germany and its allies but also planned for the post-war world. The Atlantic Charter of 1941, between FDR and Churchill, emphasized self-determination and the establishment of the United Nations. The Casablanca Conference in 1943 saw the call for unconditional surrender and the decision to invade Europe through Italy, which upset Stalin. The Tehran Conference in 1943 marked the first meeting of the 'big three' and set the stage for the Allied invasion of Western Europe and discussions on the post-war world, with Stalin agreeing to fight Japan after Germany's defeat. The paragraph highlights the growing tensions between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union over the future of Eastern Europe.
🏛 Yalta and Potsdam Conferences: Shaping the Post-War World
The Yalta Conference in 1945 saw agreements on the Soviet Union's entry into the Pacific War, free elections in Eastern Europe, and the structure of the United Nations, including a Security Council with veto power for the five major Allies. The division of Germany into occupation zones and the concept of war crimes trials were also discussed. The Potsdam Conference in 1945, attended by new leaders from Britain and the U.S., issued a warning to Japan and addressed the issue of free elections in Eastern Europe, which Stalin reneged on. The conference resulted in agreements on Germany's demilitarization, re-education, and reparations. The paragraph concludes by reflecting on the significance of these conferences in preventing a third world war and setting the stage for the Cold War, highlighting the long-term impact of these meetings on global politics.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Allied conferences
💡Atlantic Charter
💡Unconditional surrender
💡Tehran Conference
💡Yalta Conference
💡United Nations
💡Cold War
💡Potsdam Conference
💡Self-determination
💡Division of Germany
💡War crimes trials
Highlights
Introduction to the wartime conferences of World War II, emphasizing their role in shaping the post-war world.
Explanation of the Atlantic Charter in August 1941, focusing on self-determination and the establishment of the United Nations.
The significance of the Casablanca Conference in 1943, including the call for unconditional surrender and the decision to invade Europe through Italy.
The tension between the Allies and the Soviet Union over the invasion strategy, highlighting Stalin's concerns.
The Tehran Conference in November 1943, where the 'Big Three' agreed on the Allied invasion of Western Europe and post-war terms.
Stalin's agreement to fight Japan after Germany's defeat and the contentious issue of control over Eastern Europe.
The growing conflict between the West and the East, and the Soviet Union's pressure to define the post-war world.
The Yalta Conference in February 1945, where plans for the United Nations and free elections in Eastern Europe were discussed.
The division of Germany into occupation zones and the establishment of the Security Council with veto power for the major Allies.
The Potsdam Conference in August 1945, focusing on the warning to Japan for unconditional surrender.
The decision to hold war crimes trials for Nazis and the agreement on Germany's demilitarization and re-education.
The agreement on reparations and the division of Germany, reflecting the post-war power dynamics.
The impact of the conferences on the establishment of an international community aimed at preventing a third world war.
The creation of the Cold War dynamic between the communist East and the democratic West.
The long-term effects of the conferences, including the defeat of Germany and the onset of the Cold War.
Encouragement for students to study and review for the AP exam, highlighting the importance of understanding these historical events.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Post-War Rebuilding and the Cold War: Crash Course European History #41

David Kennedy, Andrew Roberts and Stephen Kotkin Discuss the Big Three of the 20th Century

The Dark Secrets Of FDR’s 4th Presidential Term | The Wheelchair President Real History

Staline vs Truman : Aux origines de la Guerre Froide

World War 1, Explained in 5 Minutes!
World War II - Summary on a Map
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: